Magnetic Force
... • Angle between v and B is 30° • F = 1.2 x 10-12 N The direction is based on a ...
... • Angle between v and B is 30° • F = 1.2 x 10-12 N The direction is based on a ...
integrated-science-5th-edition-tillery-solution
... unbalanced force occurs on a single object as the result of one or more interactions with other objects. 7. The change of momentum from hitting the ground, or impulse, is the product of the applied force and time that the force is applied. The product of the force and the time is always the same, bu ...
... unbalanced force occurs on a single object as the result of one or more interactions with other objects. 7. The change of momentum from hitting the ground, or impulse, is the product of the applied force and time that the force is applied. The product of the force and the time is always the same, bu ...
projectile
... Speed is still calculated as distance traveled divided by the time it takes to travel that distance. In the case of circular motion, the distance is the circumference of a circle or (2πr). The time it takes to go around a circle one time is called the period (T). ...
... Speed is still calculated as distance traveled divided by the time it takes to travel that distance. In the case of circular motion, the distance is the circumference of a circle or (2πr). The time it takes to go around a circle one time is called the period (T). ...
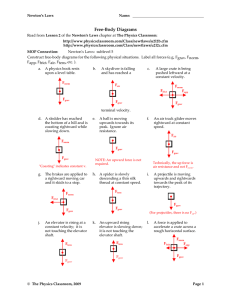
Chapter 5: Applying Newton`s Laws
... other body. The sums in equations include only forces that act on the body. Make sure you can answer the question “What other body causes that force?” for each force. If you can’t answer that question, you may be imagining a force that isn’t there. ...
... other body. The sums in equations include only forces that act on the body. Make sure you can answer the question “What other body causes that force?” for each force. If you can’t answer that question, you may be imagining a force that isn’t there. ...
Part I
... Newton’s First Law • 1st Law: (“Law of Inertia”): “In the absence of external forces and when viewed from an inertial reference frame, an object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion with a constant velocity (constant speed in a straight line).” Sir Isaac Newton as an ...
... Newton’s First Law • 1st Law: (“Law of Inertia”): “In the absence of external forces and when viewed from an inertial reference frame, an object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion with a constant velocity (constant speed in a straight line).” Sir Isaac Newton as an ...
Newton`s Second Law Notes - Mrs. Romito Teaches Science
... Have All of the Necessary Variables 6. Write down the equation(s) you need to solve for the missing variables in your final equation. 7. Convert your units and solve for the missing variables. 8. Plug in those missing variables in your final equation and solve (remember to check your units!!!) ...
... Have All of the Necessary Variables 6. Write down the equation(s) you need to solve for the missing variables in your final equation. 7. Convert your units and solve for the missing variables. 8. Plug in those missing variables in your final equation and solve (remember to check your units!!!) ...
Sample final exam
... To receive full (or partial) credit, you must show your work Note: each problem has different weighting For problems 1–2, use the following set of data: x: f(x): ...
... To receive full (or partial) credit, you must show your work Note: each problem has different weighting For problems 1–2, use the following set of data: x: f(x): ...
Week 1 - Student Classroom Worksheet
... 2. Make sure that the coefficient in front of the squared term is one. If not, divide every term on both sides of the equation by the coefficient. 3. Find (b/2)2 and add it to both sides of the equation. 4. Factor the side of the equation with the variables using the complete the square formula. 5. ...
... 2. Make sure that the coefficient in front of the squared term is one. If not, divide every term on both sides of the equation by the coefficient. 3. Find (b/2)2 and add it to both sides of the equation. 4. Factor the side of the equation with the variables using the complete the square formula. 5. ...
Linear Motion
... When a flywheel speeds up, every point of the flywheel moves at increasing speed. Consider a point on flywheel rim, at distance R from the axis of rotation. If the flywheel speeds up from initial angular speed ω1 to angular speed ω2 in time t, then the speed of the point increases from speed u = ω1 ...
... When a flywheel speeds up, every point of the flywheel moves at increasing speed. Consider a point on flywheel rim, at distance R from the axis of rotation. If the flywheel speeds up from initial angular speed ω1 to angular speed ω2 in time t, then the speed of the point increases from speed u = ω1 ...
r - UCLA IGPP
... – Forces resembling the above gravitational force can be generated by centrifugal acceleration of orbits moving along curved fields. This is the origin of the term “gravitational” instabilities which develop due to the drift of ions in a curved magnetic field (not really gravity). – In general 1st o ...
... – Forces resembling the above gravitational force can be generated by centrifugal acceleration of orbits moving along curved fields. This is the origin of the term “gravitational” instabilities which develop due to the drift of ions in a curved magnetic field (not really gravity). – In general 1st o ...
Linear momentum - Gymnázium Slovanské náměstí
... III/2 – Inovace a zkvalitnění výuky prostřednictvím ICT ...
... III/2 – Inovace a zkvalitnění výuky prostřednictvím ICT ...
Do You Remember (part 1)…
... 1. Make sure that a variable will cancel out (needs to have same number AND different signs). a. If they do not have different signs- multiply one EINTIRE equation by -1. b. If they do not have the same number- find the least common multiple and multiply the entire equation by that number. 2. Once ...
... 1. Make sure that a variable will cancel out (needs to have same number AND different signs). a. If they do not have different signs- multiply one EINTIRE equation by -1. b. If they do not have the same number- find the least common multiple and multiply the entire equation by that number. 2. Once ...