Newton`s Laws Summative Assessment
... 2. When an unbalanced force acts on an object, the force ______________________. a. changes the motion of the object b. is canceled by another force c. does not change the motion of the object d. dis equal to the weight of the object ...
... 2. When an unbalanced force acts on an object, the force ______________________. a. changes the motion of the object b. is canceled by another force c. does not change the motion of the object d. dis equal to the weight of the object ...
24 newtons laws of motion 2 - lindsey
... Newton’s 2nd Law proves that different masses accelerate to the earth at the same rate, but with different forces. ...
... Newton’s 2nd Law proves that different masses accelerate to the earth at the same rate, but with different forces. ...
Note that in the following three figures, which show
... We learned earlier that if an object is at rest, then the total of all the external forces acting on it must be zero. If we are also considering the possibility of rotational motion, we must add a second condition for a body at rest: The net torque of all the external forces acting on the body, wit ...
... We learned earlier that if an object is at rest, then the total of all the external forces acting on it must be zero. If we are also considering the possibility of rotational motion, we must add a second condition for a body at rest: The net torque of all the external forces acting on the body, wit ...
Slajd 1 - pravos.hr
... I. Every object in a state of uniform motion tends to remain in that state of motion unless an external force is applied to it. ...
... I. Every object in a state of uniform motion tends to remain in that state of motion unless an external force is applied to it. ...
Chapter 7
... The sign of the acceleration does not have to be the same as the sign of the angular speed The instantaneous angular acceleration is defined as the limit of the average acceleration as the time interval approaches zero ...
... The sign of the acceleration does not have to be the same as the sign of the angular speed The instantaneous angular acceleration is defined as the limit of the average acceleration as the time interval approaches zero ...
Newton's Laws
... directed downward and it varies from location to location. • Mass is a universal constant which is a measure of the inertia of a body. ...
... directed downward and it varies from location to location. • Mass is a universal constant which is a measure of the inertia of a body. ...
Slide 1
... diagram showing all force acting on that body and the points at which these forces act. 2. Choose a convenient coordinate system and resolve the forces into their components. 3. Using letters to represent the unknowns, write down equations for SFx = 0, SFy = 0, S = 0. 4. For the S = 0 equation, ch ...
... diagram showing all force acting on that body and the points at which these forces act. 2. Choose a convenient coordinate system and resolve the forces into their components. 3. Using letters to represent the unknowns, write down equations for SFx = 0, SFy = 0, S = 0. 4. For the S = 0 equation, ch ...
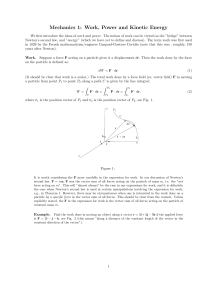
KINETICS OF A PARTICLE: FORCE MASS AND ACCELERATION
... noninertial. All accelerating references are non inertial. In contrast, observers for whom the law of inertia is valid are said to be using inertial frame of reference for their observation. A Newtonian or inertial frame of reference does not rotate and is either fixed or translates in a given dire ...
... noninertial. All accelerating references are non inertial. In contrast, observers for whom the law of inertia is valid are said to be using inertial frame of reference for their observation. A Newtonian or inertial frame of reference does not rotate and is either fixed or translates in a given dire ...
Day 01- Drawing FBDs Solutions see p2
... 107N. a )What is the force of gravity on the rocket at the Earth’s surface? b) Calculate the net force at liftoff. c) Calculate the initial acceleration of the rocket. d) What should happen to the acceleration if the force exerted by the engine remains constant as it burns? e) Why is the first stag ...
... 107N. a )What is the force of gravity on the rocket at the Earth’s surface? b) Calculate the net force at liftoff. c) Calculate the initial acceleration of the rocket. d) What should happen to the acceleration if the force exerted by the engine remains constant as it burns? e) Why is the first stag ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... The more mass an object has, the harder it is to get it to move or to stop! This is why seatbelts save people – they prevent you from maintaining a speed of 60-70 miles an hour when the ...
... The more mass an object has, the harder it is to get it to move or to stop! This is why seatbelts save people – they prevent you from maintaining a speed of 60-70 miles an hour when the ...
Projectile Motion y(final)≠0
... A block S of mass M,, attached to another block H of mass m via a rope, is sliding on a frictionless surface. a) What is the acceleration of block H? b) What is the tension in the cord ? 1)) Draw a free-bodyy diagram g showingg all forces actingg on bodyy and the points at which these forces act. 2) ...
... A block S of mass M,, attached to another block H of mass m via a rope, is sliding on a frictionless surface. a) What is the acceleration of block H? b) What is the tension in the cord ? 1)) Draw a free-bodyy diagram g showingg all forces actingg on bodyy and the points at which these forces act. 2) ...
8.3
... is measured in kilograms (kg). Newton’s second law shows that force is measured in kilograms times meters per second (kg x m/s²). This unit is also called the newton (N) which is the SI unit of force. One newton is the force required to give a 1-kg mass an acceleration of 1 m/s². Newton’s Third Law ...
... is measured in kilograms (kg). Newton’s second law shows that force is measured in kilograms times meters per second (kg x m/s²). This unit is also called the newton (N) which is the SI unit of force. One newton is the force required to give a 1-kg mass an acceleration of 1 m/s². Newton’s Third Law ...
Newton's Laws of Motion
... natural philosophy) in 1687. Today these laws are known as Newton’s Laws of Motion and describe the motion of all objects on the scale we experience in our everyday lives. ...
... natural philosophy) in 1687. Today these laws are known as Newton’s Laws of Motion and describe the motion of all objects on the scale we experience in our everyday lives. ...
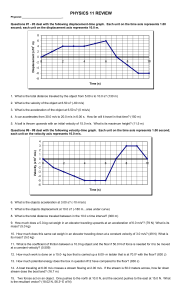
physics_11_review_be.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... (B) If it falls, what is its kinetic energy just before it hits the ground? (294 J) (C) What is its velocity just before it hits the ground? (19.7 m/s) (D) What is the velocity of the apple 7.00 meters above the ground? (16.0 m/s) 25. A 90.0 kg fullback running at 5.0 m/s attempts to dive across a g ...
... (B) If it falls, what is its kinetic energy just before it hits the ground? (294 J) (C) What is its velocity just before it hits the ground? (19.7 m/s) (D) What is the velocity of the apple 7.00 meters above the ground? (16.0 m/s) 25. A 90.0 kg fullback running at 5.0 m/s attempts to dive across a g ...