simultaneous equations
... The third equation comes from the second by focusing on nonzero components of Γ and B matrices, since the zero components are not to be estimated. Spell out the definitional relation Π Γ = B in greater detail we have two blocks of equations where the coefficients of the first structural equation ar ...
... The third equation comes from the second by focusing on nonzero components of Γ and B matrices, since the zero components are not to be estimated. Spell out the definitional relation Π Γ = B in greater detail we have two blocks of equations where the coefficients of the first structural equation ar ...
Concept Questions
... Step 1: Identify the axis of rotation Step 2: Choose a coordinate system Step 3: Identify the infinitesimal mass element dm. Step 4: Identify the radius, r ,dm , of the circular orbit of the infinitesimal mass element dm. Step 5: Set up the limits for the integral over the body in terms of the phys ...
... Step 1: Identify the axis of rotation Step 2: Choose a coordinate system Step 3: Identify the infinitesimal mass element dm. Step 4: Identify the radius, r ,dm , of the circular orbit of the infinitesimal mass element dm. Step 5: Set up the limits for the integral over the body in terms of the phys ...
AP Physics C IB
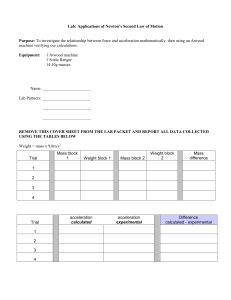
... Ex. Apparent weight of a 72 kg person in an elevator given by the scale reading (normal force). Find the apparent weight when a) the elevator is at rest or moving at a constant velocity b) accelerating upward at 3.20 m/s2 and c) accelerating downward at 3.20 m/s2. ...
... Ex. Apparent weight of a 72 kg person in an elevator given by the scale reading (normal force). Find the apparent weight when a) the elevator is at rest or moving at a constant velocity b) accelerating upward at 3.20 m/s2 and c) accelerating downward at 3.20 m/s2. ...
HS 10 course outline and benchmarks File
... of an object in terms of position, time, velocity, and acceleration. Benchmark 1: Describe the motion of an object in terms of position, time, and velocity. a. Calculate the average velocity of a moving object using data obtained from measurements of position of the object at two or more times. b. D ...
... of an object in terms of position, time, velocity, and acceleration. Benchmark 1: Describe the motion of an object in terms of position, time, and velocity. a. Calculate the average velocity of a moving object using data obtained from measurements of position of the object at two or more times. b. D ...
Two objects are acted on by equal forces for equal times
... Part A-Multiple Choice. 4 points each. Choose the best answer and write it on the line to the left of the question number. ________1. Two ice hockey pucks collide on a frictionless surface. In considering conservation of momentum of the two-puck system, we would break the total momentum into x and ...
... Part A-Multiple Choice. 4 points each. Choose the best answer and write it on the line to the left of the question number. ________1. Two ice hockey pucks collide on a frictionless surface. In considering conservation of momentum of the two-puck system, we would break the total momentum into x and ...
Lecture_6_Chapter_06
... • an object that moves on a circular path of radius r with constant speed v has an acceleration a. • The direction of the acceleration vector always points towards the center of rotation C (thus the name centripetal) Its magnitude is constant ...
... • an object that moves on a circular path of radius r with constant speed v has an acceleration a. • The direction of the acceleration vector always points towards the center of rotation C (thus the name centripetal) Its magnitude is constant ...
Document
... The terminal speed will occur when the acceleration goes to zero Solving the equation gives ...
... The terminal speed will occur when the acceleration goes to zero Solving the equation gives ...
Physics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 5 LAWS OF
... (i) Swimming becomes possible because of third law of motion. (ii) Jumping of a man from a boat onto the bank of a river. (iii) Jerk is produced in a gun when bullet is fired from it. (iv) Pulling of cart by a horse. Note Newton’s second law of motion is called real law of motion because first and t ...
... (i) Swimming becomes possible because of third law of motion. (ii) Jumping of a man from a boat onto the bank of a river. (iii) Jerk is produced in a gun when bullet is fired from it. (iv) Pulling of cart by a horse. Note Newton’s second law of motion is called real law of motion because first and t ...
Document
... Plains, Lines and Automobiles 1. Mr. Slater paid $32,000 for a car. Suppose that the car depreciates linearly at the rate of 15% per year. a. Write an equation for the value, V, of the car after t years. V(t) = _______________________________ b. Graph the equation – be very careful to use appropriat ...
... Plains, Lines and Automobiles 1. Mr. Slater paid $32,000 for a car. Suppose that the car depreciates linearly at the rate of 15% per year. a. Write an equation for the value, V, of the car after t years. V(t) = _______________________________ b. Graph the equation – be very careful to use appropriat ...
No Slide Title
... the velocity the object will follow a uniform circular path. The direction of the velocity changes while the magnitude of the velocity remains constant. The acceleration is called the centripetal acceleration which means “center-seeking” and always points toward the center of the circular path. The ...
... the velocity the object will follow a uniform circular path. The direction of the velocity changes while the magnitude of the velocity remains constant. The acceleration is called the centripetal acceleration which means “center-seeking” and always points toward the center of the circular path. The ...
Force motion and machines powerpoint
... segments (not counting the one that is attached to the effort.) ...
... segments (not counting the one that is attached to the effort.) ...
Unit 7 Vocabulary
... Friction- a force that opposes motion between objects that are touching Line graph- graph used to represent the relationship between two variables. Constant speed- to travel at a steady pace not changing the speed of an object. Relative motion- the motion of an object as compared to another object D ...
... Friction- a force that opposes motion between objects that are touching Line graph- graph used to represent the relationship between two variables. Constant speed- to travel at a steady pace not changing the speed of an object. Relative motion- the motion of an object as compared to another object D ...
On flows induced by electromagnetic fields
... fluids, different material parts in general have different velocities. We will need to find the expressions for the constitutive relations in the stationary lab frame. That is we need to transform the constitutive relations from the instantaneous rest frame, to the lab frame. Following [4] we will u ...
... fluids, different material parts in general have different velocities. We will need to find the expressions for the constitutive relations in the stationary lab frame. That is we need to transform the constitutive relations from the instantaneous rest frame, to the lab frame. Following [4] we will u ...
Morgan Rezer
... 10. Newton’s second law states that to increase acceleration, you _______________increase force or decrease mass_______________________________ 11. What units are used to measure force? ________Newtons_________ 12. A wagon is pulled down a hill with a constant velocity. All the forces on the wagon a ...
... 10. Newton’s second law states that to increase acceleration, you _______________increase force or decrease mass_______________________________ 11. What units are used to measure force? ________Newtons_________ 12. A wagon is pulled down a hill with a constant velocity. All the forces on the wagon a ...
Connecting Force and Motion, and Newton`s First Law of Motion
... Example: The force you are exerting on your seat is the same force your seat is exerting on you - You are pushing the seat down and the seat is holding you up. 2. Back to the initial question: What happens? You fall in a. Why? When you leap from the boat, the boat exerts a force on your feet, moving ...
... Example: The force you are exerting on your seat is the same force your seat is exerting on you - You are pushing the seat down and the seat is holding you up. 2. Back to the initial question: What happens? You fall in a. Why? When you leap from the boat, the boat exerts a force on your feet, moving ...