Day - Hamelinck
... Goal: To introduce Newton’s second law of motion, its equation, and how to solve problems involving this law. Part 1: History Leading to the Law Recall Newton’s First Law – what is it? What does it mean? History * Newton spent many years of his life trying to understand the motion of objects. After ...
... Goal: To introduce Newton’s second law of motion, its equation, and how to solve problems involving this law. Part 1: History Leading to the Law Recall Newton’s First Law – what is it? What does it mean? History * Newton spent many years of his life trying to understand the motion of objects. After ...
Newton`s 2nd Law
... Have All of the Necessary Variables 6. Write down the equation(s) you need to solve for the missing variables in your final equation. 7. Convert your units and solve for the missing variables. 8. Plug in those missing variables in your final equation and solve (remember to check your units!!!) ...
... Have All of the Necessary Variables 6. Write down the equation(s) you need to solve for the missing variables in your final equation. 7. Convert your units and solve for the missing variables. 8. Plug in those missing variables in your final equation and solve (remember to check your units!!!) ...
Energy3
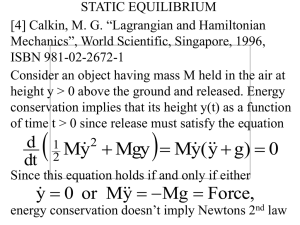
... equilibrium only if the virtual work associated with every virtual displacement is zero Example 1 Consider an unconstrained object that is subjected to a force F. Then, if the object is in static equilibrium, we obtain from the principle above that ...
... equilibrium only if the virtual work associated with every virtual displacement is zero Example 1 Consider an unconstrained object that is subjected to a force F. Then, if the object is in static equilibrium, we obtain from the principle above that ...
Do now
... writing the formula and then explaining if there is a direct or inverse relationship between the force and the acceleration (1 pt), what happens to the acceleration if the mass changes (1 pt), and then explain what conditions must be necessary for equilibrium to exist in the system (1 pt). ...
... writing the formula and then explaining if there is a direct or inverse relationship between the force and the acceleration (1 pt), what happens to the acceleration if the mass changes (1 pt), and then explain what conditions must be necessary for equilibrium to exist in the system (1 pt). ...
orces and Motion Test
... ____ 22. Which of the following objects has the LEAST (smallest) acceleration? (S8P3ab) a. an empty shopping cart pushed with a hard force b. a full shopping cart pushed with a hard force c. an empty shopping cart pushed with a light force d. a full shopping cart pushed with a light force ____ 23. A ...
... ____ 22. Which of the following objects has the LEAST (smallest) acceleration? (S8P3ab) a. an empty shopping cart pushed with a hard force b. a full shopping cart pushed with a hard force c. an empty shopping cart pushed with a light force d. a full shopping cart pushed with a light force ____ 23. A ...
notes chapter 5 complex numbers and quadratics
... IF: b 2 4ac 0 the roots are Imaginary b 2 4ac 0 The roots are Real, Rational, Equal ...
... IF: b 2 4ac 0 the roots are Imaginary b 2 4ac 0 The roots are Real, Rational, Equal ...
CHAPTER THREE NOTES - NEWTON`S SECOND LAW OF
... Force and acceleration can be represented by vectors which are lines with arrows. The longer a vector, the greater the force or rate of acceleration. Arrow indicates direction. Note: Students need to draw and interpret velocity-time graphs, acceleration - time graphs and force vectors. VECTOR QUANTI ...
... Force and acceleration can be represented by vectors which are lines with arrows. The longer a vector, the greater the force or rate of acceleration. Arrow indicates direction. Note: Students need to draw and interpret velocity-time graphs, acceleration - time graphs and force vectors. VECTOR QUANTI ...
Energy - Madison County Schools
... Now that you've answered the first question correctly, try this one: which car (red, green, or blue) experiences the greatest acceleration? ...
... Now that you've answered the first question correctly, try this one: which car (red, green, or blue) experiences the greatest acceleration? ...
Forces and Newton*s Laws
... • 2nd Law: Force equals mass times acceleration • 3rd Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. • Law of Universal Gravitation: There is a gravitational force between every two objects. They pull on each other equally. ...
... • 2nd Law: Force equals mass times acceleration • 3rd Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. • Law of Universal Gravitation: There is a gravitational force between every two objects. They pull on each other equally. ...
Acceleration - Sikeston R-6
... Teacher Page •IV. Force, motion and mechanical energy •A. Relative Motion •7th grade assessment •Science standards 3.1; 3.3; 4.1 •Students should be able to explain how an object’s acceleration is affected by outside forces and its mass. •View lesson before using with students. Click mouse to view s ...
... Teacher Page •IV. Force, motion and mechanical energy •A. Relative Motion •7th grade assessment •Science standards 3.1; 3.3; 4.1 •Students should be able to explain how an object’s acceleration is affected by outside forces and its mass. •View lesson before using with students. Click mouse to view s ...
Newton*s Laws of Motion
... • He was born in England on December 25, 1643. He was born the same year that Galileo died. • Newton attended Trinity College Cambridge where he became interested in math, physics, and astronomy. • Newton had new ideas about motion, which he called his three laws of motion. ...
... • He was born in England on December 25, 1643. He was born the same year that Galileo died. • Newton attended Trinity College Cambridge where he became interested in math, physics, and astronomy. • Newton had new ideas about motion, which he called his three laws of motion. ...