Exam
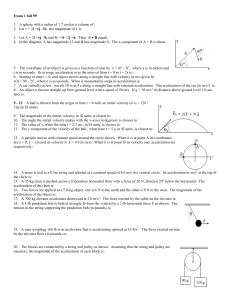
... potential Ф both inside and outside of the sphere, by solving the Poisson’s equation in spherical coordinates ( 2 / 0 ). Assume that the solution depends on r only: Ф=Ф(r). 6. (7) Consider two point charges located at Cartesian points (0,0,0) and (2,0,0), with electric charges equal to Q ...
... potential Ф both inside and outside of the sphere, by solving the Poisson’s equation in spherical coordinates ( 2 / 0 ). Assume that the solution depends on r only: Ф=Ф(r). 6. (7) Consider two point charges located at Cartesian points (0,0,0) and (2,0,0), with electric charges equal to Q ...
PED-HSM11A2TR-08-1103-001
... $25 per week. How many weeks will it take for them to earn a total of $275? To start, record what you know. ...
... $25 per week. How many weeks will it take for them to earn a total of $275? To start, record what you know. ...
Physics 106a – Problem Set 7 – Due Nov 30,... Version 2 November 29, 2004
... force constant k at the four corners of the plate. The plate is free to oscillate but with the constraint that its center must remain on the z axis. Thus, we have three degrees of freedom: (1) vertical motion, with the center of the plate moving along the z axis; (2) a tipping motion lengthwise, wit ...
... force constant k at the four corners of the plate. The plate is free to oscillate but with the constraint that its center must remain on the z axis. Thus, we have three degrees of freedom: (1) vertical motion, with the center of the plate moving along the z axis; (2) a tipping motion lengthwise, wit ...
Action/Reaction
... that resists changes in motion. Objects with more mass have more inertia and are more resistant to changes in their motion. ...
... that resists changes in motion. Objects with more mass have more inertia and are more resistant to changes in their motion. ...
Keplers-Laws
... • The orbits of the planets are elliptical (not circular) with the Sun at one focus of the ellipse. • There is one point called aphelion, where the object is farthest from the sun. • The other point is called perihelion, where the object is closest to sun ...
... • The orbits of the planets are elliptical (not circular) with the Sun at one focus of the ellipse. • There is one point called aphelion, where the object is farthest from the sun. • The other point is called perihelion, where the object is closest to sun ...
Part I - Otterbein
... • … has a different weight • Its weight is unchanged, but g has a different value • Need more information ...
... • … has a different weight • Its weight is unchanged, but g has a different value • Need more information ...
Ch. 11.3
... at the same time but may not have equal effects. Example a bouncing ball never rebounds as high as tossed down. • Action/reaction is everywhere. ...
... at the same time but may not have equal effects. Example a bouncing ball never rebounds as high as tossed down. • Action/reaction is everywhere. ...
Physics GCSE Year 9
... Explain that inertial mass is a measure of how difficult it is to change the velocity of an object (including from rest) and know that it is defined as the ratio of force over acceleration. Investigate the relationship between force, mass and acceleration ...
... Explain that inertial mass is a measure of how difficult it is to change the velocity of an object (including from rest) and know that it is defined as the ratio of force over acceleration. Investigate the relationship between force, mass and acceleration ...
Ch 9 HW Day 1
... difference between the weight of the object and the tension is the net force acting on the hanging object. We can use Newton’s 2nd law to obtain two equations in a and T that we can solve ...
... difference between the weight of the object and the tension is the net force acting on the hanging object. We can use Newton’s 2nd law to obtain two equations in a and T that we can solve ...
APS Science Curriculum Unit Planner
... Knowledge and Skills Students should know: • A force is a push or a pull and is measured in Newtons • There are 4 fundamental forces in the universe. We perceive the effects of two of them daily. • Friction is a force that acts against movement. • Net force is the sum of all the forces acting on a m ...
... Knowledge and Skills Students should know: • A force is a push or a pull and is measured in Newtons • There are 4 fundamental forces in the universe. We perceive the effects of two of them daily. • Friction is a force that acts against movement. • Net force is the sum of all the forces acting on a m ...
magnetic field - The Physics Doctor
... NB: remember this assumes the angle is perpendicular (if not it’s F=Bevsinθ) ...
... NB: remember this assumes the angle is perpendicular (if not it’s F=Bevsinθ) ...
Chapter 2 - Gordon State College
... • = is the property that determines how much an object resists a change in motion (inertia) • The greater the mass of an object, the greater the inertia. this is the reason that big rigs takes a longer distance and time to come to a standstill when the brakes are ...
... • = is the property that determines how much an object resists a change in motion (inertia) • The greater the mass of an object, the greater the inertia. this is the reason that big rigs takes a longer distance and time to come to a standstill when the brakes are ...
U2_Physics - Orange Public Schools
... terms of distance between them. 2. Describe Coulomb’s law in terms of distance. 3. Demonstrate that the relationships are the same between the two forces. 4. Demonstrate that gravity is weaker because G is small and works over longer distances but electric force is stronger but one at small distance ...
... terms of distance between them. 2. Describe Coulomb’s law in terms of distance. 3. Demonstrate that the relationships are the same between the two forces. 4. Demonstrate that gravity is weaker because G is small and works over longer distances but electric force is stronger but one at small distance ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... Explain Newton's third law of motion. Identify action-reaction pairs of forces. Recognize how Newton's third law of motion explains the physics behind many common activities and useful objects. ...
... Explain Newton's third law of motion. Identify action-reaction pairs of forces. Recognize how Newton's third law of motion explains the physics behind many common activities and useful objects. ...
Systems of equations and the elimination method
... We know how to solve an equation in one variable; we use inverse operations. If we add two linear equations and one of the variables gets eliminated, we get one equation in one variable. …We know how to solve one of these! We can then use the first variable to find the second variable. Can you use t ...
... We know how to solve an equation in one variable; we use inverse operations. If we add two linear equations and one of the variables gets eliminated, we get one equation in one variable. …We know how to solve one of these! We can then use the first variable to find the second variable. Can you use t ...
Newton`s Laws Gravity & Falling Objects Energy, Work
... force on the object and indirectly related to its mass F = m*a ...
... force on the object and indirectly related to its mass F = m*a ...
Document
... 5. The coordinate of an object is given as a function of time by x = 4t 2 - 3t3 , where x is in meters and t is in seconds. Its average acceleration over the interval from t = 0 to t = 2s is: 6. Starting at time t = 0, and object moves along a straight line with velocity in m/s given by v(t) = 98 - ...
... 5. The coordinate of an object is given as a function of time by x = 4t 2 - 3t3 , where x is in meters and t is in seconds. Its average acceleration over the interval from t = 0 to t = 2s is: 6. Starting at time t = 0, and object moves along a straight line with velocity in m/s given by v(t) = 98 - ...
Review - Hingham Schools
... Be able to identify and diagram the forces on an object. Know what net force means and understand the direction it points relative to a and v for different types of motion. Know the differences between mass and weight. Be able to calculate weight given the mass and vice versa. Be able to apply Newto ...
... Be able to identify and diagram the forces on an object. Know what net force means and understand the direction it points relative to a and v for different types of motion. Know the differences between mass and weight. Be able to calculate weight given the mass and vice versa. Be able to apply Newto ...
Example 11-3.
... For SHM, the period does not depend on the amplitude. For a pendulum with small , this is true, so a pendulum exhibits SHM for small displacements. For large (greater than 15 degrees or so) the smallangle approximation is not valid and the period does depend on the amplitude (max). Example 11-8 ...
... For SHM, the period does not depend on the amplitude. For a pendulum with small , this is true, so a pendulum exhibits SHM for small displacements. For large (greater than 15 degrees or so) the smallangle approximation is not valid and the period does depend on the amplitude (max). Example 11-8 ...
T3 F2013 9 30
... 0.30 kg putty wad that sticks to the end of the rod. If the rod's angular speed just before collision is 2.4 rad/s, what is the angular speed of the rod–putty system immediately after collision? ...
... 0.30 kg putty wad that sticks to the end of the rod. If the rod's angular speed just before collision is 2.4 rad/s, what is the angular speed of the rod–putty system immediately after collision? ...