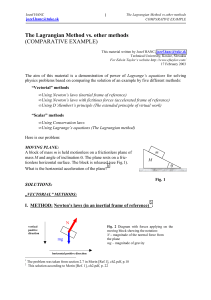
PS-5
... If an object is traveling at a constant speed, the instantaneous speed at each point will be equal to the average speed. If an object is traveling with varying speeds, the average speed is the total distance covered divided by the total time. Understand Velocity: ○ Velocity refers to both the ...
... If an object is traveling at a constant speed, the instantaneous speed at each point will be equal to the average speed. If an object is traveling with varying speeds, the average speed is the total distance covered divided by the total time. Understand Velocity: ○ Velocity refers to both the ...
CHAPTER 5 Newton`s Laws of Motion
... 5.2 Newton’s First Law of Motion: An object continues in a state of rest or in a state of uniform motion at a constant speed along a straight line unless compelled to change that state by a net force. In other words; ...
... 5.2 Newton’s First Law of Motion: An object continues in a state of rest or in a state of uniform motion at a constant speed along a straight line unless compelled to change that state by a net force. In other words; ...
Elementary Mechanics and Thermodynamics
... speed and ends up hitting the ground with a large speed. Actually, if you think about it, that’s a pretty amazing phenomenom. WHY did the speed of the ball increase ? You might say gravity. But what’s that ? The speed of the ball increased, and therefore gravity provided an acceleration. But how ? W ...
... speed and ends up hitting the ground with a large speed. Actually, if you think about it, that’s a pretty amazing phenomenom. WHY did the speed of the ball increase ? You might say gravity. But what’s that ? The speed of the ball increased, and therefore gravity provided an acceleration. But how ? W ...
4. Circular Motion and SHM (all higher level)
... {This is another sh1t question, because the speed at the bottom should be greater than the speed at the top, but here they simply tell you that it is 13 m s-1 in both cases.} ...
... {This is another sh1t question, because the speed at the bottom should be greater than the speed at the top, but here they simply tell you that it is 13 m s-1 in both cases.} ...
Lecture 06: Conservation of Angular Momentum
... L is conserved separately for x, y, z direction For an isolated system consisting of particles, ...
... L is conserved separately for x, y, z direction For an isolated system consisting of particles, ...
Solutions to Assignment #1
... #4. A long jumper takes off with a velocity of 11.00 m/s at an angle of 25.0o. The athlete’s centre of gravity was 1.250 m above the ground at takeoff and 0.500 m above the ground at landing. (a) Compute the rectangular components of the takeoff velocity. (b) What will be the flight time? (c) How fa ...
... #4. A long jumper takes off with a velocity of 11.00 m/s at an angle of 25.0o. The athlete’s centre of gravity was 1.250 m above the ground at takeoff and 0.500 m above the ground at landing. (a) Compute the rectangular components of the takeoff velocity. (b) What will be the flight time? (c) How fa ...
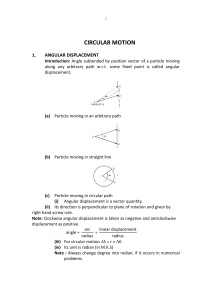
CIRCULAR MOTION
... Note : If the particle is revolving in the clockwise direction then the direction of angular velocity is perpendicular to the plane downwards. Whereas in case of anticlockwise direction the direction will be upwards. (iii) Its unit is Radian/sec (iv) Its dimension is [M0L0T–1] ...
... Note : If the particle is revolving in the clockwise direction then the direction of angular velocity is perpendicular to the plane downwards. Whereas in case of anticlockwise direction the direction will be upwards. (iii) Its unit is Radian/sec (iv) Its dimension is [M0L0T–1] ...
Chapter 10 Rotational Motion
... When using conservation of energy, both rotational and translational kinetic energy must be taken into account. All these objects have the same potential energy at the top, but the time it takes them to get down the incline depends on how much rotational inertia they have. ...
... When using conservation of energy, both rotational and translational kinetic energy must be taken into account. All these objects have the same potential energy at the top, but the time it takes them to get down the incline depends on how much rotational inertia they have. ...
ENGINEERING ADMISSIONS ASSESSMENT SPECIMEN PAPER
... The two particles are moving in opposite directions along a straight line on a smooth plane. Particle P has a speed of 3 m s–1 and particle Q has a speed of r m s–1. The particles collide directly. After the collision the direction of each particle is reversed. The speed of P is now 1 m s–1 and the ...
... The two particles are moving in opposite directions along a straight line on a smooth plane. Particle P has a speed of 3 m s–1 and particle Q has a speed of r m s–1. The particles collide directly. After the collision the direction of each particle is reversed. The speed of P is now 1 m s–1 and the ...
Energy of a System
... Since the raindrop is falling at constant velocity, all forces acting on the drop must be in balance, and R = mg, so ...
... Since the raindrop is falling at constant velocity, all forces acting on the drop must be in balance, and R = mg, so ...
The Science Behind Safe Driving:
... driving. As speed and/or mass of a vehicle increases (e.g. a large delivery truck vs. a car or an unloaded car vs. a car pulling a trailer), the distance needed to safely stop increases. Aw ...
... driving. As speed and/or mass of a vehicle increases (e.g. a large delivery truck vs. a car or an unloaded car vs. a car pulling a trailer), the distance needed to safely stop increases. Aw ...
05 - UTSC
... We soon learn as well that once the block is moving, less force is required to keep the block moving at constant speed than is required to get the block moving in the first place. This implies the existence of a force of kinetic (moving) friction. If a force is applied to keep the block moving at co ...
... We soon learn as well that once the block is moving, less force is required to keep the block moving at constant speed than is required to get the block moving in the first place. This implies the existence of a force of kinetic (moving) friction. If a force is applied to keep the block moving at co ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.