kg m/s 2
... mE = mass of the earth m = mass of the object d = distance from the center of the earth to the object • but the weight of an object is: W = mg • therefore: mg = G (mEm) / d2 which gives: ...
... mE = mass of the earth m = mass of the object d = distance from the center of the earth to the object • but the weight of an object is: W = mg • therefore: mg = G (mEm) / d2 which gives: ...
In what ways do forces affect an object`s motion?
... • Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change of motion Newton’s first law of motion states that an object will remain at rest or in constant straight-line motion unless unbalanced forces act on the object. • Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object incre ...
... • Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change of motion Newton’s first law of motion states that an object will remain at rest or in constant straight-line motion unless unbalanced forces act on the object. • Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object incre ...
Review Questions
... 1. During a relay race, runner A runs a certain distance due north and then hands off the baton to runner B, who runs for the same distance in a direction south of east. The two displacement vectors A and B can be added together to give a resultant vector R. Which drawing correctly shows the resulta ...
... 1. During a relay race, runner A runs a certain distance due north and then hands off the baton to runner B, who runs for the same distance in a direction south of east. The two displacement vectors A and B can be added together to give a resultant vector R. Which drawing correctly shows the resulta ...
During a relay race, runner A runs a certain distance due north and
... 1. During a relay race, runner A runs a certain distance due north and then hands off the baton to runner B, who runs for the same distance in a direction south of east. The two displacement vectors A and B can be added together to give a resultant vector R. Which drawing correctly shows the resulta ...
... 1. During a relay race, runner A runs a certain distance due north and then hands off the baton to runner B, who runs for the same distance in a direction south of east. The two displacement vectors A and B can be added together to give a resultant vector R. Which drawing correctly shows the resulta ...
Review Sheet for Test 3
... 3. (a) Find the equation of the line with slope 7 which passes through the point (1, −5). (b) Find the equation of the line which passes through the points (1, −3) and (2, 5). (c) Find the equation of the line with slope 5 and y-intercept 42. (d) What is the x-intercept of the line y = 7x − 28? (e) ...
... 3. (a) Find the equation of the line with slope 7 which passes through the point (1, −5). (b) Find the equation of the line which passes through the points (1, −3) and (2, 5). (c) Find the equation of the line with slope 5 and y-intercept 42. (d) What is the x-intercept of the line y = 7x − 28? (e) ...
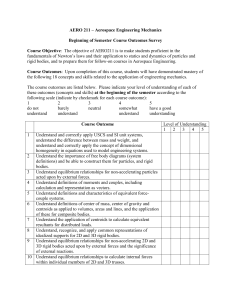
Outcomes Survey Begi.. - Aerospace Engineering Courses page
... and be able to model friction correctly, including the relationship between forces acting normal to a plane of contact and friction forces in the plane of contact. 13 Understand 2D (planar) definitions for velocity and acceleration for Cartesian, polar and path coordinate systems, and be able to tra ...
... and be able to model friction correctly, including the relationship between forces acting normal to a plane of contact and friction forces in the plane of contact. 13 Understand 2D (planar) definitions for velocity and acceleration for Cartesian, polar and path coordinate systems, and be able to tra ...
APiE Assignments – Introduction
... In order to solve this differential equation numerically, you can use the so-called Verlet integration algorithm. It was derived in class, but we also show the steps here - repeat them for yourself! 1. Write down the Taylor-series for x(t+∆t) and x(t−∆t) up to second order in time (terms higher than ...
... In order to solve this differential equation numerically, you can use the so-called Verlet integration algorithm. It was derived in class, but we also show the steps here - repeat them for yourself! 1. Write down the Taylor-series for x(t+∆t) and x(t−∆t) up to second order in time (terms higher than ...
32. (5.1, 5.4) Newton`s second law In an inertial reference frame, the
... object is at a position 5m below the release point; v0=0 m/s - the initial velocity of the object v1=? m/s - the velocity of the object at instant t1 a=[0,-g] - the acceleration (constant) of the object Only the y-direction provides nontrivial equations. v y ( t1 ) = 0 − 10 t1 ...
... object is at a position 5m below the release point; v0=0 m/s - the initial velocity of the object v1=? m/s - the velocity of the object at instant t1 a=[0,-g] - the acceleration (constant) of the object Only the y-direction provides nontrivial equations. v y ( t1 ) = 0 − 10 t1 ...
Force and Motion
... 1. Was your hypothesis proven correct or incorrect? 2. Did the vehicle accelerate? Why or why not? 3. What is the relationship between the dependent and independent variable? ...
... 1. Was your hypothesis proven correct or incorrect? 2. Did the vehicle accelerate? Why or why not? 3. What is the relationship between the dependent and independent variable? ...
Chemical
... left, which side of the car do you want to sit on so you won’t get squished? Explain your answer (you may use a diagram) ...
... left, which side of the car do you want to sit on so you won’t get squished? Explain your answer (you may use a diagram) ...
Lesson 9 - The Link Between Force and Motion
... Newton's second law of motion predicts the behavior of objects when all existing forces are not balanced. The second law states that the acceleration of an object is dependent upon two variables o the net force acting upon the object, and o the mass of the object. As the force acting upon an obj ...
... Newton's second law of motion predicts the behavior of objects when all existing forces are not balanced. The second law states that the acceleration of an object is dependent upon two variables o the net force acting upon the object, and o the mass of the object. As the force acting upon an obj ...
Honors FORCE Study Guide KEY
... 5. You are pushing two boxes across the floor with the same amount of force. One box is more massive than the other. What happens to the acceleration the more massive box? decreases 6. Two students are moving a cart of science supplies for the ninth grade science teachers. The full cart has a mass o ...
... 5. You are pushing two boxes across the floor with the same amount of force. One box is more massive than the other. What happens to the acceleration the more massive box? decreases 6. Two students are moving a cart of science supplies for the ninth grade science teachers. The full cart has a mass o ...