In the previous chapter we discussed energy, and
... In the previous chapter we discussed energy, and in this chapter we discuss momentum. The concepts of momentum and energy provide alternative perspectives to Newton's laws of motion and pathways into deeper understandings of Newtonian mechanics. The basic understanding of Newton's second law that we ...
... In the previous chapter we discussed energy, and in this chapter we discuss momentum. The concepts of momentum and energy provide alternative perspectives to Newton's laws of motion and pathways into deeper understandings of Newtonian mechanics. The basic understanding of Newton's second law that we ...
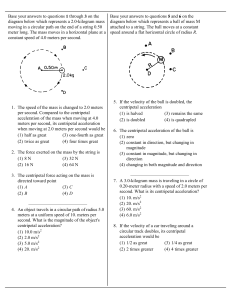
Circular Review with Ans - Physics 12
... path, with an inward acceleration. (2) Its velocity is directed tangent to the circular path, with an outward acceleration. (3) Its velocity is directed perpendicular to the circular path, with an inward acceleration. (4) Its velocity is directed perpendicular to the circular path, with an outward a ...
... path, with an inward acceleration. (2) Its velocity is directed tangent to the circular path, with an outward acceleration. (3) Its velocity is directed perpendicular to the circular path, with an inward acceleration. (4) Its velocity is directed perpendicular to the circular path, with an outward a ...
CHAPTER Conservation of Energy
... 36 · True or false: (a) The total energy of a system cannot change. (b) When you jump into the air, the floor does work on you, increasing your potential energy. (a) False (b) False 37* · A man stands on roller skates next to a rigid wall. To get started, he pushes off against the wall. Discuss the ...
... 36 · True or false: (a) The total energy of a system cannot change. (b) When you jump into the air, the floor does work on you, increasing your potential energy. (a) False (b) False 37* · A man stands on roller skates next to a rigid wall. To get started, he pushes off against the wall. Discuss the ...
Tuesday, June 27, 2006
... The above condition is sufficient for a point-like particle to be at its translational equilibrium. However for object with size this is not sufficient. One more condition is needed. What is it? Let’s consider two forces equal magnitude but in opposite direction acting on a rigid object as shown in ...
... The above condition is sufficient for a point-like particle to be at its translational equilibrium. However for object with size this is not sufficient. One more condition is needed. What is it? Let’s consider two forces equal magnitude but in opposite direction acting on a rigid object as shown in ...
7 - Landerson.net
... passing through the wheel’s center. How can we measure the distance traveled by an object on the edge of the Ferris wheel? A point on an object that rotates about a single axis undergoes circular motion around that axis. In other words, regardless of the shape of the object, any single point on the ...
... passing through the wheel’s center. How can we measure the distance traveled by an object on the edge of the Ferris wheel? A point on an object that rotates about a single axis undergoes circular motion around that axis. In other words, regardless of the shape of the object, any single point on the ...
Unit 11
... external work, Wext, needed to move a mass at constant velocity through a distance y against the force of gravity. Since this amount of work is positive while the work done by the gravitational force has the same magnitude but is negative, this definition can be expressed mathematically as Epot = We ...
... external work, Wext, needed to move a mass at constant velocity through a distance y against the force of gravity. Since this amount of work is positive while the work done by the gravitational force has the same magnitude but is negative, this definition can be expressed mathematically as Epot = We ...
Physics Review
... to the mass of the objects and the distance between them. The more mass an object has, the greater the gravitational force it exerts. The moon has less mass than Earth. The resulting lower gravitational force made the astronauts appear nearly “weightless” as they moved across the lunar surface. One ...
... to the mass of the objects and the distance between them. The more mass an object has, the greater the gravitational force it exerts. The moon has less mass than Earth. The resulting lower gravitational force made the astronauts appear nearly “weightless” as they moved across the lunar surface. One ...
Newton`s First Law of Motion
... Horses can run much much faster than humans, but if the length of the course is right, a human can beat a horse in a race. When, and why, can a man outrun a horse? Copyright © 2007, Pearson Education, Inc., Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley. ...
... Horses can run much much faster than humans, but if the length of the course is right, a human can beat a horse in a race. When, and why, can a man outrun a horse? Copyright © 2007, Pearson Education, Inc., Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley. ...
Rigid Body - Kinematics
... dr = d Φn × r = dΩ × r Sign opposite from last lecture because the rotation is CCW ...
... dr = d Φn × r = dΩ × r Sign opposite from last lecture because the rotation is CCW ...
20150126075555
... object (projectile) after it is given an initial forward velocity. The only forces acting upon it are air resistance and ______ • When you throw a ball it actually follows a _____ path because of gravity and air resistance, example of projectile motion ...
... object (projectile) after it is given an initial forward velocity. The only forces acting upon it are air resistance and ______ • When you throw a ball it actually follows a _____ path because of gravity and air resistance, example of projectile motion ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.