Solving Two-Step Equations
... Nancy saved $87 of the money she made babysitting. She wants to buy CDs that cost $15 each, along with a set of headphones that costs $12. How many CDs can she buy? Solve the equation. 15x + 12 ...
... Nancy saved $87 of the money she made babysitting. She wants to buy CDs that cost $15 each, along with a set of headphones that costs $12. How many CDs can she buy? Solve the equation. 15x + 12 ...
AP Physics - eLearning
... c. conservation of energy d. the law of universal gravitation e. conservation of mass ...
... c. conservation of energy d. the law of universal gravitation e. conservation of mass ...
Newton`s Second Law 2 PPT
... The man who follows the crowd will usually get no further than the crowd. The man who walks alone is likely to find himself in places no one has ever been. —Albert Einstein. ...
... The man who follows the crowd will usually get no further than the crowd. The man who walks alone is likely to find himself in places no one has ever been. —Albert Einstein. ...
Forces Webquest Focus Questions
... other forces. It is the force of attraction that every object in the universe exerts on every other object in the universe. This force acts over long distances and pulls objects toward one another. It is an important force in shaping the structure of our galaxy and the universe. You feel this force ...
... other forces. It is the force of attraction that every object in the universe exerts on every other object in the universe. This force acts over long distances and pulls objects toward one another. It is an important force in shaping the structure of our galaxy and the universe. You feel this force ...
phy211_4 - Personal.psu.edu
... If an object has zero component of acceleration in a certain direction then there is a NET FORCE of ZERO acting on the object in that direction Newtons Laws and circular motion acceleration associated with uniform circular motion must be produced a force ...
... If an object has zero component of acceleration in a certain direction then there is a NET FORCE of ZERO acting on the object in that direction Newtons Laws and circular motion acceleration associated with uniform circular motion must be produced a force ...
force=mass times acceleration
... 17. Motion: any change in an object's position 18. Net force: combination of all forces acting on an object 19. Newton: the SI unit of force; N 20. Newton's First Law of Motion: Law of Inertia: An object at rest will remain at rest unless an unbalanced force acts upon the object. An object in motion ...
... 17. Motion: any change in an object's position 18. Net force: combination of all forces acting on an object 19. Newton: the SI unit of force; N 20. Newton's First Law of Motion: Law of Inertia: An object at rest will remain at rest unless an unbalanced force acts upon the object. An object in motion ...
Rotational Motion
... rotational velocity of 5 rev/s about a vertical axis. The rotational inertia of the wheel is 2 kg·m2 about its center and the rotational inertia of the student and wheel and platform about the rotational axis of the platform is 6 kg·m2. What is the initial angular momentum of the system? a) ...
... rotational velocity of 5 rev/s about a vertical axis. The rotational inertia of the wheel is 2 kg·m2 about its center and the rotational inertia of the student and wheel and platform about the rotational axis of the platform is 6 kg·m2. What is the initial angular momentum of the system? a) ...
Unit_2_AP_Forces_Review_Problems
... 6. Let’s say your textbooks have a total mass of 3.0 kg. What would be the mass of the books if they were taken to Jupiter where the acceleration due to gravity is 10 times that of Earth? 7. Suppose the acceleration of an object is zero. Does this mean there are no forces acting on it? 8. Only one f ...
... 6. Let’s say your textbooks have a total mass of 3.0 kg. What would be the mass of the books if they were taken to Jupiter where the acceleration due to gravity is 10 times that of Earth? 7. Suppose the acceleration of an object is zero. Does this mean there are no forces acting on it? 8. Only one f ...
PHY–302 K. Solutions for Problem set # 8. Textbook problem 7.16
... (b) Eq. (49) gives us one relation between displacements of the man and the boat relative to the pier. We also know that the man starts at the boat’s stern and ends at its prow, which gives us his displacement relative to the boat, ∆X rel = L = 12 ft, the length of the boat. In terms of the man’s an ...
... (b) Eq. (49) gives us one relation between displacements of the man and the boat relative to the pier. We also know that the man starts at the boat’s stern and ends at its prow, which gives us his displacement relative to the boat, ∆X rel = L = 12 ft, the length of the boat. In terms of the man’s an ...
StudyGuideForcesAP2016
... d. A person standing in an elevator that is moving downward and slowing down. e. A box sliding down an incline plane of θ and speeding up. 2. Write the net force equation in both the x and y directions for the FBDs in #1 3. What is the normal force and how can it change in different situations (disc ...
... d. A person standing in an elevator that is moving downward and slowing down. e. A box sliding down an incline plane of θ and speeding up. 2. Write the net force equation in both the x and y directions for the FBDs in #1 3. What is the normal force and how can it change in different situations (disc ...
Worked solutions Chapter 2: Collisions and
... The horizontal displacement of the ball at t = 1.0 s = 11.3 × 1.0 = 11.3 m, while the vertical displacement at t = 1.0 s using x = ut + 0.5at2 = 11.3 × 1.0 – 0.5 × 9.8 × 1.02 = 6.41 m The resultant displacement after 1.0 s = [(11.3)2 + (6.41)2] ½ = 13.0 m The angle of the displacement from the hor ...
... The horizontal displacement of the ball at t = 1.0 s = 11.3 × 1.0 = 11.3 m, while the vertical displacement at t = 1.0 s using x = ut + 0.5at2 = 11.3 × 1.0 – 0.5 × 9.8 × 1.02 = 6.41 m The resultant displacement after 1.0 s = [(11.3)2 + (6.41)2] ½ = 13.0 m The angle of the displacement from the hor ...
SHM Part 1 - Ask Physics
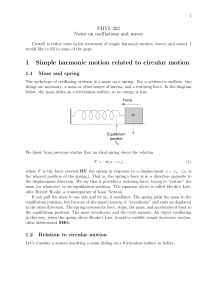
... We know that if we stretch or compress a spring, the mass will oscillate back and forth about its equilibrium (mean) position. Equilibrium position is the point where net force and net torque is zero. Here, equilibrium position corresponds to the point at which spring is at its natural length, i.e., ...
... We know that if we stretch or compress a spring, the mass will oscillate back and forth about its equilibrium (mean) position. Equilibrium position is the point where net force and net torque is zero. Here, equilibrium position corresponds to the point at which spring is at its natural length, i.e., ...
Centripetal Force
... bicycle rounding a flat curve will have a static force of friction maintain its circular motion. A bicycle rounding a banked curve will have a component of the normal force maintain its circular motion. A bicycle at the bottom of a circular dip in the road will have a centripetal force that is the d ...
... bicycle rounding a flat curve will have a static force of friction maintain its circular motion. A bicycle rounding a banked curve will have a component of the normal force maintain its circular motion. A bicycle at the bottom of a circular dip in the road will have a centripetal force that is the d ...