28Newtons-Laws-Test - Mr-Hubeny
... b. the first object is unaffected by that force. c. the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first object. d. the second object exerts a less powerful force on the first object. 7. According to Newton’s first law of motion, a moving object that is not acted on by an unbalanced for ...
... b. the first object is unaffected by that force. c. the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first object. d. the second object exerts a less powerful force on the first object. 7. According to Newton’s first law of motion, a moving object that is not acted on by an unbalanced for ...
Newton on K’s 3 Law, To Frame the World—30 Sept • Announcements
... • The force of the gravity of the sun is causing the direction of the motion to change. ...
... • The force of the gravity of the sun is causing the direction of the motion to change. ...
Chap06_lecture
... Newton’s laws: Relations between motions of bodies and the forces acting on them. Newton’s first law: A body at rest remains at rest, and a body in motion remains in motion at the same velocity in a straight path when the net force acting on it is zero. Therefore, a body tends to preserve its state ...
... Newton’s laws: Relations between motions of bodies and the forces acting on them. Newton’s first law: A body at rest remains at rest, and a body in motion remains in motion at the same velocity in a straight path when the net force acting on it is zero. Therefore, a body tends to preserve its state ...
t = 0
... •The acceleration is proportional to the position of the block, and its direction is opposite the direction of the displacement from the equilibrium position. •Systems that behave in this way is called Simple Harmonic Motion. •Object moves with Simple Harmonic Motion its acceleration is proportional ...
... •The acceleration is proportional to the position of the block, and its direction is opposite the direction of the displacement from the equilibrium position. •Systems that behave in this way is called Simple Harmonic Motion. •Object moves with Simple Harmonic Motion its acceleration is proportional ...
Chapter-04-1 - High Point University
... If the net force on an object is zero, then the object will remain at rest or will move with a constant speed in a straight line (uniform motion). 2. Newton’s second law: (accelerating motion) The net force on an object will cause an object to accelerate with an acceleration equal to the net force o ...
... If the net force on an object is zero, then the object will remain at rest or will move with a constant speed in a straight line (uniform motion). 2. Newton’s second law: (accelerating motion) The net force on an object will cause an object to accelerate with an acceleration equal to the net force o ...
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum Linear Momentum and Kinetic Energy
... defined as mass x speed, would remain constant. Although Descartes’ analysis of specific examples was weak, he had sown the seed of an extremely important idea in physics: There is some physical quantity that does not change within an isolated system. This is called a principle of conservation. In 1 ...
... defined as mass x speed, would remain constant. Although Descartes’ analysis of specific examples was weak, he had sown the seed of an extremely important idea in physics: There is some physical quantity that does not change within an isolated system. This is called a principle of conservation. In 1 ...
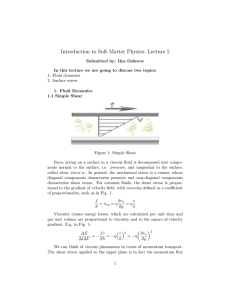
Introduction to Soft Matter Physics- Lecture 5
... where v and l are respectively the characteristic velocities and characteristic sizes of the objects. In colloidal physics, the objects are so small (typically < 1µm), that Re 1 and nonlinear term in the Navier-Stokes equation is neglected in most of the cases. Solving field equations is not an e ...
... where v and l are respectively the characteristic velocities and characteristic sizes of the objects. In colloidal physics, the objects are so small (typically < 1µm), that Re 1 and nonlinear term in the Navier-Stokes equation is neglected in most of the cases. Solving field equations is not an e ...
Circular motion: Extra problems
... on the tire has a linear speed of 2.50 m/s. If the magnitude of the centripetal force is 88.0 N, what is the girls mass? 19. A bicyclist is riding at a linear speed of 13.2 m/s around a circular track. The magnitude of the centripetal force is 377 N, and the combined mass of the bike and the rider i ...
... on the tire has a linear speed of 2.50 m/s. If the magnitude of the centripetal force is 88.0 N, what is the girls mass? 19. A bicyclist is riding at a linear speed of 13.2 m/s around a circular track. The magnitude of the centripetal force is 377 N, and the combined mass of the bike and the rider i ...
Centripetal force - mrhsluniewskiscience
... acceleration, and net force vectors for an object in uniform circular motion. • identify centrifugal force as a fictitious force and explain how it results from an accelerated frame of reference. • use Newton's laws of motion and the concept of centripetal acceleration to solve word problems. ...
... acceleration, and net force vectors for an object in uniform circular motion. • identify centrifugal force as a fictitious force and explain how it results from an accelerated frame of reference. • use Newton's laws of motion and the concept of centripetal acceleration to solve word problems. ...
Unit 8 Momentum 6 lessons - science-b
... The 1st car has a mass of 1875 Kg and an initial velocity of 23.00 m/s @ 0.00º The 2nd car has a mass of 1025 Kg and an initial velocity of 17.00 m/s @ 0.00º After the collision: What is the velocity of the two cars if they both move off @ 0.00º ? #2 Two cars collide…and they stick together. The 1st ...
... The 1st car has a mass of 1875 Kg and an initial velocity of 23.00 m/s @ 0.00º The 2nd car has a mass of 1025 Kg and an initial velocity of 17.00 m/s @ 0.00º After the collision: What is the velocity of the two cars if they both move off @ 0.00º ? #2 Two cars collide…and they stick together. The 1st ...
Wksht Momentum and Collisions
... with a second plastic ball which has half the mass of the first ball. The second ball is moving in the same direction as the first, but has a speed of 0.10 m/s. After the collision, the second ball has a velocity of 0.28 m/s [R]. What is the final velocity of the first ball? 2. An ivory ball of mass ...
... with a second plastic ball which has half the mass of the first ball. The second ball is moving in the same direction as the first, but has a speed of 0.10 m/s. After the collision, the second ball has a velocity of 0.28 m/s [R]. What is the final velocity of the first ball? 2. An ivory ball of mass ...
Lecture 5 : Particle motion
... Note that the alpha particles have an energy of 3.5 MeV and consequently a Larmor radius of 5.4 cm Typical values of the cyclotron frequency are 80 MHz for Hydrogen and 130 GHz for the electrons Often the frequency is much larger than that of the physics processes of interest. One can average over t ...
... Note that the alpha particles have an energy of 3.5 MeV and consequently a Larmor radius of 5.4 cm Typical values of the cyclotron frequency are 80 MHz for Hydrogen and 130 GHz for the electrons Often the frequency is much larger than that of the physics processes of interest. One can average over t ...
Mechanics - Modeling Instruction Program
... Advanced Placement Physics C, commonly known as AP-C Physics, is similar to a college preengineering physics course. To be honest, it is more difficult than most college courses of that level. This AP-C course is a physics course that uses calculus in many of the problems students are asked to solve ...
... Advanced Placement Physics C, commonly known as AP-C Physics, is similar to a college preengineering physics course. To be honest, it is more difficult than most college courses of that level. This AP-C course is a physics course that uses calculus in many of the problems students are asked to solve ...
Document
... speed in a circle is directed towards the center of the circle. A particle is said to be in uniform circular motion if it travels in a circle (or arc) with constant speed v. v red Observe that the velocity vector is always r blue tangent to the circle. y Note that the magnitude of the v velocity ...
... speed in a circle is directed towards the center of the circle. A particle is said to be in uniform circular motion if it travels in a circle (or arc) with constant speed v. v red Observe that the velocity vector is always r blue tangent to the circle. y Note that the magnitude of the v velocity ...
HW #5
... b. Find the average acceleration [added later: and the average force on the torso due to the legs] during deceleration. (Hint: Draw that free-body diagram!) 3. A block on a smooth horizontal surface is connected by a thin rope passing over a pulley to a block of different mass hanging vertically wit ...
... b. Find the average acceleration [added later: and the average force on the torso due to the legs] during deceleration. (Hint: Draw that free-body diagram!) 3. A block on a smooth horizontal surface is connected by a thin rope passing over a pulley to a block of different mass hanging vertically wit ...