circular motion
... A train is moving towards North. At one place it turns towards North-East. Here we observe that (A) the radius of curvature of outer rail will be greater than that of the inner rail (B) the radius of curvature of one of the rails will be greater (C) the radius of curvature of inner rail will be grea ...
... A train is moving towards North. At one place it turns towards North-East. Here we observe that (A) the radius of curvature of outer rail will be greater than that of the inner rail (B) the radius of curvature of one of the rails will be greater (C) the radius of curvature of inner rail will be grea ...
Homeroom
... •The rate at which velocity changes with time is called acceleration •Acceleration is a measure of how quickly velocity is changing. •If velocity does not change, there is no acceleration. ...
... •The rate at which velocity changes with time is called acceleration •Acceleration is a measure of how quickly velocity is changing. •If velocity does not change, there is no acceleration. ...
Physics booklet 1
... In the SI system (metres, kilograms, seconds) the unit of speed is the metre per second. This is not the only unit that can be used. Some alternative, equally correct units are mile per hour, kilometre per hour, centimetre per minute, etc. All of these have one thing in common: each is a unit of len ...
... In the SI system (metres, kilograms, seconds) the unit of speed is the metre per second. This is not the only unit that can be used. Some alternative, equally correct units are mile per hour, kilometre per hour, centimetre per minute, etc. All of these have one thing in common: each is a unit of len ...
Anonymous-VibrationTheoryFundamentals.pdf
... passed through 360°, or 2π radians. Then the sine function resumes its previous path. Thus, when ωt = 2π, the time interval t is equal to the period T, or T = 2π/ω seconds. Since f is the reciprocal of T, f = ω/2π cycles per second. For reciprocating machinery the frequency is often expressed as cyc ...
... passed through 360°, or 2π radians. Then the sine function resumes its previous path. Thus, when ωt = 2π, the time interval t is equal to the period T, or T = 2π/ω seconds. Since f is the reciprocal of T, f = ω/2π cycles per second. For reciprocating machinery the frequency is often expressed as cyc ...
241.0 KB - NZTA Education Portal
... 1. Change the slope of the plank. Use stacking blocks or books to change the starting height of the trolley car. Make a prediction about any change in the trolley car’s motion before testing. Repeat your experiment three times, taking the average result under each condition as the speed or distance ...
... 1. Change the slope of the plank. Use stacking blocks or books to change the starting height of the trolley car. Make a prediction about any change in the trolley car’s motion before testing. Repeat your experiment three times, taking the average result under each condition as the speed or distance ...
6-2 Equilibrium
... Consider the only simplifying situations: the forces only act on the body lie in the xy plane. then the only torques that can act on the body must tend to cause rotation around an axis parallel to the z axis. With this assumption, we can eliminate one force equation and two ...
... Consider the only simplifying situations: the forces only act on the body lie in the xy plane. then the only torques that can act on the body must tend to cause rotation around an axis parallel to the z axis. With this assumption, we can eliminate one force equation and two ...
Chap06_lecture
... Newton’s laws: Relations between motions of bodies and the forces acting on them. Newton’s first law: A body at rest remains at rest, and a body in motion remains in motion at the same velocity in a straight path when the net force acting on it is zero. Therefore, a body tends to preserve its state ...
... Newton’s laws: Relations between motions of bodies and the forces acting on them. Newton’s first law: A body at rest remains at rest, and a body in motion remains in motion at the same velocity in a straight path when the net force acting on it is zero. Therefore, a body tends to preserve its state ...
Skill Sheet 1 Speed Problems
... toddler, for example, is a lot heavier to carry around than an 8-pound newborn. Force, on the other hand, is defined as a push, pull, or any action that has the ability to change motion. So what does pushing or pulling have to do with weight? To understand why we say that weight is a force, it helps ...
... toddler, for example, is a lot heavier to carry around than an 8-pound newborn. Force, on the other hand, is defined as a push, pull, or any action that has the ability to change motion. So what does pushing or pulling have to do with weight? To understand why we say that weight is a force, it helps ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... A one piece cylinder is shaped as in the figure with core section protruding from the larger drum. The cylinder is free to rotate around the central axis shown in the picture. A rope wrapped around the drum whose radius is R1 exerts force F1 to the right on the cylinder, and another force exerts F2 ...
... A one piece cylinder is shaped as in the figure with core section protruding from the larger drum. The cylinder is free to rotate around the central axis shown in the picture. A rope wrapped around the drum whose radius is R1 exerts force F1 to the right on the cylinder, and another force exerts F2 ...
Newton`s 2nd Law, Energy and Power - physics-stk
... If there is a frictional force of 12N acting against the blocks, what is the size of the force exerted by the 9kg block on the 6 kg block? (You may assume that the frictional force is shared by the blocks in proportion to their mass). F 9kg on 6kg = 6.6 N ...
... If there is a frictional force of 12N acting against the blocks, what is the size of the force exerted by the 9kg block on the 6 kg block? (You may assume that the frictional force is shared by the blocks in proportion to their mass). F 9kg on 6kg = 6.6 N ...
Time Average Seconds
... According to Newton’s Second Law, F=MA, a heavier plane with the same thrust will experience a smaller acceleration. Therefore, a heavier plane will travel a greater distance around the pylon, while its speed increases to the point at which it can lift off the ground. Conversely, Newton’s 2nd law pr ...
... According to Newton’s Second Law, F=MA, a heavier plane with the same thrust will experience a smaller acceleration. Therefore, a heavier plane will travel a greater distance around the pylon, while its speed increases to the point at which it can lift off the ground. Conversely, Newton’s 2nd law pr ...
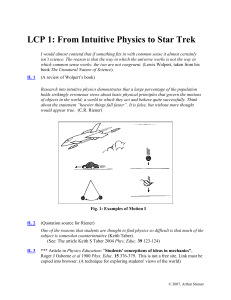
From Intuitive Physics to Star Trek
... research in conceptual development and especially refer to the findings and ideas of the New Zealand physics educator Roger Osborne (See IL 3 ). He argued that students see the world of motion by way of what he calls “clusters of mini-theories” that allows them to interact with their environment, to ...
... research in conceptual development and especially refer to the findings and ideas of the New Zealand physics educator Roger Osborne (See IL 3 ). He argued that students see the world of motion by way of what he calls “clusters of mini-theories” that allows them to interact with their environment, to ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.