Document
... • Flux is the property of every vector field. • Flux means “ To Flow”. It is the measure of the “flow” or penetration of the field vectors through an imaginary fixed surface in the field. • Flux is the rate at which field lines passes through the surface area. ...
... • Flux is the property of every vector field. • Flux means “ To Flow”. It is the measure of the “flow” or penetration of the field vectors through an imaginary fixed surface in the field. • Flux is the rate at which field lines passes through the surface area. ...
Thermodynamic Processes
... The thermodynamic process of an ideal nozzle is adiabatic with no loss of energy. (As defined by Princeton University: “In thermodynamics, an adiabatic process or an isocaloric process is a thermodynamic process in which no heat is transferred to or from the working fluid. The term ‘adiabatic’ liter ...
... The thermodynamic process of an ideal nozzle is adiabatic with no loss of energy. (As defined by Princeton University: “In thermodynamics, an adiabatic process or an isocaloric process is a thermodynamic process in which no heat is transferred to or from the working fluid. The term ‘adiabatic’ liter ...
candidate predicts the correct volume V = hb /3
... 2. Solve the equations together with the continuity equation ∇·v = 0 to find the pressure and velocity gradient at the surface of the cone; 3. Use the pressure and velocity gradient to find the net force and torque on the cone; 4. Use the net force and torque to find the motion of the cone, ensuring ...
... 2. Solve the equations together with the continuity equation ∇·v = 0 to find the pressure and velocity gradient at the surface of the cone; 3. Use the pressure and velocity gradient to find the net force and torque on the cone; 4. Use the net force and torque to find the motion of the cone, ensuring ...
L 13: F
... the table. Ask your TA for help if needed. This will be used as a calibration for volume measurement later. You will enter this value into the computer. Open the experimental file L13.A1-1 Pressure vs. Depth. The calculator window appears. Enter the volume (in ml) that was equal to the 30 cm and cli ...
... the table. Ask your TA for help if needed. This will be used as a calibration for volume measurement later. You will enter this value into the computer. Open the experimental file L13.A1-1 Pressure vs. Depth. The calculator window appears. Enter the volume (in ml) that was equal to the 30 cm and cli ...
Slides - LPGPU.org
... • Relaxed consistency • Designed to support both managed language (such as Java) and unmanaged languages (such as C) • Will make it much easier to develop 3rd party compilers for a wide range of heterogeneous products • E.g. Fortran, C++, C++AMP, Java et al ...
... • Relaxed consistency • Designed to support both managed language (such as Java) and unmanaged languages (such as C) • Will make it much easier to develop 3rd party compilers for a wide range of heterogeneous products • E.g. Fortran, C++, C++AMP, Java et al ...
Air Pressure
... 1. Sea breezes are an example of how temperature differences can generate a horizontal pressure gradient 2. During the day, the land heats up more than the sea. This means that the pressure at a particular altitude increases over the land, but not the sea. The resulting horizontal pressure gradient ...
... 1. Sea breezes are an example of how temperature differences can generate a horizontal pressure gradient 2. During the day, the land heats up more than the sea. This means that the pressure at a particular altitude increases over the land, but not the sea. The resulting horizontal pressure gradient ...
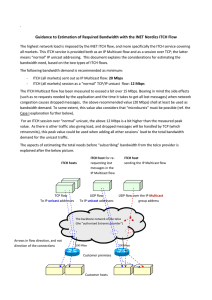
Guidance to Estimation of Required Bandwidth with the INET
... (Megabits per second). This does not necessarily mean that the telco commits to this load as expressed in Mbps. It may be so that the Mbps value is said to be committed if the load is more or less well distributed over the period of time (i.e. over the period being one second), but not if so-called ...
... (Megabits per second). This does not necessarily mean that the telco commits to this load as expressed in Mbps. It may be so that the Mbps value is said to be committed if the load is more or less well distributed over the period of time (i.e. over the period being one second), but not if so-called ...
Chapter 8
... The resultant force, F, can be decomposed into parallel and perpendicular components. The component parallel to the direction of motion is called the drag, D, and the component perpendicular to the direction of motion is called the drag, D, and the component perpendicular to the direction of motion ...
... The resultant force, F, can be decomposed into parallel and perpendicular components. The component parallel to the direction of motion is called the drag, D, and the component perpendicular to the direction of motion is called the drag, D, and the component perpendicular to the direction of motion ...
Chapter 2 - Viscosity of Fluids
... gradient lies below the straight line for Newtonian fluids. The curve begins with a low slope, indicating a low apparent viscosity. Then, the slope increases with increasing velocity gradient. Eg. Starch in water, TiO2 3. Bingham Fluids Sometimes called plug-flow fluids, Bingham fluids require the d ...
... gradient lies below the straight line for Newtonian fluids. The curve begins with a low slope, indicating a low apparent viscosity. Then, the slope increases with increasing velocity gradient. Eg. Starch in water, TiO2 3. Bingham Fluids Sometimes called plug-flow fluids, Bingham fluids require the d ...
... Benthic marine organisms in the intertidal and shallow subtidal zones must contend with harsh and oftentimes highly variable environmental conditions. At sites exposed to wave action, wave-induced hydrodynamic forces can be the dominant environmental stress. For example, water velocities in breaking ...
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids (liquids and gases) in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Some of its principles are even used in traffic engineering, where traffic is treated as a continuous fluid, and crowd dynamics. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves calculating various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space and time.Before the twentieth century, hydrodynamics was synonymous with fluid dynamics. This is still reflected in names of some fluid dynamics topics, like magnetohydrodynamics and hydrodynamic stability, both of which can also be applied to gases.