Dynamics: The Why of Motion
... fixed on the earth (since earth rotates, technically the frame is accelerating) Two frames of reference- inertial and non inertial (or accelerating) ...
... fixed on the earth (since earth rotates, technically the frame is accelerating) Two frames of reference- inertial and non inertial (or accelerating) ...
Turning Effect Pre-Lab (print version)
... Not only the force is responsible for the turning effect, but also where the force is applied with respect to the axis of rotation. ...
... Not only the force is responsible for the turning effect, but also where the force is applied with respect to the axis of rotation. ...
Below is a box at rest on the floor with... What would I have to do to get it to...
... Not only the force is responsible for the turning effect, but also where the force is applied with respect to the axis of rotation. ...
... Not only the force is responsible for the turning effect, but also where the force is applied with respect to the axis of rotation. ...
Chapter 6 Forces and Motion
... Terminal Velocity- The constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of gravity. Free fall - the motion of a body when only the force of gravity is acting on the body. Projectile motion- the curved path that an obj ...
... Terminal Velocity- The constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of gravity. Free fall - the motion of a body when only the force of gravity is acting on the body. Projectile motion- the curved path that an obj ...
No Slide Title
... Newton knew that at the surface of the earth bodies (apples) fall 5 m in the first second, and that this acceleration is due to earth’s gravity. He showed that the gravity force is the same as if all earth’s mass were at its center, 4000 mi from the surface. He wondered whether the same force attrac ...
... Newton knew that at the surface of the earth bodies (apples) fall 5 m in the first second, and that this acceleration is due to earth’s gravity. He showed that the gravity force is the same as if all earth’s mass were at its center, 4000 mi from the surface. He wondered whether the same force attrac ...
Force, Motion, and Newton`s Laws
... 6. The force that pulls on objects and causes acceleration if the objects are not balanced by an opposing force 8. Newton's Second Law of Motion 11. The result of unbalanced forces 12. Motion of the object is towards the source of the force 13. Amount of matter in an object or a measure of the inert ...
... 6. The force that pulls on objects and causes acceleration if the objects are not balanced by an opposing force 8. Newton's Second Law of Motion 11. The result of unbalanced forces 12. Motion of the object is towards the source of the force 13. Amount of matter in an object or a measure of the inert ...
Rotational Motion
... Center of Mass (COM) Each object has a center of mass (COM) This COM follows all motion laws, the rest of the object rotates around this point To find COM, suspend the object at 2 different points. Draw a vertical line down the object from that point. Where the two lines cross is the COM Th ...
... Center of Mass (COM) Each object has a center of mass (COM) This COM follows all motion laws, the rest of the object rotates around this point To find COM, suspend the object at 2 different points. Draw a vertical line down the object from that point. Where the two lines cross is the COM Th ...
hp1f2013_class15_rolling_motion_and_accelerating_frames
... Principle of Equivalence In the example problem, we treated acceleration A in the same way as we treated gravitational acceleration. The Principle of Equivalence states that there is no way to distinguish locally* between a gravitational acceleration and an acceleration of the coordinate system. *L ...
... Principle of Equivalence In the example problem, we treated acceleration A in the same way as we treated gravitational acceleration. The Principle of Equivalence states that there is no way to distinguish locally* between a gravitational acceleration and an acceleration of the coordinate system. *L ...
Jeopardy - QuestGarden.com
... equal pull, the reason the Earth goes around the Sun and not the other way round is due to the Sun’s _____ ______ ...
... equal pull, the reason the Earth goes around the Sun and not the other way round is due to the Sun’s _____ ______ ...
Ch. 23 Review sheet answers 1. Every force has an opposite force
... 2. Motion is a change in position. 3. The force that opposes motion is friction. 4. Speed is rate of change of position. 5. An unbalanced force acting on an object causes it to accelerate. 6. When two ...
... 2. Motion is a change in position. 3. The force that opposes motion is friction. 4. Speed is rate of change of position. 5. An unbalanced force acting on an object causes it to accelerate. 6. When two ...
Chapter 7
... • When a wheel of radius r rotates about an axis whose direction is fixed, a point on the rim of the wheel is described in terms of the circumferential distance l it has moved, its tangential speed v, and its tangential acceleration aT. • These quantities are related to the angular quantities q, w, ...
... • When a wheel of radius r rotates about an axis whose direction is fixed, a point on the rim of the wheel is described in terms of the circumferential distance l it has moved, its tangential speed v, and its tangential acceleration aT. • These quantities are related to the angular quantities q, w, ...
Forces Power Point
... A push or pull on an object that can result in a change in shape, direction or velocity of the object. ...
... A push or pull on an object that can result in a change in shape, direction or velocity of the object. ...
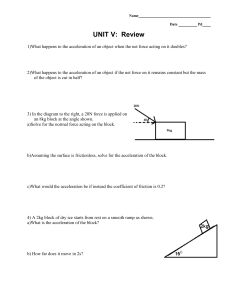
Unit 5 Review
... 3) In the diagram to the right, a 20N force is applied on an 8kg block at the angle shown. a)Solve for the normal force acting on the block. ...
... 3) In the diagram to the right, a 20N force is applied on an 8kg block at the angle shown. a)Solve for the normal force acting on the block. ...
Newton*s Second Law
... Find the force of gravity on the ball in terms of the mass of the object m and the acceleration of gravity g. In general, the force of gravity on any ...
... Find the force of gravity on the ball in terms of the mass of the object m and the acceleration of gravity g. In general, the force of gravity on any ...
physics jeopardy unit 2a
... The width of the flag (1cm) divided by the time it took to pass through the photogate. ...
... The width of the flag (1cm) divided by the time it took to pass through the photogate. ...
Practice Problems Semester 1 Exam 1. Express the measurements
... 24. A 1150 kg car is applying a 2,500 N force to accelerate it forward. The force of friction the wheels apply to the road is 500. N. A. Draw the free body diagram, identifying the forces. B. Determine the size of all the forces and label them on the drawing. C. Determine the net force on the object ...
... 24. A 1150 kg car is applying a 2,500 N force to accelerate it forward. The force of friction the wheels apply to the road is 500. N. A. Draw the free body diagram, identifying the forces. B. Determine the size of all the forces and label them on the drawing. C. Determine the net force on the object ...
Name:
... 7. What is the acceleration of both the hammer and the feather? Why is the acceleration the same for both objects? ...
... 7. What is the acceleration of both the hammer and the feather? Why is the acceleration the same for both objects? ...