Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... 8. A net force of 5.0 N [S] is applied to a toy electric train of mass 2.5 kg. Calculate the train’s acceleration. 9. Calculate the net force needed to give a 250 kg boat an acceleration of 2.8 m/s2 [W]. ...
... 8. A net force of 5.0 N [S] is applied to a toy electric train of mass 2.5 kg. Calculate the train’s acceleration. 9. Calculate the net force needed to give a 250 kg boat an acceleration of 2.8 m/s2 [W]. ...
Projectile Motion
... The vertical motion of a projectile is not affected by its horizontal motion -meaning: The vertical motion of a projectile is identical to an object in free fall The horizontal motion of a projectile is not affected by its vertical motion - meaning the projectile will travel the same horizontal ...
... The vertical motion of a projectile is not affected by its horizontal motion -meaning: The vertical motion of a projectile is identical to an object in free fall The horizontal motion of a projectile is not affected by its vertical motion - meaning the projectile will travel the same horizontal ...
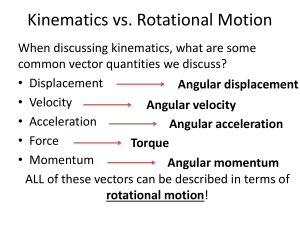
Ch. 9 Rotational Kinematics
... Information is stored on a CD or DVD in a coded pattern of tiny pits. The pits are arranged in a track that spirals outward toward the rim of the disc. As the disc spins inside a player, the track is scanned at a constant linear speed. How must the rotation speed of the disc change as the player’s s ...
... Information is stored on a CD or DVD in a coded pattern of tiny pits. The pits are arranged in a track that spirals outward toward the rim of the disc. As the disc spins inside a player, the track is scanned at a constant linear speed. How must the rotation speed of the disc change as the player’s s ...
Intro to Physics - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Inertia is the tendency of any object to resist any change in motion. This means that if the object is in equilibrium (at rest or constant velocity), it will require an unbalanced force to change its motion. In other words, once set in motion, an object does not seek to change its motion, and will c ...
... Inertia is the tendency of any object to resist any change in motion. This means that if the object is in equilibrium (at rest or constant velocity), it will require an unbalanced force to change its motion. In other words, once set in motion, an object does not seek to change its motion, and will c ...
Lecture Notes on Classical Mechanics for Physics 106ab – Errata
... where the (c) superscript restricts the sum to constraint forces but the sum is over all constraint forces and all particles. with the new text At this point, we specialize to constraints that do no net work when a virtual displacement is applied. This assumption is critical. Making this assumption ...
... where the (c) superscript restricts the sum to constraint forces but the sum is over all constraint forces and all particles. with the new text At this point, we specialize to constraints that do no net work when a virtual displacement is applied. This assumption is critical. Making this assumption ...
Classical Mechanics
... greater than the force of kinetic friction The coefficient of friction (µ) depends on the surfaces in contact The direction of the frictional force is opposite the direction of motion The coefficients of friction are nearly independent of the area of contact ...
... greater than the force of kinetic friction The coefficient of friction (µ) depends on the surfaces in contact The direction of the frictional force is opposite the direction of motion The coefficients of friction are nearly independent of the area of contact ...
Pitt County Schools
... 4.01 Determine that an object will How would you determine that an object continue in its state of motion unless acted would continue in its state of motion unless upon by a net outside force (Newton's acted upon by a net outside force? First Law of Motion, The Law of Inertia). What is inertia? What ...
... 4.01 Determine that an object will How would you determine that an object continue in its state of motion unless acted would continue in its state of motion unless upon by a net outside force (Newton's acted upon by a net outside force? First Law of Motion, The Law of Inertia). What is inertia? What ...
Midway High School Science TAKS Review
... strikes a stationary bowling pin. The ball has 120 kg·m/s of momentum before the collision. If the ball has 100 kg·m/s of momentum after the collision, what is the momentum transferred to the pin? ...
... strikes a stationary bowling pin. The ball has 120 kg·m/s of momentum before the collision. If the ball has 100 kg·m/s of momentum after the collision, what is the momentum transferred to the pin? ...
force problem set 1: 2/17/12
... 16. Refer back to the box in question 15. What is the mass of the box? 17. Refer back to the box in question 15. What is the acceleration of the box? 18. Refer back to the box in question 15. Which of the following could possibly be the velocity of the box? A. 8.5m/s B. 2.2m/s C. 16m/s D. 0m/s 19. W ...
... 16. Refer back to the box in question 15. What is the mass of the box? 17. Refer back to the box in question 15. What is the acceleration of the box? 18. Refer back to the box in question 15. Which of the following could possibly be the velocity of the box? A. 8.5m/s B. 2.2m/s C. 16m/s D. 0m/s 19. W ...
Getting Ready SPH4U Significant figures 1. Indicate the number of
... (a) Based on the units of acceleration, what measuring devices could the inspector use to take measurements to determine the acceleration? (b) Name the independent and dependent variables. ...
... (a) Based on the units of acceleration, what measuring devices could the inspector use to take measurements to determine the acceleration? (b) Name the independent and dependent variables. ...