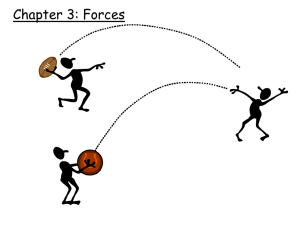
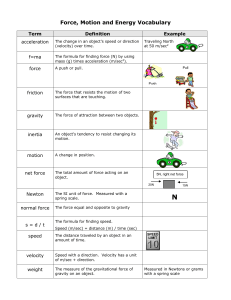
Connecting Motion with Force
... Force- a push or pull one body exerts on another. -Force does not always change velocity. Balanced forces- forces on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction. Ex: Tug of War. ...
... Force- a push or pull one body exerts on another. -Force does not always change velocity. Balanced forces- forces on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction. Ex: Tug of War. ...
Newton`s Second Law
... Types of forces Friction: a force that occurs when two touching objects move past each other. Frictional force is always in the opposite direction to the motion. ...
... Types of forces Friction: a force that occurs when two touching objects move past each other. Frictional force is always in the opposite direction to the motion. ...
Force and Motion-II
... • When an object travels in a circle, its velocity is constantly changing (in direction-at least). ...
... • When an object travels in a circle, its velocity is constantly changing (in direction-at least). ...
A baseball is thrown vertically upward
... 7) Label the points on the graphs that correspond to the force diagrams drawn in 2-5. 8) What conclusions can you draw based on this exercise about force, velocity and acceleration? Explain and defend your conclusions on a whiteboard. ...
... 7) Label the points on the graphs that correspond to the force diagrams drawn in 2-5. 8) What conclusions can you draw based on this exercise about force, velocity and acceleration? Explain and defend your conclusions on a whiteboard. ...
Circular Motion
... circular motion is continually accelerating. The direction and velocity of a particle moving in a circular path of radius r are shown at two instants in the figure. The vectors are the same size because the velocity is constant but the changing direction means acceleration is occurring. ...
... circular motion is continually accelerating. The direction and velocity of a particle moving in a circular path of radius r are shown at two instants in the figure. The vectors are the same size because the velocity is constant but the changing direction means acceleration is occurring. ...
Newton`s Second Law
... Newton’s First Law: An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion with the same speed and direction (maintains its velocity) unless it experiences an unbalanced force. Example: A soccer ball resting on the grass remains motionless until a force is applied (a kick). Th ...
... Newton’s First Law: An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion with the same speed and direction (maintains its velocity) unless it experiences an unbalanced force. Example: A soccer ball resting on the grass remains motionless until a force is applied (a kick). Th ...
PHY 101 ... ______________________ Take home exam #1 Solution Key
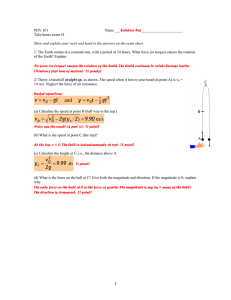
... Show and explain your work and hand in the answers on the exam sheet. 1/ The Earth rotates at a constant rate, with a period of 24 hours. What force (or torque) causes the rotation of the Earth? Explain. No force (or torque) causes the rotation of the Earth. The Earth continues to rotate because ine ...
... Show and explain your work and hand in the answers on the exam sheet. 1/ The Earth rotates at a constant rate, with a period of 24 hours. What force (or torque) causes the rotation of the Earth? Explain. No force (or torque) causes the rotation of the Earth. The Earth continues to rotate because ine ...
Newton’s Second Law
... Two students are playing tug-of-war over a 15 kg crate. Joe pulls to the right with 40 N of force, while Bob pulls to the left with 60 N of force. The frictional force between the crate and the ground is 5 N. a) Draw a free-body diagram. b) Write an “FNET Equation” for the vertical and horizontal di ...
... Two students are playing tug-of-war over a 15 kg crate. Joe pulls to the right with 40 N of force, while Bob pulls to the left with 60 N of force. The frictional force between the crate and the ground is 5 N. a) Draw a free-body diagram. b) Write an “FNET Equation” for the vertical and horizontal di ...
Ch. 2-3
... 2. Newton was the first to discover the notion of _________ or an object’s resistance to motion. 3. During free fall an object accelerates toward the Earth at this rate: __________ 4. Velocity differs from speed in that velocity has a ___________. 5. Newton’s Second Law states the acceleration is __ ...
... 2. Newton was the first to discover the notion of _________ or an object’s resistance to motion. 3. During free fall an object accelerates toward the Earth at this rate: __________ 4. Velocity differs from speed in that velocity has a ___________. 5. Newton’s Second Law states the acceleration is __ ...
以人为本 深化改革 努力探索实验室开放的新路子
... 4. Assume that the Earth is a sphere and that the force of gravity (mg) points precisely toward the center of the Earth. Taking into account the rotation of the earth about its axis, calculate the angle between the direction of a plumb line and the direction of the Earth’s radius as a function of l ...
... 4. Assume that the Earth is a sphere and that the force of gravity (mg) points precisely toward the center of the Earth. Taking into account the rotation of the earth about its axis, calculate the angle between the direction of a plumb line and the direction of the Earth’s radius as a function of l ...
Magic Square Vocabulary Game Combinations
... G. Friction H. 3rd Law of Motion I. Gravitational Force ...
... G. Friction H. 3rd Law of Motion I. Gravitational Force ...