Concept review
... When the fly hit the truck, it exerted a force on the truck (only for a fraction of a second). So, in this time period, the truck accelerated (backwards) up to some speed. After the fly was squashed, it no longer exerted a force, and the truck simply continued moving at constant speed. Follow-up: Wh ...
... When the fly hit the truck, it exerted a force on the truck (only for a fraction of a second). So, in this time period, the truck accelerated (backwards) up to some speed. After the fly was squashed, it no longer exerted a force, and the truck simply continued moving at constant speed. Follow-up: Wh ...
Forces - Cloudfront.net
... move with a constant velocity. Since velocity is a vector, this means the speed (how fast) and the direction remain unchanged. Example: Take a look at a hockey game. When the puck (small black projectile) is hit, the puck travels at nearly the same speed and in a straight line across the ice. All re ...
... move with a constant velocity. Since velocity is a vector, this means the speed (how fast) and the direction remain unchanged. Example: Take a look at a hockey game. When the puck (small black projectile) is hit, the puck travels at nearly the same speed and in a straight line across the ice. All re ...
Galileo`s Great Discovery: How Things Fall
... the y direction. This was a fundamental intuition, and helped lay the conceptual foundation for Newton’s work on the action of forces, and the concept of vectors. Using the ramp, however, came with a price. Any object falling through the atmosphere will experience friction, whose effects will vary w ...
... the y direction. This was a fundamental intuition, and helped lay the conceptual foundation for Newton’s work on the action of forces, and the concept of vectors. Using the ramp, however, came with a price. Any object falling through the atmosphere will experience friction, whose effects will vary w ...
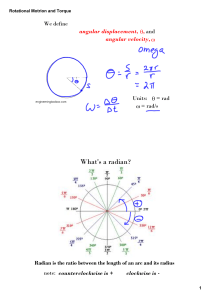
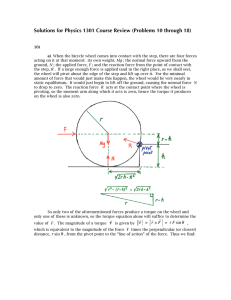
Solutions for Physics 1301 Course Review (Problems 10 through 18)
... is solved in much the same way in both cases. From the point of view of someone standing near the conveyor belt, the graphite block falls straight down, lands with zero horizontal velocity, and is accelerated up to the speed of the belt. Fron a viewpoint on the belt, the block falls along a paraboli ...
... is solved in much the same way in both cases. From the point of view of someone standing near the conveyor belt, the graphite block falls straight down, lands with zero horizontal velocity, and is accelerated up to the speed of the belt. Fron a viewpoint on the belt, the block falls along a paraboli ...
fan cart physics
... below. 1. Look at the blue lines coming from the fan. In which direction is the air pushed? ____________________ 2. Press Play ( ) and observe the cart. In which direction does the cart move? __________________ By blowing to the left, the fans exert a force on the cart that pushes it to the right. T ...
... below. 1. Look at the blue lines coming from the fan. In which direction is the air pushed? ____________________ 2. Press Play ( ) and observe the cart. In which direction does the cart move? __________________ By blowing to the left, the fans exert a force on the cart that pushes it to the right. T ...
Preview Sample 1
... average speed? How about average speed being greater than the magnitude of the average velocity? Please explain. ANS: The magnitude of the average velocity for an object may be less than its average speed but not the other way around. One can look at the definition of the two quantities involved for ...
... average speed? How about average speed being greater than the magnitude of the average velocity? Please explain. ANS: The magnitude of the average velocity for an object may be less than its average speed but not the other way around. One can look at the definition of the two quantities involved for ...
Test Problems for Oscillatory motion (L9). Make sure you
... back to one platform. The time for the forward and return motion is ...
... back to one platform. The time for the forward and return motion is ...
Lesson 1: Newton`s First Law of Motion
... The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. In terms of an equation, the net force is equal to the product of the object's mass and i ...
... The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. In terms of an equation, the net force is equal to the product of the object's mass and i ...