2-11. Third Law of Motion
... Centripetal force is the inward force exerted on an object to keep it moving in a curved path. Centrifugal force is the outward force exerted on the object that makes it want to fly off into space. ...
... Centripetal force is the inward force exerted on an object to keep it moving in a curved path. Centrifugal force is the outward force exerted on the object that makes it want to fly off into space. ...
King Abdulaziz University
... B) Everybody continues in its state of rest or motion, unless it's forced to change that state by force. C) F12 = - F21 ...
... B) Everybody continues in its state of rest or motion, unless it's forced to change that state by force. C) F12 = - F21 ...
GOT GAME? - Duluth High School
... substituting into 4x + 3y = -10. If the coordinates make both equations true, then the solution is correct. ...
... substituting into 4x + 3y = -10. If the coordinates make both equations true, then the solution is correct. ...
Document
... A wave is anything that moves. To displace any function f(x) to the right, just change its argument from x to x-a, where a is a positive number. ...
... A wave is anything that moves. To displace any function f(x) to the right, just change its argument from x to x-a, where a is a positive number. ...
Newton*s 2nd Law for Rotation, Angular Momentum
... • Angular momentum is “the product of a rotating object’s moment of inertia and angular speed about the same axis – Symbol: L , Unit: kg m2 / s –L=Iω – angular momentum = moment of inertia x angular speed ...
... • Angular momentum is “the product of a rotating object’s moment of inertia and angular speed about the same axis – Symbol: L , Unit: kg m2 / s –L=Iω – angular momentum = moment of inertia x angular speed ...
NEWTON`S LAWS OF MOTION
... • NEWTON’S FIRST LAW OF MOTION: Every object continues in its state of rest, or uniform velocity in a straight line, as long as no net force acts on it. • MASS: measure of the inertia of an object • FORCE: measure of the magnitude and direction of the interactions ...
... • NEWTON’S FIRST LAW OF MOTION: Every object continues in its state of rest, or uniform velocity in a straight line, as long as no net force acts on it. • MASS: measure of the inertia of an object • FORCE: measure of the magnitude and direction of the interactions ...
Numerical Integration of Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... to 0.9 sec). And we can check these results because we know how to calculate all these quantities for simple projectile motion: R = (v02/g) sin 2Θ = 8.837 m, yMAX = (v0 sin Θ)2/2g = 1.276 m, time for yMAX is t=(v0 sin Θ)/g = 0.510 sec and time for R is t=(2v0 sin Θ)/g = 1.020 sec. Notice that all th ...
... to 0.9 sec). And we can check these results because we know how to calculate all these quantities for simple projectile motion: R = (v02/g) sin 2Θ = 8.837 m, yMAX = (v0 sin Θ)2/2g = 1.276 m, time for yMAX is t=(v0 sin Θ)/g = 0.510 sec and time for R is t=(2v0 sin Θ)/g = 1.020 sec. Notice that all th ...
Forces
... Due to inertia, all objects fall with the same acceleration regardless of mass. Weight—gravitational force exerted on an object 1. Weight decreases as an object moves away from Earth 2. Weight results from a force. Mass is a measure of how much matter an object contains. ...
... Due to inertia, all objects fall with the same acceleration regardless of mass. Weight—gravitational force exerted on an object 1. Weight decreases as an object moves away from Earth 2. Weight results from a force. Mass is a measure of how much matter an object contains. ...
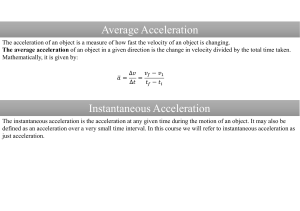
Average Acceleration Instantaneous Acceleration
... 3. Write down the available values for the kinematic variables (s, u, v, a and t). Be careful to assign the appropriate sign depending on the choice of coordinate axes made in 2. 4. At least three of the kinematic variables should have values. Be sure to read the question carefully. There may be imp ...
... 3. Write down the available values for the kinematic variables (s, u, v, a and t). Be careful to assign the appropriate sign depending on the choice of coordinate axes made in 2. 4. At least three of the kinematic variables should have values. Be sure to read the question carefully. There may be imp ...
Forces & Motion Review - Warren County Schools
... • Acceleration is caused by unbalanced forces More ...
... • Acceleration is caused by unbalanced forces More ...