4.3 Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... resistance increases with speed, it eventually equals the downward force of gravity. At that point, there is no net force on the object and it falls with a constant velocity called the terminal ...
... resistance increases with speed, it eventually equals the downward force of gravity. At that point, there is no net force on the object and it falls with a constant velocity called the terminal ...
Chapter 13 ppt
... • Because air resistance is a force, free fall can happen only where there is no air. • The term vacuum is used to describe a place in which there is no matter. Vacuum chambers are special containers from which air can be removed to make a vacuum. ...
... • Because air resistance is a force, free fall can happen only where there is no air. • The term vacuum is used to describe a place in which there is no matter. Vacuum chambers are special containers from which air can be removed to make a vacuum. ...
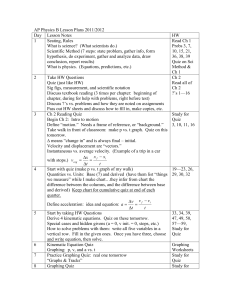
AP Physics B Lesson Plans
... Show how to set up problems related to both diagrams. 1 more example problem: like #26 in the book. Intro to friction. Two factors influence frictional force: and n. F = n. Two kinds of static and kinetic. Both are dimensionless. Go over graph on p. 101. Masses on flat and inclined surfaces WI ...
... Show how to set up problems related to both diagrams. 1 more example problem: like #26 in the book. Intro to friction. Two factors influence frictional force: and n. F = n. Two kinds of static and kinetic. Both are dimensionless. Go over graph on p. 101. Masses on flat and inclined surfaces WI ...
Core Review 1 - davis.k12.ut.us
... Standard 2: Students will understand the relation between force, mass, and acceleration. Objective 1: Analyze forces acting on an object. Write 1st, 2nd or 3rd law in each blank for the law the best explains the situation. _________ 18) An object’s acceleration is proportional to the net force on it ...
... Standard 2: Students will understand the relation between force, mass, and acceleration. Objective 1: Analyze forces acting on an object. Write 1st, 2nd or 3rd law in each blank for the law the best explains the situation. _________ 18) An object’s acceleration is proportional to the net force on it ...
Categories
... 200 Points An airplane traveling 200 km/hr slows as it approaches the ground. Is this an example of speed, velocity, or acceleration? Categories ...
... 200 Points An airplane traveling 200 km/hr slows as it approaches the ground. Is this an example of speed, velocity, or acceleration? Categories ...
PHYSICS 2325 EXAM 2 REVIEW
... a. the angular velocity remains constant. b. the object keeps on returning to its original angular position. c. the axis of rotation ends up perpendicular to its original position. d. the angular displacement remains constant. e. the rotational kinetic energy never changes. ANS: b 69. A sphere with ...
... a. the angular velocity remains constant. b. the object keeps on returning to its original angular position. c. the axis of rotation ends up perpendicular to its original position. d. the angular displacement remains constant. e. the rotational kinetic energy never changes. ANS: b 69. A sphere with ...
Newton`s Laws and Momentum – Script Draft Introduction One value
... essential analytical knowledge about motion such as position, velocity and acceleration. In this module we apply the laws of motion developed by Sir Isaac Newton to gain more insight about the most effective ways to perform a skill and how incorrect technique can affect overall performance. Newton a ...
... essential analytical knowledge about motion such as position, velocity and acceleration. In this module we apply the laws of motion developed by Sir Isaac Newton to gain more insight about the most effective ways to perform a skill and how incorrect technique can affect overall performance. Newton a ...
Physics 121C Mechanics
... Work Done by a Constant Force If there is more than one force acting on an object, we can find the work done by each force, and also the work done by the net force: ...
... Work Done by a Constant Force If there is more than one force acting on an object, we can find the work done by each force, and also the work done by the net force: ...
Rotational Motion - My Teacher Pages
... • Example- Spinning Ferris wheel or an orbiting satellite • Object moves in a circular path and at a constant speed • The object is accelerating, however, because the direction of the object’s velocity is constantly changing • Centripetal acceleration Directed toward the center of the circle • Net ...
... • Example- Spinning Ferris wheel or an orbiting satellite • Object moves in a circular path and at a constant speed • The object is accelerating, however, because the direction of the object’s velocity is constantly changing • Centripetal acceleration Directed toward the center of the circle • Net ...
7th class Physics Bridge Program
... called oscillatory or vibratory motion. A motion in which the body as a whole moves to-and-fro about its mean position is called oscillatory motion. Ex : The needle of a sewing machine moving up and down. Distance : It is defined as the actual path followed by a body between the points between which ...
... called oscillatory or vibratory motion. A motion in which the body as a whole moves to-and-fro about its mean position is called oscillatory motion. Ex : The needle of a sewing machine moving up and down. Distance : It is defined as the actual path followed by a body between the points between which ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.