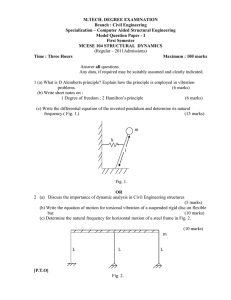
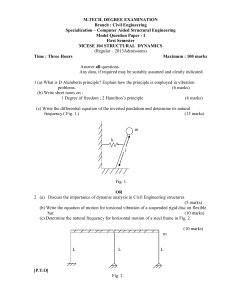
(e) None of the above
... deemed more serious? A. Copernicus didn’t publish his ideas until just before he died. B. Copernicus’ family was more influential in Poland than Galileo’s was in Italy. C. More people in Italy could read Italian than could read Latin. D. Galileo’s ideas were also presented in pictures, which everyon ...
... deemed more serious? A. Copernicus didn’t publish his ideas until just before he died. B. Copernicus’ family was more influential in Poland than Galileo’s was in Italy. C. More people in Italy could read Italian than could read Latin. D. Galileo’s ideas were also presented in pictures, which everyon ...
DYN.A – Original Assignment Name: Speed and Velocity Concepts
... a. in the same direction as the net force that acts upon it b. in the opposite direction as the net force that acts upon it c. in the same direction as the object is moving d. in the opposite direction as the object is moving e. ... none of these! ...
... a. in the same direction as the net force that acts upon it b. in the opposite direction as the net force that acts upon it c. in the same direction as the object is moving d. in the opposite direction as the object is moving e. ... none of these! ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... Provides a reality check (if dimensional analysis fails then there is no sense in putting in numbers) ...
... Provides a reality check (if dimensional analysis fails then there is no sense in putting in numbers) ...
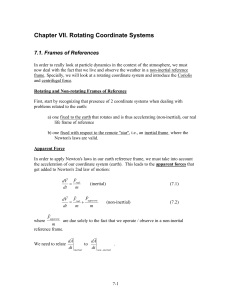
Chapter VII. Rotating Coordinate Systems
... fine the components of Fcor = −2Ω × V in a chosen Cartesian coordinate system. We can also obtain them in a more physical way. Let's do it in the physical way first. Consider first the situation where we have a particle of unit mass moving freely on the frictionless surface of the rotating earth if ...
... fine the components of Fcor = −2Ω × V in a chosen Cartesian coordinate system. We can also obtain them in a more physical way. Let's do it in the physical way first. Consider first the situation where we have a particle of unit mass moving freely on the frictionless surface of the rotating earth if ...
14_Lecture_Outline
... • The amplitude, A, is the maximum magnitude of displacement from equilibrium. • The period, T, is the time for one cycle. • The frequency, f, is the number of cycles per unit time. • The angular frequency, , is 2π times the frequency: = 2πf. • The frequency and period are reciprocals of each oth ...
... • The amplitude, A, is the maximum magnitude of displacement from equilibrium. • The period, T, is the time for one cycle. • The frequency, f, is the number of cycles per unit time. • The angular frequency, , is 2π times the frequency: = 2πf. • The frequency and period are reciprocals of each oth ...
Lecture Outline
... • The amplitude, A, is the maximum magnitude of displacement from equilibrium. • The period, T, is the time for one cycle. • The frequency, f, is the number of cycles per unit time. • The angular frequency, , is 2π times the frequency: = 2πf. • The frequency and period are reciprocals of each oth ...
... • The amplitude, A, is the maximum magnitude of displacement from equilibrium. • The period, T, is the time for one cycle. • The frequency, f, is the number of cycles per unit time. • The angular frequency, , is 2π times the frequency: = 2πf. • The frequency and period are reciprocals of each oth ...
Topic 2 Notes 2 Linear systems: input-response models Jeremy Orloff 2.1 Goals
... answer: First we need to name the function that measures the temperature: Let x(t) = root beer temperature at time t. The simplest model of this situation is Newton’s law of cooling. It says that the rate the temperature of the root beer changes is proportional to the difference between the temperat ...
... answer: First we need to name the function that measures the temperature: Let x(t) = root beer temperature at time t. The simplest model of this situation is Newton’s law of cooling. It says that the rate the temperature of the root beer changes is proportional to the difference between the temperat ...
Physical Principles Handout
... We can rewrite Newton’s second law in a more familiar form knowing that ...
... We can rewrite Newton’s second law in a more familiar form knowing that ...
7.3 Uniform Circular Motion and Centripetal
... object can be described using polar coordinates—r and θ— rather than x and y. The figure at left gives the conversion between the two descriptions. ...
... object can be described using polar coordinates—r and θ— rather than x and y. The figure at left gives the conversion between the two descriptions. ...