Electricity
... For example, David Beckham takes a free kick by kicking a stationary football with a force of 40N. If the ball has a mass of 0.5kg and his foot is in contact with the ball for 0.1s calculate: 1) The change in momentum of the ball (its impulse), 2) The speed the ball moves away with ...
... For example, David Beckham takes a free kick by kicking a stationary football with a force of 40N. If the ball has a mass of 0.5kg and his foot is in contact with the ball for 0.1s calculate: 1) The change in momentum of the ball (its impulse), 2) The speed the ball moves away with ...
circular motion
... (B) acceleration and speed are constant but velocity changes (C) both acceleration and velocity change (D) both acceleration and speed are constant ...
... (B) acceleration and speed are constant but velocity changes (C) both acceleration and velocity change (D) both acceleration and speed are constant ...
6 Newton`s Second Law of Motion–Force and
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...
Oaks_Park - TuHS Physics Homepage
... the train for this!) Also calculate what the coefficient of friction has to be in order for the locomotive to do this. (The normal force would be due to the mass of only the locomotive.) (10 pts) D) Power Using the kinetic energy as work and the time from A), calculate the power output of the train ...
... the train for this!) Also calculate what the coefficient of friction has to be in order for the locomotive to do this. (The normal force would be due to the mass of only the locomotive.) (10 pts) D) Power Using the kinetic energy as work and the time from A), calculate the power output of the train ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
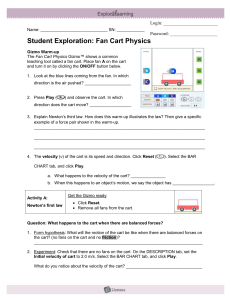
... C. What does this tell us about the forces acting upon the cart? _________________________ 5. Draw conclusions: Explain Newton’s first law. How do experiments 2 and 3 illustrate this law? _________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________ ...
... C. What does this tell us about the forces acting upon the cart? _________________________ 5. Draw conclusions: Explain Newton’s first law. How do experiments 2 and 3 illustrate this law? _________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________ ...
Edexcel AS/A level Physics Student Book 1
... 2 To find h, we need to know the time of flight, ttotal so we can split this into a time to reach hmax, and see how much time is left to fall height h. We will use gravitational acceleration vertically to calculate the vertical drop in that remaining time: s ttotal = __v horizontal From fig B, we can s ...
... 2 To find h, we need to know the time of flight, ttotal so we can split this into a time to reach hmax, and see how much time is left to fall height h. We will use gravitational acceleration vertically to calculate the vertical drop in that remaining time: s ttotal = __v horizontal From fig B, we can s ...
SPH4U: Forces
... A force diagram uses our understanding of the interactions to construct a picture of the forces acting on a system. When you construct a force diagram: Identify the object or objects of interest – we will call these objects the system. Objects outside the system are parts of the environment. Rep ...
... A force diagram uses our understanding of the interactions to construct a picture of the forces acting on a system. When you construct a force diagram: Identify the object or objects of interest – we will call these objects the system. Objects outside the system are parts of the environment. Rep ...
eBook AQA GCSE Physics Unit P2 Part 1
... potential energy to kinetic energy when you drop an object and it falls to the floor. When engineers are designing cars, they need to be able to predict what will happen to the car and its occupants in order to minimise possible injuries if the car is in a crash. In this unit you will look at how th ...
... potential energy to kinetic energy when you drop an object and it falls to the floor. When engineers are designing cars, they need to be able to predict what will happen to the car and its occupants in order to minimise possible injuries if the car is in a crash. In this unit you will look at how th ...
Document
... Angular Force: force of a muscle contributing to bone's movement around a joint axis; greatest when muscles angle of pull is perpendicular to bone (i.e. 90 degrees). Stabilizing force: degree of parallel forces generated on the lever (bone and joint) when the muscles angle of pull is less than 90 de ...
... Angular Force: force of a muscle contributing to bone's movement around a joint axis; greatest when muscles angle of pull is perpendicular to bone (i.e. 90 degrees). Stabilizing force: degree of parallel forces generated on the lever (bone and joint) when the muscles angle of pull is less than 90 de ...
Wells Problem Workbook Pack
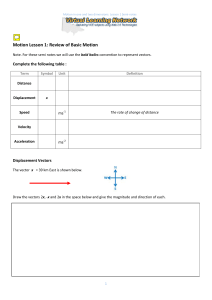
... Just look at the y axis and read off the axis what the velocity is, include a direction with the answer. - Displacement at a certain time (implies from when you started until that time), Find the areas between the motion line and the x axis for each section from start to the point in question. If yo ...
... Just look at the y axis and read off the axis what the velocity is, include a direction with the answer. - Displacement at a certain time (implies from when you started until that time), Find the areas between the motion line and the x axis for each section from start to the point in question. If yo ...
Slide 1
... teacher if the demonstration were performed with fewer nails. The resulting greater pressure would cause harm. ...
... teacher if the demonstration were performed with fewer nails. The resulting greater pressure would cause harm. ...
ch08_LecturePPT
... drawing a line straight down from the point of suspension in each case, and locating the point of intersection of the two lines. ...
... drawing a line straight down from the point of suspension in each case, and locating the point of intersection of the two lines. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 15 Thermodynamics
... drawing a line straight down from the point of suspension in each case, and locating the point of intersection of the two lines. ...
... drawing a line straight down from the point of suspension in each case, and locating the point of intersection of the two lines. ...