kinematics of rotation of rigid bodies
... momentum about any axis is the sum of the individual angular momenta. The conservation of angular moment also applies to such systems. In the absence of external forces acting on the system, the total angular momentum of the system remains constant. Note: ...
... momentum about any axis is the sum of the individual angular momenta. The conservation of angular moment also applies to such systems. In the absence of external forces acting on the system, the total angular momentum of the system remains constant. Note: ...
Lecture13
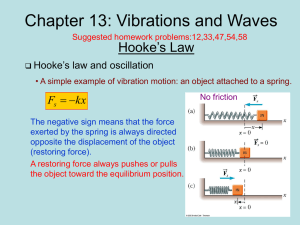
... by restoring forces and the system do not oscillate indefinitely. The friction reduces the mechanical energy of the system as time passes, and the motion is said to be damped. ...
... by restoring forces and the system do not oscillate indefinitely. The friction reduces the mechanical energy of the system as time passes, and the motion is said to be damped. ...
Momentum - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... Collisions and explosions happen so quickly that it is often impossible to calculate anything more than an average force. This is because the force changes so quickly. By examining the momentum before and after the interaction between 2 objects, we can determine impulse. ...
... Collisions and explosions happen so quickly that it is often impossible to calculate anything more than an average force. This is because the force changes so quickly. By examining the momentum before and after the interaction between 2 objects, we can determine impulse. ...
TCSS Physical Science Unit 7 – Force and Motion Information
... SPS8. Students will determine relationships among force, mass, and motion. a. Calculate velocity and acceleration b. Apply Newton’s three laws to everyday situations by explaining the following: Inertia; Relationship between force, mass and acceleration; Equal and opposite forces c. Relate falling o ...
... SPS8. Students will determine relationships among force, mass, and motion. a. Calculate velocity and acceleration b. Apply Newton’s three laws to everyday situations by explaining the following: Inertia; Relationship between force, mass and acceleration; Equal and opposite forces c. Relate falling o ...
Newton`s Laws PPT
... Why then, do we observe every day objects in motion slowing down and becoming motionless seemingly without an outside force? It’s a force we sometimes cannot see – friction. ...
... Why then, do we observe every day objects in motion slowing down and becoming motionless seemingly without an outside force? It’s a force we sometimes cannot see – friction. ...
Momentum and Collisions
... in the truck than in the car. Why is this? Many people imagine that the collision force exerted on the car is much greater than that experienced by the truck. To substantiate this view, they point out that the car is crushed, whereas the truck is only dented. This idea of unequal forces, of course, ...
... in the truck than in the car. Why is this? Many people imagine that the collision force exerted on the car is much greater than that experienced by the truck. To substantiate this view, they point out that the car is crushed, whereas the truck is only dented. This idea of unequal forces, of course, ...
NEWTON`S SECOND LAW FROM QUANTUM PHYSICS
... argue that quantum mechanics and classical particle mechanics must coincide for certain cases. Then we will derive Newton’s Second Law as the first term in a power series and will examine the next (correction) term to determine the circumstances under which Newton’s Second Law is a good approximatio ...
... argue that quantum mechanics and classical particle mechanics must coincide for certain cases. Then we will derive Newton’s Second Law as the first term in a power series and will examine the next (correction) term to determine the circumstances under which Newton’s Second Law is a good approximatio ...
Unit A: Kinematics Exam
... When talking about vertical circular motion we often refer to scenarios dealing with roller coasters or a bucket swinging Things to remember: - Gravity will always act downwards at the same force - Normal force will always be perpendicular from its surface - Tension will always be towards the center ...
... When talking about vertical circular motion we often refer to scenarios dealing with roller coasters or a bucket swinging Things to remember: - Gravity will always act downwards at the same force - Normal force will always be perpendicular from its surface - Tension will always be towards the center ...
Plan of Lectures - The Budker Group
... most commonly used systems are SI (MKS) and Gaussian (CGS). Many working physicists still use CGS as it is particular convenient for E&M. In mechanics, it really does not matter, and we will use all kinds of units. Warning: watch out for unit consistency. Use of the K&K book. We will heavily rely on ...
... most commonly used systems are SI (MKS) and Gaussian (CGS). Many working physicists still use CGS as it is particular convenient for E&M. In mechanics, it really does not matter, and we will use all kinds of units. Warning: watch out for unit consistency. Use of the K&K book. We will heavily rely on ...
Circular Motion - Manchester HEP
... Newton 2 for hanging mass T mg ma (1) Newton 2 for rotating disk I Torque from tension applied at distance r Tr Hence T I / r (2) Angular and linear acceleration v r hence differentiating a r (3) Sub (2),(3) into (1): I mg mr r ...
... Newton 2 for hanging mass T mg ma (1) Newton 2 for rotating disk I Torque from tension applied at distance r Tr Hence T I / r (2) Angular and linear acceleration v r hence differentiating a r (3) Sub (2),(3) into (1): I mg mr r ...
lab 3: newton`s second law of motion
... Force can be defined as any influence that tends to change the motion of an object, and can be thought of as a push or a pull acting on an object. Mass is the measure of the inertia of an object. Inertia or mass relates to how difficult it is to start a resting object into motion, or alternatively, ...
... Force can be defined as any influence that tends to change the motion of an object, and can be thought of as a push or a pull acting on an object. Mass is the measure of the inertia of an object. Inertia or mass relates to how difficult it is to start a resting object into motion, or alternatively, ...