Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
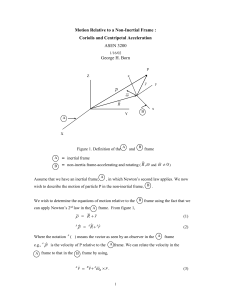
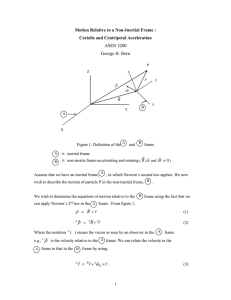
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
DYNAMICS
... • He was born on Christmas day, the year Galileo died. • His work influenced today’s world at a monumental level. • He developed three laws that describe the motion of everything. • He very well may have been one of the most influential human beings to ever live. • And you thought he was just some d ...
... • He was born on Christmas day, the year Galileo died. • His work influenced today’s world at a monumental level. • He developed three laws that describe the motion of everything. • He very well may have been one of the most influential human beings to ever live. • And you thought he was just some d ...
Regular Physics Mid-Term Review Packet
... 18. At what position during the trajectory does the projectile have minimum velocity? If Vi = 20 m/s is the launch velocity, then what is its final velocity Vf just before it hits the ground. Neglect air resistance. 19. If you are in a train traveling at a constant velocity of 70 km/h and throw a ba ...
... 18. At what position during the trajectory does the projectile have minimum velocity? If Vi = 20 m/s is the launch velocity, then what is its final velocity Vf just before it hits the ground. Neglect air resistance. 19. If you are in a train traveling at a constant velocity of 70 km/h and throw a ba ...
Review - Hingham Schools
... Be able to identify and diagram the forces on an object. Know what net force means and understand the direction it points relative to a and v for different types of motion. Know the differences between mass and weight. Be able to calculate weight given the mass and vice versa. Be able to apply Newto ...
... Be able to identify and diagram the forces on an object. Know what net force means and understand the direction it points relative to a and v for different types of motion. Know the differences between mass and weight. Be able to calculate weight given the mass and vice versa. Be able to apply Newto ...
File
... A passenger of mass m= 72.2 kg stands on a bathroom scale in an elevator. What are the scale readings when the cab is stationary, when it is moving up and moving down? (a) Find the general equation for the scale reading, whatever the vertical motion of the cab. (b) What does the scale read if the ...
... A passenger of mass m= 72.2 kg stands on a bathroom scale in an elevator. What are the scale readings when the cab is stationary, when it is moving up and moving down? (a) Find the general equation for the scale reading, whatever the vertical motion of the cab. (b) What does the scale read if the ...
HW#6: Fallin` Up
... Please answer in complete sentences. 1) Galileo figured out that all objects fall toward the earth at the same rate regardless of their mass. In fact, all objects accelerate toward the Earth at a rate of 9.8 meters per second every second. What is one factor that could affect the acceleration of an ...
... Please answer in complete sentences. 1) Galileo figured out that all objects fall toward the earth at the same rate regardless of their mass. In fact, all objects accelerate toward the Earth at a rate of 9.8 meters per second every second. What is one factor that could affect the acceleration of an ...
ESS 303 -- Biomechanics
... Action/Reaction: Objects “push back” with equal force and in the opposite direction as the force impressed (equal and opposite) ...
... Action/Reaction: Objects “push back” with equal force and in the opposite direction as the force impressed (equal and opposite) ...
3rd quarter study guide
... a. a bird taking off for flight b. a baseball released by a pitcher c. a bike approaching a stop sign d. an airplane following a straight flight ...
... a. a bird taking off for flight b. a baseball released by a pitcher c. a bike approaching a stop sign d. an airplane following a straight flight ...
the vector product - Tennessee State University
... impressed; and is made in the direction of the right line in which that force is impressed.”) ...
... impressed; and is made in the direction of the right line in which that force is impressed.”) ...
Slideshow
... If a force is applied to a moving object, the object can speed up, slow down or come to a stop. ...
... If a force is applied to a moving object, the object can speed up, slow down or come to a stop. ...
Ch. 12 Test Review Write the complete definition for the following
... 14. As the ____________________ of the objects increase, the ___________________ ____________________ of the objects also increase. 15. As the _______________________ between the objects increases, the ___________________ ______________________ of the objects decreases. 16. Mass x Acceleration = __ ...
... 14. As the ____________________ of the objects increase, the ___________________ ____________________ of the objects also increase. 15. As the _______________________ between the objects increases, the ___________________ ______________________ of the objects decreases. 16. Mass x Acceleration = __ ...
DiffLinearMotion
... motion • Newton’s 1st Law of Motion: an object moving at a constant velocity or at rest will remain that way unless it is acted upon by a force • Why should we wear ...
... motion • Newton’s 1st Law of Motion: an object moving at a constant velocity or at rest will remain that way unless it is acted upon by a force • Why should we wear ...
Newtons Laws - Cardinal Newman High School
... For example: When you kick a soccer ball, do you feel anything in your foot? ...
... For example: When you kick a soccer ball, do you feel anything in your foot? ...
Forces
... A 50.0 kg bucket is being lifted by a rope. The rope will not break if the tension is 525 N or less. The bucket started at rest, and after being lifted 3.0 m, it is moving at 3.0 m/s. If the acceleration is constant, is the rope in danger of breaking? ...
... A 50.0 kg bucket is being lifted by a rope. The rope will not break if the tension is 525 N or less. The bucket started at rest, and after being lifted 3.0 m, it is moving at 3.0 m/s. If the acceleration is constant, is the rope in danger of breaking? ...