
Weeks_4
... the universe” (quote page 323 David Burton) I. Each planet moves around the sun in an ellipse, with the sun at one focus. II. The radius vector from the sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. III. The squares of the periods of any two planets are proportional to the cub ...
... the universe” (quote page 323 David Burton) I. Each planet moves around the sun in an ellipse, with the sun at one focus. II. The radius vector from the sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. III. The squares of the periods of any two planets are proportional to the cub ...
Chapter 4
... An object in motion will stay in motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force Will this occur forever? What forces act everyday? If forces acting on the object are balanced, then the velocity of the object doesn’t change! Inertia- the tendency of an object to resist a change in motion Exa ...
... An object in motion will stay in motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force Will this occur forever? What forces act everyday? If forces acting on the object are balanced, then the velocity of the object doesn’t change! Inertia- the tendency of an object to resist a change in motion Exa ...
ch5-Solving Problems_Force
... with above the horizontal. The tow rope is parallel to the incline and has a tension of 150 N. Assume that the wagon starts from rest at the bottom of the hill, and neglect friction. How fast is the wagon going after moving 60.0 m up the hill? ...
... with above the horizontal. The tow rope is parallel to the incline and has a tension of 150 N. Assume that the wagon starts from rest at the bottom of the hill, and neglect friction. How fast is the wagon going after moving 60.0 m up the hill? ...
background
... * isolated system, sum of external forces acting on system is zero S F = 0 * collision or explosion * S(initial momentum) = S(final momentum) * S(initial momentum)k = S(final momentum)k subscript k represents x, y or z component of momentum ...
... * isolated system, sum of external forces acting on system is zero S F = 0 * collision or explosion * S(initial momentum) = S(final momentum) * S(initial momentum)k = S(final momentum)k subscript k represents x, y or z component of momentum ...
connection
... Some statements about dance technique can be restated using a physics vocabulary… Lifts “feel” the way they do for the same reason that a large star will collapse to form a black hole... ...
... Some statements about dance technique can be restated using a physics vocabulary… Lifts “feel” the way they do for the same reason that a large star will collapse to form a black hole... ...
Section 7: Centripetal Acceleration Misconceptions
... moving nearly in the direction of the applied perpendicular force. Since velocity is a vector quantity, an object that is traveling in a circle is constantly changing its direction and is constantly accelerating. And if the change is constant as in uniform circular motion (constant speed), its accel ...
... moving nearly in the direction of the applied perpendicular force. Since velocity is a vector quantity, an object that is traveling in a circle is constantly changing its direction and is constantly accelerating. And if the change is constant as in uniform circular motion (constant speed), its accel ...
14.1 Force changes motion
... If the net force is zero, an object at rest will stay at rest. If an object is acted upon by unbalanced forces, its motion will change. ...
... If the net force is zero, an object at rest will stay at rest. If an object is acted upon by unbalanced forces, its motion will change. ...
Standard - Peak to Peak Charter School
... Use a calculator to correctly calculate the values of trig functions for given angles (laws of sines & cosines) MAT.10. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve for one side of a right triangle, given the other two sides ...
... Use a calculator to correctly calculate the values of trig functions for given angles (laws of sines & cosines) MAT.10. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve for one side of a right triangle, given the other two sides ...
Circular Motion & Gravity
... – inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the centers of the two masses – If the objects are large (e.g. planets, moons) then the radii would be included in r ...
... – inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the centers of the two masses – If the objects are large (e.g. planets, moons) then the radii would be included in r ...
Honors - Peak to Peak Charter School
... Use a calculator to correctly calculate the values of trig functions for given angles (laws of sines & cosines) MAT.10. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve for one side of a right triangle, given the other two sides ...
... Use a calculator to correctly calculate the values of trig functions for given angles (laws of sines & cosines) MAT.10. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve for one side of a right triangle, given the other two sides ...
Motion Review Notes - Ms. Guggenheimer`s Education Connection
... Motion is a change in position relative to some fixed object or place, measured by distance and time Reference point: a place or object used for comparison to determine if something is in motion (frame of reference) The point from which movement is determined. The reference point is stationary (not ...
... Motion is a change in position relative to some fixed object or place, measured by distance and time Reference point: a place or object used for comparison to determine if something is in motion (frame of reference) The point from which movement is determined. The reference point is stationary (not ...
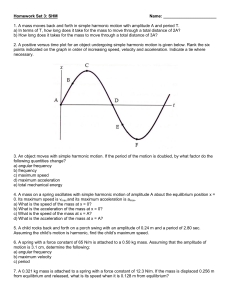
Name - BigEngine
... 12. Two objects, each with a mass of 8.0 x 102 kg produce a gravitational force between them of 3.7 x 10-6 N. What is the distance between them? (2 marks) ...
... 12. Two objects, each with a mass of 8.0 x 102 kg produce a gravitational force between them of 3.7 x 10-6 N. What is the distance between them? (2 marks) ...
Newton second Law of Motion HP 1314
... Net Force Causes Acceleration • To increase the acceleration of an object, you must increase the net force acting on it. • An object’s acceleration is directly proportional to the net force acting on it: acceleration ~ net force ...
... Net Force Causes Acceleration • To increase the acceleration of an object, you must increase the net force acting on it. • An object’s acceleration is directly proportional to the net force acting on it: acceleration ~ net force ...
Presentation
... mass m and radius r. The three objects are arranged so that an axis of rotation passes through the center of each object. The rotation axis is perpendicular to the plane of the flat disk. Which of the three objects has the largest moment of inertia? a) The solid sphere and hollow sphere have the sam ...
... mass m and radius r. The three objects are arranged so that an axis of rotation passes through the center of each object. The rotation axis is perpendicular to the plane of the flat disk. Which of the three objects has the largest moment of inertia? a) The solid sphere and hollow sphere have the sam ...
speed momentum acceleration
... Write ONE, TWO, or THREE 1. The relationship between an objects mass, its acceleration and its force: TWO 2. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction: THREE 3. Every object in motion tends to stay in motion unless another force is acted on it: ONE 4. Inertia: ONE 5. Shooting a rocket ...
... Write ONE, TWO, or THREE 1. The relationship between an objects mass, its acceleration and its force: TWO 2. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction: THREE 3. Every object in motion tends to stay in motion unless another force is acted on it: ONE 4. Inertia: ONE 5. Shooting a rocket ...
ppt - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... barrel is 1.5m long. Assume that the force, and the acceleration, of the shell is constant while the shell is in the gun barrel. What is the force on the shell while it is in the gun ...
... barrel is 1.5m long. Assume that the force, and the acceleration, of the shell is constant while the shell is in the gun barrel. What is the force on the shell while it is in the gun ...


















![[force and motion]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006065207_1-8bff05158caa0c6fdea67b84566f5781-300x300.png)



