Newton`s Laws and Forces
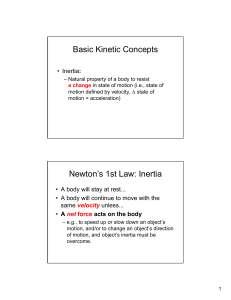
... continues in its state of rest or of uniform speed in a straight line unless acted on by a non-zero net force. ...
... continues in its state of rest or of uniform speed in a straight line unless acted on by a non-zero net force. ...
Complete the following on a separate sheet of paper
... 7. If a car is able to accelerate at 6.0 m/s2, what acceleration can it attain if it is towing another car of equal mass? Explain your answer. 8. A constant unchanging force of 30.25 N is applied to a 12.02 kg object for exactly 15.00 seconds. What is the final velocity of the object after the 15.00 ...
... 7. If a car is able to accelerate at 6.0 m/s2, what acceleration can it attain if it is towing another car of equal mass? Explain your answer. 8. A constant unchanging force of 30.25 N is applied to a 12.02 kg object for exactly 15.00 seconds. What is the final velocity of the object after the 15.00 ...
Newton`s Second Law Contineud
... • Once you throw a ball no other force accelerates it forward (ignoring a tail wind and air resistance) so its horizontal velocity is constant. ...
... • Once you throw a ball no other force accelerates it forward (ignoring a tail wind and air resistance) so its horizontal velocity is constant. ...
covers topics:
... 1. While driving down the road, you observe a bug striking the windshield of your car. Quite obviously, a case of Newton's _____ law of motion. The bug hit the windshield and the windshield hit the bug. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the bug or the force on the windshield? 2. A 2-k ...
... 1. While driving down the road, you observe a bug striking the windshield of your car. Quite obviously, a case of Newton's _____ law of motion. The bug hit the windshield and the windshield hit the bug. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the bug or the force on the windshield? 2. A 2-k ...
Ex. A 650 kg car accelerates at 4.0 m/s2 south. What is the net force
... Inertia is how much an object does not want to ___________ how it is moving. It is the tendency of an object to ____________a change in motion. The greater the mass, the ___________ its inertia. o ...
... Inertia is how much an object does not want to ___________ how it is moving. It is the tendency of an object to ____________a change in motion. The greater the mass, the ___________ its inertia. o ...
Section 1 Newton`s Second Law
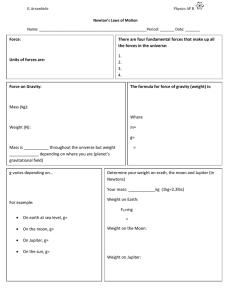
... A. Law of gravitation—any two masses exert an attractive force on each other 1. Gravity is one of the four basic forces that also include the electromagnetic force, the strong nuclear force, and the weak nuclear force. 2. Gravity is a long-range force that gives the universe its structure. B. Due to ...
... A. Law of gravitation—any two masses exert an attractive force on each other 1. Gravity is one of the four basic forces that also include the electromagnetic force, the strong nuclear force, and the weak nuclear force. 2. Gravity is a long-range force that gives the universe its structure. B. Due to ...
Name: Sect:______ Date
... actions such as twisting, ___squeezing, stretching__ and ___bending_. 2. What do you call the sum of all of the forces acting on an object? The net force. 3. Describe the difference between a balanced and unbalance force. Balanced forces are equal but in opposite directions so there is no motion as ...
... actions such as twisting, ___squeezing, stretching__ and ___bending_. 2. What do you call the sum of all of the forces acting on an object? The net force. 3. Describe the difference between a balanced and unbalance force. Balanced forces are equal but in opposite directions so there is no motion as ...
Gravity & Motion
... • Free fall~ the condition and object is in when gravity is the only force acting on it • Projectile motion~ the curved path an object follows when thrown or propelled near the surface of the Earth ...
... • Free fall~ the condition and object is in when gravity is the only force acting on it • Projectile motion~ the curved path an object follows when thrown or propelled near the surface of the Earth ...
Artificial Gravity - Northern Illinois University
... This is the same for a freely falling object. Velocity does not change the force or acceleration. ...
... This is the same for a freely falling object. Velocity does not change the force or acceleration. ...
Newton`s 1st Law
... opposite in direction of the frictional force – the vector sum is zero Inertia - what Galileo called the tendency of an object to maintain its initial state ...
... opposite in direction of the frictional force – the vector sum is zero Inertia - what Galileo called the tendency of an object to maintain its initial state ...
angular velocity
... Centrifugal force “center-fleeing”, away from center Apparent outward force experienced by a rotating body Fictitious force – it is not real but do to the effect of inertia ...
... Centrifugal force “center-fleeing”, away from center Apparent outward force experienced by a rotating body Fictitious force – it is not real but do to the effect of inertia ...
M - Otterbein University
... acceleration does not change: a constant force acts on the ball and accelerates it steadily. ...
... acceleration does not change: a constant force acts on the ball and accelerates it steadily. ...
rotational motion & law of gravity
... • Required to maintain centripetal acceleration (Newton’s Laws) • Directed toward the center • Acts at right angles to motion • Ex: gravity, friction, strings… Fc = mac = mr2 = mvt2/r ...
... • Required to maintain centripetal acceleration (Newton’s Laws) • Directed toward the center • Acts at right angles to motion • Ex: gravity, friction, strings… Fc = mac = mr2 = mvt2/r ...