... E is everywhere perpendicular to the sphere and S is perpendicular to E and B, S is everywhere tangential to the surface of the sphere, so I do not expect a component of S normal to the sphere and so there is no energy flux going through my spherical surface, so the 2nd integral of equation [4] is i ...
CLASSICAL_PHYSICS_edit
... Describing Motion continued • Speed is the distance traveled divided by the time taken to travel that distance. • Speed is important in describing motion because it tells how fast an object is moving away from its beginning position. • The units for speed are often m/s, but can be any distance unit ...
... Describing Motion continued • Speed is the distance traveled divided by the time taken to travel that distance. • Speed is important in describing motion because it tells how fast an object is moving away from its beginning position. • The units for speed are often m/s, but can be any distance unit ...
Rotational Motion
... How are torques and forces different? • Forces can cause a change in motion in translational motion. • Forces can cause a change motion in rotational motion. HOWEVER, the further the force is from the axis of rotation, the more “effective” it will be in changing motion. Thus, the force as well as t ...
... How are torques and forces different? • Forces can cause a change in motion in translational motion. • Forces can cause a change motion in rotational motion. HOWEVER, the further the force is from the axis of rotation, the more “effective” it will be in changing motion. Thus, the force as well as t ...
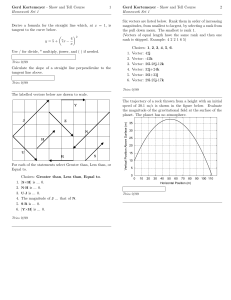
Chapter 4: Newton`s Second Law F = ma First Law
... An object of mass M is on a frictionless horizontal table. This object is connected by a massless string going over a pulley onto a second object m which is falling because of gravity ? What is the acceleration of M , and what are the net forces acting on each of M and m. Free–body diagrams It is ne ...
... An object of mass M is on a frictionless horizontal table. This object is connected by a massless string going over a pulley onto a second object m which is falling because of gravity ? What is the acceleration of M , and what are the net forces acting on each of M and m. Free–body diagrams It is ne ...
Inertia And Force Diagrams
... An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion with constant velocity unless the object experiences a net external force. ...
... An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion with constant velocity unless the object experiences a net external force. ...
Force_motion - Forces-Motion
... • Balanced forces do not cause a change in motion • Click on the web link below: • http://www.mansfieldct.org/schools/mms/st aff/hand/lawsunbalancedforce.htm ...
... • Balanced forces do not cause a change in motion • Click on the web link below: • http://www.mansfieldct.org/schools/mms/st aff/hand/lawsunbalancedforce.htm ...
AP Rotational Motion 9_05 rev
... perpendicular to the original vectors in the problem In these cases a standard convention is needed to establish positive or negative vector direction The “right hand rule” is used in these cases ...
... perpendicular to the original vectors in the problem In these cases a standard convention is needed to establish positive or negative vector direction The “right hand rule” is used in these cases ...
force
... An airboat of mass 3.50 x 102 kg, including passengers, has an engine that produces a net horizontal force of 7.70 x 102 N, after accounting for forces of resistance. (a) Find the acceleration of the airboat (b) Starting from rest, how long does it take the airboat to reach a speed of 12.0 m/s? (c) ...
... An airboat of mass 3.50 x 102 kg, including passengers, has an engine that produces a net horizontal force of 7.70 x 102 N, after accounting for forces of resistance. (a) Find the acceleration of the airboat (b) Starting from rest, how long does it take the airboat to reach a speed of 12.0 m/s? (c) ...
Name - BigEngine
... away from m2 than it was originally. What is the gravitational force between the objects now? A. F/9 B. F/3 C. 3F D. 9F 14. The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Mars is 3.8 m/s2. How much would a 6.3 kg watermelon weigh on Mars? ...
... away from m2 than it was originally. What is the gravitational force between the objects now? A. F/9 B. F/3 C. 3F D. 9F 14. The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Mars is 3.8 m/s2. How much would a 6.3 kg watermelon weigh on Mars? ...
Grade 8 Science Unit 3 – Motion, Stability, Forces, and Interactions
... relationships between variables, and clarifying arguments and models. Ask questions that can be investigated within the scope of the classroom, outdoor environment, and museums and other public facilities with available resources and, when appropriate, frame a hypothesis based on observations and ...
... relationships between variables, and clarifying arguments and models. Ask questions that can be investigated within the scope of the classroom, outdoor environment, and museums and other public facilities with available resources and, when appropriate, frame a hypothesis based on observations and ...