study guide answers
... Since going downhill increases velocity, the car will be harder to stop. Mass does not affect the velocity but it does affect how easy or hard it is to stop the car. 5. How does friction affect cars going downhill? Cars with less friction tend to travel faster. 6. Name one way to increase friction M ...
... Since going downhill increases velocity, the car will be harder to stop. Mass does not affect the velocity but it does affect how easy or hard it is to stop the car. 5. How does friction affect cars going downhill? Cars with less friction tend to travel faster. 6. Name one way to increase friction M ...
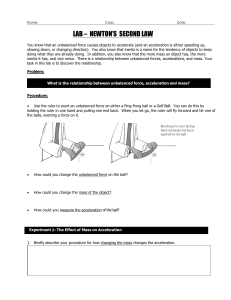
LAB – NEWTON`S SECOND LAW
... is because acceleration and force change in the same way. The equation also shows that if you apply the same force to two objects, the one with the smaller mass will accelerate more. This is because acceleration and mass change in the opposite way. ...
... is because acceleration and force change in the same way. The equation also shows that if you apply the same force to two objects, the one with the smaller mass will accelerate more. This is because acceleration and mass change in the opposite way. ...
Day 3
... As you hurry to catch your flight at the local airport, you encounter a moving walkway that is 85 m long and has a speed of 2.2 m/s relative to the ground. If it takes you 68 s to cover 85 m when walking on the ground, how long will it take you to cover the same distance on the walkway? Assume that ...
... As you hurry to catch your flight at the local airport, you encounter a moving walkway that is 85 m long and has a speed of 2.2 m/s relative to the ground. If it takes you 68 s to cover 85 m when walking on the ground, how long will it take you to cover the same distance on the walkway? Assume that ...
Chapter 10 PowerPoint
... lift off - Newton’s third law gasses expelled with a downward force, exert an equal but opposite force upward on the rocket. Satellite - any object that orbits another object in space centripetal force - any force that causes an object to move in a circular path ...
... lift off - Newton’s third law gasses expelled with a downward force, exert an equal but opposite force upward on the rocket. Satellite - any object that orbits another object in space centripetal force - any force that causes an object to move in a circular path ...
Force
... • He discovered laws of motion and gravity. • Much more: Experiments with light; first reflecting telescope, calculus… Sir Isaac Newton ...
... • He discovered laws of motion and gravity. • Much more: Experiments with light; first reflecting telescope, calculus… Sir Isaac Newton ...
Spring-Mass Problems An object has weight w (in pounds
... coefficients of t. This results in an overdamped system. The mass won’t bob at all. It will just move slowly back to the rest state. 3. One repeated real solution. In this case, the system is critically damped. Below this, the mass will bob up and down, past this, it won’t bob at all. In the case of ...
... coefficients of t. This results in an overdamped system. The mass won’t bob at all. It will just move slowly back to the rest state. 3. One repeated real solution. In this case, the system is critically damped. Below this, the mass will bob up and down, past this, it won’t bob at all. In the case of ...
Simple Harmonic Motion
... Cycle: One complete oscillation of the body. Period (T): The time (in s) for one complete cycle. Frequency (f): The number of complete cycles made per second (in Hertz or s-1). (Note: f = 1 / T) Angular frequency (ω): Also called angular speed, in circular motion this is a measure of the rate of rot ...
... Cycle: One complete oscillation of the body. Period (T): The time (in s) for one complete cycle. Frequency (f): The number of complete cycles made per second (in Hertz or s-1). (Note: f = 1 / T) Angular frequency (ω): Also called angular speed, in circular motion this is a measure of the rate of rot ...
kinematics of rotation of rigid bodies
... momentum about any axis is the sum of the individual angular momenta. The conservation of angular moment also applies to such systems. In the absence of external forces acting on the system, the total angular momentum of the system remains constant. Note: ...
... momentum about any axis is the sum of the individual angular momenta. The conservation of angular moment also applies to such systems. In the absence of external forces acting on the system, the total angular momentum of the system remains constant. Note: ...