Midterms: Place, Rules, How to study
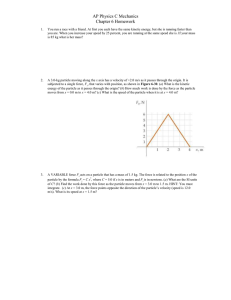
... B. How far does the book go up the slope before it stops? C. Calculate the Tension in the string ...
... B. How far does the book go up the slope before it stops? C. Calculate the Tension in the string ...
PPA6_Lecture_Ch_05
... explain any differences using the physics you know. 4. For v vs. t graph, describe the change in velocity 5. Explain possible reasons for this v vs. t behavior using what you know about gasses and physics. 6. Due Tuesday 15 Dec at beginning of class. 7. Analysis: Type 1-2 page of report plus graphs. ...
... explain any differences using the physics you know. 4. For v vs. t graph, describe the change in velocity 5. Explain possible reasons for this v vs. t behavior using what you know about gasses and physics. 6. Due Tuesday 15 Dec at beginning of class. 7. Analysis: Type 1-2 page of report plus graphs. ...
kinematics of rotation of rigid bodies
... Angular momentum and torque are really vector quantities. Their direction is always along the axis of rotation. For two dimensional motion they always point either out of the page (if they are positive) or into the page (if they are negative). Thus we don't need to explicitly consider their vector p ...
... Angular momentum and torque are really vector quantities. Their direction is always along the axis of rotation. For two dimensional motion they always point either out of the page (if they are positive) or into the page (if they are negative). Thus we don't need to explicitly consider their vector p ...
Motion & Newton`s Laws
... • A car or truck stuck in the mud spins its wheels but doesn’t move. Rolling friction makes a wheel roll forward or backward. A car stuck in the mud doesn’t have enough rolling friction to keep the wheels from slipping. ...
... • A car or truck stuck in the mud spins its wheels but doesn’t move. Rolling friction makes a wheel roll forward or backward. A car stuck in the mud doesn’t have enough rolling friction to keep the wheels from slipping. ...
Physics I - Rose
... 13.23. Model: A circular plastic disk rotating on an axle through its center is a rigid body. Assume axis is perpendicular to the disk. Solve: To determine the torque () needed to take the plastic disk from i 0 rad/s to f 1800 rpm (1800)(2)/ 60 rad/s 60 rad/s in tf – ti 4.0 s, we nee ...
... 13.23. Model: A circular plastic disk rotating on an axle through its center is a rigid body. Assume axis is perpendicular to the disk. Solve: To determine the torque () needed to take the plastic disk from i 0 rad/s to f 1800 rpm (1800)(2)/ 60 rad/s 60 rad/s in tf – ti 4.0 s, we nee ...
Rotary Motion
... What happens when they are released at the same time on the same incline from the same height? The sphere reaches the bottom first, followed by the solid cylinder, and lastly the hollow cylinder. The hollow cylinder because of its largest moment of inertia will be the hardest to start and stop ...
... What happens when they are released at the same time on the same incline from the same height? The sphere reaches the bottom first, followed by the solid cylinder, and lastly the hollow cylinder. The hollow cylinder because of its largest moment of inertia will be the hardest to start and stop ...
48.5 KB - KFUPM Resources v3
... An object is dropped from a tall building. Just before hitting the ground, its inertia will A) B) C) D) E) ...
... An object is dropped from a tall building. Just before hitting the ground, its inertia will A) B) C) D) E) ...
WORD - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... center of the Earth and neither of these quantities has changed. It could be made to land on Earth if it could be slowed down and pulled into Earth’s atmosphere. 12. The passengers, as seen in the diagram, are standing on the floor. (a) If a passenger held an object beside their waist and then relea ...
... center of the Earth and neither of these quantities has changed. It could be made to land on Earth if it could be slowed down and pulled into Earth’s atmosphere. 12. The passengers, as seen in the diagram, are standing on the floor. (a) If a passenger held an object beside their waist and then relea ...
Fall Final Review 15-16 File
... Calculate the range (horizontal distance) of a projectile and calculate its height at any given time Understand that an object in circular motion is accelerating because it is changing directions and thus a centripetal force must be acting on such an object Calculate the period, frequency, and linea ...
... Calculate the range (horizontal distance) of a projectile and calculate its height at any given time Understand that an object in circular motion is accelerating because it is changing directions and thus a centripetal force must be acting on such an object Calculate the period, frequency, and linea ...
Lectures 34
... point x = B, y=H. Find the torque produced by gravity about the origin as a function of time. ...
... point x = B, y=H. Find the torque produced by gravity about the origin as a function of time. ...