Practice 4
... 1. A flywheel of radius 27.0 cm has an angular speed of 47.0 rpm. What is that in rad/s? 2. Convert 620 rad/s into rpm 3. A shaft of radius 8.50 cm rotates 7.00 rad/s. Through what angular displacement does it go in 1.20 s? 4. Find the angular speed in rpm of the second hand of a wall clock. 5. Find ...
... 1. A flywheel of radius 27.0 cm has an angular speed of 47.0 rpm. What is that in rad/s? 2. Convert 620 rad/s into rpm 3. A shaft of radius 8.50 cm rotates 7.00 rad/s. Through what angular displacement does it go in 1.20 s? 4. Find the angular speed in rpm of the second hand of a wall clock. 5. Find ...
Chapter 5 Worksheets - School District of La Crosse
... 15. What is Newton’s first law of motion? 16. To understand forces acting in 2 directions, what must we do? ...
... 15. What is Newton’s first law of motion? 16. To understand forces acting in 2 directions, what must we do? ...
Laws of motion Power Point
... walking, her feet push against the ground while the ground pushes against her feet. Thus action/reaction – pair is the feet and ground pushing off of one another. ...
... walking, her feet push against the ground while the ground pushes against her feet. Thus action/reaction – pair is the feet and ground pushing off of one another. ...
Elastically Deformable Models
... The carpets slides off the bodies due to the interaction between gravity and repulsive collision force. ...
... The carpets slides off the bodies due to the interaction between gravity and repulsive collision force. ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... While approaching a red light a semi truck takes longer and uses more force on the breaks to stop than a small car does. Which of the following gives reasoning for this situation? a. The truck is going too fast. b. The truck has more inertia c. The truck has more momentum due to its’ mass. d. BOTH B ...
... While approaching a red light a semi truck takes longer and uses more force on the breaks to stop than a small car does. Which of the following gives reasoning for this situation? a. The truck is going too fast. b. The truck has more inertia c. The truck has more momentum due to its’ mass. d. BOTH B ...
PHY820 Homework Set 5
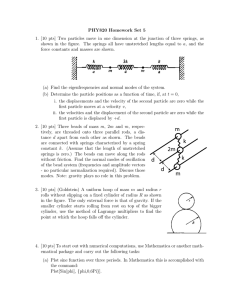
... (a) Find the eigenfrequencies and normal modes of the system. (b) Determine the particle positions as a function of time, if, at t = 0, i. the displacements and the velocity of the second particle are zero while the first particle moves at a velocity v, ii. the velocities and the displacement of the ...
... (a) Find the eigenfrequencies and normal modes of the system. (b) Determine the particle positions as a function of time, if, at t = 0, i. the displacements and the velocity of the second particle are zero while the first particle moves at a velocity v, ii. the velocities and the displacement of the ...
Objects in Motion
... • A penny is dropped from the top of the Empire State Building (381 m). Ignoring the effect of air resistance, the penny will fall for approximately 9 s. What will be its final velocity in m/s? – Assume that the acceleration due to gravity (g) is 10 m/s2 and that the penny starts from rest. Velocit ...
... • A penny is dropped from the top of the Empire State Building (381 m). Ignoring the effect of air resistance, the penny will fall for approximately 9 s. What will be its final velocity in m/s? – Assume that the acceleration due to gravity (g) is 10 m/s2 and that the penny starts from rest. Velocit ...
Honors Homework
... A proton collides elastically with another proton that is initially at rest. The incoming proton has an initial speed of 3.5 x 105 m/s and makes a collision with the second proton. After the collision, one proton moves off at an angle of 37.0 o to the original direction of motion and the second defl ...
... A proton collides elastically with another proton that is initially at rest. The incoming proton has an initial speed of 3.5 x 105 m/s and makes a collision with the second proton. After the collision, one proton moves off at an angle of 37.0 o to the original direction of motion and the second defl ...
chapter7_PC
... The booster rocket casing of 1500 kg is separated from a 12,000 kg spaceship by explosive bolts. An impulse of at least 480 Ns is needed for safe separation. The speed of the booster casing relative to the spaceship after separation is: ...
... The booster rocket casing of 1500 kg is separated from a 12,000 kg spaceship by explosive bolts. An impulse of at least 480 Ns is needed for safe separation. The speed of the booster casing relative to the spaceship after separation is: ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide
... Be able to calculate the speed of an object: 20. What is the formula for speed: ______________________________________________________ Be able to calculate average speed: 21. What is average speed? _____________________________________________________________ 22. What is the formula for average spee ...
... Be able to calculate the speed of an object: 20. What is the formula for speed: ______________________________________________________ Be able to calculate average speed: 21. What is average speed? _____________________________________________________________ 22. What is the formula for average spee ...
7TH CLASSES PHYSICS DAILY PLAN
... Ex: Electrons having 107 m/s velocity are shot into magnetic field of 8 x 10-4 T. Find radius of trajectory. (me = 9 x 10-31kg, e = 1.6 x 10-19 C) Ex: a) Determine of charges. b) Find q1/q2=? masses of particles are ...
... Ex: Electrons having 107 m/s velocity are shot into magnetic field of 8 x 10-4 T. Find radius of trajectory. (me = 9 x 10-31kg, e = 1.6 x 10-19 C) Ex: a) Determine of charges. b) Find q1/q2=? masses of particles are ...
Physics: Principles and Applications, 6e Giancoli
... 2) The resultant of two vectors is the smallest when the angle between them is A) 0°. B) 45°. C) 90°. D) 180°. 3) Two displacement vectors have magnitudes of 5.0 m and 7.0 m, respectively. When these two vectors are added, the magnitude of the sum A) is 2.0 m. B) could be as small as 2.0 m, or as la ...
... 2) The resultant of two vectors is the smallest when the angle between them is A) 0°. B) 45°. C) 90°. D) 180°. 3) Two displacement vectors have magnitudes of 5.0 m and 7.0 m, respectively. When these two vectors are added, the magnitude of the sum A) is 2.0 m. B) could be as small as 2.0 m, or as la ...
Forces
... Newton’s Law of Gravity • Gravity is the natural force that pulls one object toward another. The strength of this pull depends on the mass of the objects involved. • The pull is directly proportional to the masses of the objects and inversely proportional to the distance between the objects. ...
... Newton’s Law of Gravity • Gravity is the natural force that pulls one object toward another. The strength of this pull depends on the mass of the objects involved. • The pull is directly proportional to the masses of the objects and inversely proportional to the distance between the objects. ...