Atmospheric Pressure - Wind - General Circulation
... • Generally, air is either divergent or convergent aloft (in the upper atmosphere) and the opposite in the lower atmosphere. There is a gradual change from divergence to convergence, or vise versa as you go from the surface upward. Somewhere in between the surface and the upper atmosphere is a leve ...
... • Generally, air is either divergent or convergent aloft (in the upper atmosphere) and the opposite in the lower atmosphere. There is a gradual change from divergence to convergence, or vise versa as you go from the surface upward. Somewhere in between the surface and the upper atmosphere is a leve ...
Lesson 10 notes - Angular Measurement - science
... pull it to the left, so no centripetal force. An interesting example is a helium-filled balloon inside a cornering car. The balloon leans in towards the centre of the circle. The air in the car tries to continue in a straight line, so it is slewing to the right inside the car. The balloon is lighter ...
... pull it to the left, so no centripetal force. An interesting example is a helium-filled balloon inside a cornering car. The balloon leans in towards the centre of the circle. The air in the car tries to continue in a straight line, so it is slewing to the right inside the car. The balloon is lighter ...
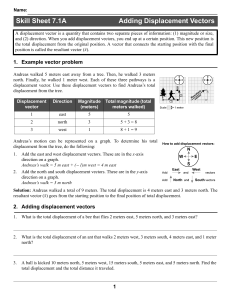
Vectors
... The distance covered by the walker is _______. Note that the distance is a ________ and does not get a direction, only a magnitude. The displacement is another story. Using the ___________________, we can determine the length of the displacement (resultant). It will come out to _____________________ ...
... The distance covered by the walker is _______. Note that the distance is a ________ and does not get a direction, only a magnitude. The displacement is another story. Using the ___________________, we can determine the length of the displacement (resultant). It will come out to _____________________ ...
1st Sem. Practice and Review
... ____ 11. A ball tossed vertically upward rises, reaches its highest point, and then falls back to its starting point. During this time the acceleration of the ball is always a. in the direction of motion. b. opposite its velocity. c. directed downward. d. directed upward. ____ 12. If a freely fallin ...
... ____ 11. A ball tossed vertically upward rises, reaches its highest point, and then falls back to its starting point. During this time the acceleration of the ball is always a. in the direction of motion. b. opposite its velocity. c. directed downward. d. directed upward. ____ 12. If a freely fallin ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... the Figure. The rod is released from rest in the horizontal position. What is (A) its angular speed when it reaches the lowest point ? (B) its initial angular acceleration ? (C) initial linear acceleration of its free end ? L m ...
... the Figure. The rod is released from rest in the horizontal position. What is (A) its angular speed when it reaches the lowest point ? (B) its initial angular acceleration ? (C) initial linear acceleration of its free end ? L m ...
dhanalakshmi college of engineering, chennai department of
... Newton‟s first law: Everybody preserves in its state of rest, or of uniform motion in a straight line unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed there on. Newton‟s second law: The acceleration of a particle will be proportional to the force and will be in the direction of the fo ...
... Newton‟s first law: Everybody preserves in its state of rest, or of uniform motion in a straight line unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed there on. Newton‟s second law: The acceleration of a particle will be proportional to the force and will be in the direction of the fo ...
Chapter 13 ppt
... ball to fall to the ground? In your Science Journal, write one or two sentences describing the motion of the ball as it falls. Describe the direction of motion and tell whether the ball falls at a constant velocity or whether its velocity changes. Remember that the ball is not moving until you let g ...
... ball to fall to the ground? In your Science Journal, write one or two sentences describing the motion of the ball as it falls. Describe the direction of motion and tell whether the ball falls at a constant velocity or whether its velocity changes. Remember that the ball is not moving until you let g ...
Concept review
... When the fly hit the truck, it exerted a force on the truck (only for a fraction of a second). So, in this time period, the truck accelerated (backwards) up to some speed. After the fly was squashed, it no longer exerted a force, and the truck simply continued moving at constant speed. Follow-up: Wh ...
... When the fly hit the truck, it exerted a force on the truck (only for a fraction of a second). So, in this time period, the truck accelerated (backwards) up to some speed. After the fly was squashed, it no longer exerted a force, and the truck simply continued moving at constant speed. Follow-up: Wh ...