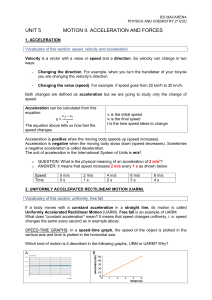
Circuit Of Math and Physics Questions Begin Here : 3x – 2y = 11
... Algebraically manipulate the gain equation to solve for R2, then determine the necessary value of R2 in this circuit to give it a voltage gain of 6.8. Outer 6: A satellite with the mass of 1*103kg is orbiting the Earth which has a mass of 5.97*1024kg. The (x,y) coordinates of the satellite is (2*108 ...
... Algebraically manipulate the gain equation to solve for R2, then determine the necessary value of R2 in this circuit to give it a voltage gain of 6.8. Outer 6: A satellite with the mass of 1*103kg is orbiting the Earth which has a mass of 5.97*1024kg. The (x,y) coordinates of the satellite is (2*108 ...
rotation
... Constant Angular Acceleration Kinematics The equations for 1-D motion with constant acceleration are a result the dv definitions of the quantities; because a dt it immediately follows that v v0 at if acceleration is constant. Since the angular variables θ, ω, α are related to each other in ex ...
... Constant Angular Acceleration Kinematics The equations for 1-D motion with constant acceleration are a result the dv definitions of the quantities; because a dt it immediately follows that v v0 at if acceleration is constant. Since the angular variables θ, ω, α are related to each other in ex ...
force
... Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation ...
... Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation ...
Chapter 7 – Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity
... The light bulb on the Ferris wheel is moving about an axis. The axis is a fixed point in the center of the Ferris wheel. Establish a reference line. Use 0 on the right side of a horizontal line. The light bulb is locate at a distance r from the axel as it moves counter clockwise from 0. It moves t ...
... The light bulb on the Ferris wheel is moving about an axis. The axis is a fixed point in the center of the Ferris wheel. Establish a reference line. Use 0 on the right side of a horizontal line. The light bulb is locate at a distance r from the axel as it moves counter clockwise from 0. It moves t ...
Chapter 3 Parent Description
... inequalities with the same variables. The solution is the region where the shadings overlap. ...
... inequalities with the same variables. The solution is the region where the shadings overlap. ...
Quantum Mechanics II, Ex 4730
... Given a spherical shell with radius R and a particle with mass M and charge e. Notice that the standard variables which show the particle are (θ, φ, Lx, Ly, Lz) In this question we have to assume that the particle can be excited from ground state to first energy level but not beyond so the state spa ...
... Given a spherical shell with radius R and a particle with mass M and charge e. Notice that the standard variables which show the particle are (θ, φ, Lx, Ly, Lz) In this question we have to assume that the particle can be excited from ground state to first energy level but not beyond so the state spa ...
Chapter 5 Ions/Ionic Bonds and Force
... motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
... motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
Sec 4.8 Solving Equations with fractions Add Chapter 4 test # 1
... 3. Combine like terms on either side of the equation Isolate the variables: 4. Use the addition and subtraction properties of equality to get the variables on one side and the constant terms on the other 5. Combine like terms when necessary 6. Undo the operations of multiplication and division to is ...
... 3. Combine like terms on either side of the equation Isolate the variables: 4. Use the addition and subtraction properties of equality to get the variables on one side and the constant terms on the other 5. Combine like terms when necessary 6. Undo the operations of multiplication and division to is ...
drburtsphysicsnotes2 - hardingscienceinstitute
... What is the sum of the forces on you right now Assume you are not moving relative to other objects on earth (even though we are moving relative to the rest of the solar system) ...
... What is the sum of the forces on you right now Assume you are not moving relative to other objects on earth (even though we are moving relative to the rest of the solar system) ...
Laws of Motion
... When ever a first body exerts a force F on a second body, the second body exerts a force −F on the first body. F and −F are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Newton's three laws of motion, along with his law of universal gravitation, explain Kepler's laws of planetary motion, which were ...
... When ever a first body exerts a force F on a second body, the second body exerts a force −F on the first body. F and −F are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Newton's three laws of motion, along with his law of universal gravitation, explain Kepler's laws of planetary motion, which were ...
26a Dynamics Review A - stpats-sph3u-sem1-2013
... Provide a complete description of the sensations one feels as a result of the ride and an explanation of these sensations using Newton’s laws of motion. 3. Newton’s first law states that objects will remain at rest or in uniform motion provided no external unbalanced force acts on them. Newton’s thi ...
... Provide a complete description of the sensations one feels as a result of the ride and an explanation of these sensations using Newton’s laws of motion. 3. Newton’s first law states that objects will remain at rest or in uniform motion provided no external unbalanced force acts on them. Newton’s thi ...