Easy to see when the projectile initial angle is 45 the range is a
... Easy to see when the projectile initial angle is 45 the range is a maximum, however for range values less than the maximum there are 2 possible initial projectile angles and consequently 2 different trajectory paths. For example, 30 and 60 degrees projectiles find the same mark. The horizontal veloc ...
... Easy to see when the projectile initial angle is 45 the range is a maximum, however for range values less than the maximum there are 2 possible initial projectile angles and consequently 2 different trajectory paths. For example, 30 and 60 degrees projectiles find the same mark. The horizontal veloc ...
chapter 7 notes - School District of La Crosse
... B) how far from the base of the cliff does the stone strike? C) sketch the trajectory ...
... B) how far from the base of the cliff does the stone strike? C) sketch the trajectory ...
Name - forehandspace
... C. Use the WORD BANK to fill in the blanks in the paragraph. Some words may be used once, twice or not at all. Today in class Sarah and Michael are doing an experiment with a rocket. They first write down their (9)______________which they came to by using their knowledge from doing research. Mich ...
... C. Use the WORD BANK to fill in the blanks in the paragraph. Some words may be used once, twice or not at all. Today in class Sarah and Michael are doing an experiment with a rocket. They first write down their (9)______________which they came to by using their knowledge from doing research. Mich ...
Notes for Newton
... 6. On a D-T graph a curved line indicates acceleration (unbalanced force) 7. On a V-T graph an object in equilibrium has constant velocity (horizontal line) C. Newton’s Third Law 1. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. (forces come in pairs) 2. Examples – you kick a wall, the wa ...
... 6. On a D-T graph a curved line indicates acceleration (unbalanced force) 7. On a V-T graph an object in equilibrium has constant velocity (horizontal line) C. Newton’s Third Law 1. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. (forces come in pairs) 2. Examples – you kick a wall, the wa ...
Physics/Science/Math Days Crossword Puzzle
... 1. An energy form based on position above or below another point 6. Product of force and distance moved; amount of energy changed from one form to another 8. No net force between object and its surroundings; free fall 10. Ability to do work; comes in many forms at the amusement park 11. Resistance t ...
... 1. An energy form based on position above or below another point 6. Product of force and distance moved; amount of energy changed from one form to another 8. No net force between object and its surroundings; free fall 10. Ability to do work; comes in many forms at the amusement park 11. Resistance t ...
NOTES AP1 Angular Motion
... Line of action – extended line collinear with the force Lever arm – distance l between the line of action and the axis of rotation, measured on the line perpendicular to both. ...
... Line of action – extended line collinear with the force Lever arm – distance l between the line of action and the axis of rotation, measured on the line perpendicular to both. ...
Name: Date:______ Period:_____ Chapter 19 Honors Study Guide
... 1. What is a reference point? The starting point you use to describe the motion or the position of an object 2. What is acceleration? Negative acceleration? The measure of how quickly the velocity of an object changes; when an object’s initial velocity is greater than its final velocity 3. Define sp ...
... 1. What is a reference point? The starting point you use to describe the motion or the position of an object 2. What is acceleration? Negative acceleration? The measure of how quickly the velocity of an object changes; when an object’s initial velocity is greater than its final velocity 3. Define sp ...
Circular Motion - Northwest ISD Moodle
... around a circle with a fixed radius Can the velocity be accelerated even though it has constant speed? Yes, because the velocity may change due to direction. If direction changes and velocity changes then an object can accelerate. ...
... around a circle with a fixed radius Can the velocity be accelerated even though it has constant speed? Yes, because the velocity may change due to direction. If direction changes and velocity changes then an object can accelerate. ...
Definitions
... Normal force is often equal and opposite to weight, but not always. Consider an elevator cab. How does the normal force compare to weight if the cab is moving at a constant velocity? Accelerating upward? Accelerating downward? ...
... Normal force is often equal and opposite to weight, but not always. Consider an elevator cab. How does the normal force compare to weight if the cab is moving at a constant velocity? Accelerating upward? Accelerating downward? ...
Newton`s Second Law 1 PPT
... Objective • SWBAT describe Newton’s second law of motion and use it to explain the movement of objects. ...
... Objective • SWBAT describe Newton’s second law of motion and use it to explain the movement of objects. ...
Document
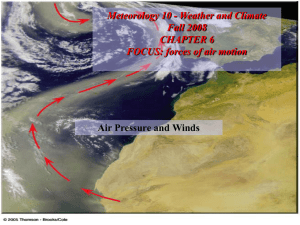
... Figure 6.19: An upper-level 500-mb map showing wind direction, as indicated by lines that parallel the wind. Wind speeds are indicated by barbs and flags. (See the blue insert.) Solid gray lines are contours in meters above sea level. Dashed red lines are isotherms in °C. ...
... Figure 6.19: An upper-level 500-mb map showing wind direction, as indicated by lines that parallel the wind. Wind speeds are indicated by barbs and flags. (See the blue insert.) Solid gray lines are contours in meters above sea level. Dashed red lines are isotherms in °C. ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... around a circle with a fixed radius Can the velocity be accelerated even though it has constant speed? Yes, because the velocity may change due to direction. If direction changes and velocity changes then an object can accelerate. ...
... around a circle with a fixed radius Can the velocity be accelerated even though it has constant speed? Yes, because the velocity may change due to direction. If direction changes and velocity changes then an object can accelerate. ...
Name - Wsfcs
... Velocity has both magnitude and direction, so if an object’s direction changes, it _________________________ even if the speed remains constant. When an object moves in a circular path, it is accelerating because its direction is always changing. This is called ___________________________ __________ ...
... Velocity has both magnitude and direction, so if an object’s direction changes, it _________________________ even if the speed remains constant. When an object moves in a circular path, it is accelerating because its direction is always changing. This is called ___________________________ __________ ...
Force and Motion
... Shove a book across the table Some are obvious (car hits tree), others are not (floor pushing on feet). ...
... Shove a book across the table Some are obvious (car hits tree), others are not (floor pushing on feet). ...
Newton`s Laws - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... In most situations, there is more than one force acting on an object at any given time When we draw the FBD we should label all forces that are acting on an object and also determine which would cancel each other out Ones that do not completely cancel out will be used to determine the net force ...
... In most situations, there is more than one force acting on an object at any given time When we draw the FBD we should label all forces that are acting on an object and also determine which would cancel each other out Ones that do not completely cancel out will be used to determine the net force ...
NOTES Circular Motion
... A hiker who has broken his forearm rigs a temporary sling using a cord stretching from his shoulder to his hand. The cord holds the forearm level and makes an angle of 40° with the horizontal where it attaches to the hand. Considering the forearm and the hand to be uniform, with a total mass of 1.31 ...
... A hiker who has broken his forearm rigs a temporary sling using a cord stretching from his shoulder to his hand. The cord holds the forearm level and makes an angle of 40° with the horizontal where it attaches to the hand. Considering the forearm and the hand to be uniform, with a total mass of 1.31 ...