PS 5.9 - S2TEM Centers SC
... The force is equal to the mass times the acceleration. (Fw =mag) The force called weight is equal to an object’s mass times the acceleration due to gravity. (9.8m/s2) It is essential for students to Solve problems involving the relationship among the weight and mass of objects and the acceleration ...
... The force is equal to the mass times the acceleration. (Fw =mag) The force called weight is equal to an object’s mass times the acceleration due to gravity. (9.8m/s2) It is essential for students to Solve problems involving the relationship among the weight and mass of objects and the acceleration ...
lesson plan
... 6. Which procedure do we follow to find the resultant force when forces with the same direction and sense come to scene? 7. And what about forces with the same direction and opposite sense? 8. Which procedure do we follow to find the resultant force when we have forces forming an angle with the dire ...
... 6. Which procedure do we follow to find the resultant force when forces with the same direction and sense come to scene? 7. And what about forces with the same direction and opposite sense? 8. Which procedure do we follow to find the resultant force when we have forces forming an angle with the dire ...
Force and Motion
... Forces • An object is said to be in equilibrium when there is no unbalanced force acting upon it. ...
... Forces • An object is said to be in equilibrium when there is no unbalanced force acting upon it. ...
- Smart Science
... graphical representation of motion in depth. The students then move on to looking at forces in Unit 2, starting with their representation on diagrams and their effects. The two concepts are then combined to describe how resultant forces affect movement. Forces are also used to explain why objects fl ...
... graphical representation of motion in depth. The students then move on to looking at forces in Unit 2, starting with their representation on diagrams and their effects. The two concepts are then combined to describe how resultant forces affect movement. Forces are also used to explain why objects fl ...
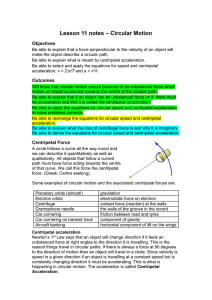
Lesson 22 notes – Circular Motion - science
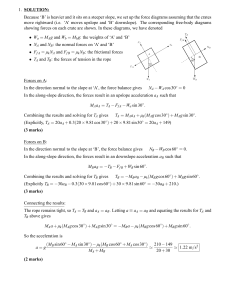
... centripetal force that is proportional to a centripetal acceleration. If there is no more centripetal force the object does not fly out of the circle away from the centre of the circle it just carries along in a straight line out of the circle. Think of the following examples: Sitting in the back se ...
... centripetal force that is proportional to a centripetal acceleration. If there is no more centripetal force the object does not fly out of the circle away from the centre of the circle it just carries along in a straight line out of the circle. Think of the following examples: Sitting in the back se ...
document
... Static Friction: Push with a force F and block does not move because fs = F. The force of friction varies from 0 up to some maximum. The maximum value equals fs = msN, where N is the normal force. Above we would have fs = msmg. The coefficient of static friction ranges from 0 to 1.2 Kinetic Friction ...
... Static Friction: Push with a force F and block does not move because fs = F. The force of friction varies from 0 up to some maximum. The maximum value equals fs = msN, where N is the normal force. Above we would have fs = msmg. The coefficient of static friction ranges from 0 to 1.2 Kinetic Friction ...
chapter 5
... When an object is in motion on a surface or through a viscous medium, there will be a resistance to the motion. This is due to the interactions between the object and its environment. This resistance is called the force of friction. ...
... When an object is in motion on a surface or through a viscous medium, there will be a resistance to the motion. This is due to the interactions between the object and its environment. This resistance is called the force of friction. ...
More Unit #3 Review Questions
... 1. State the reaction force for each of the following forces. (a) the southward force of a field goal kicker’s toe on a football (b) the backward force of a jogger’s shoe on the ground (c) the downward force of a book on a desk (d) the backward force of a jet’s engines on its exhaust gases (e) the b ...
... 1. State the reaction force for each of the following forces. (a) the southward force of a field goal kicker’s toe on a football (b) the backward force of a jogger’s shoe on the ground (c) the downward force of a book on a desk (d) the backward force of a jet’s engines on its exhaust gases (e) the b ...
Jeopardy
... What is the net force on a 10 kg box if it is being dragged to the left with a force of 30 N and there is a 12 N frictional force? ...
... What is the net force on a 10 kg box if it is being dragged to the left with a force of 30 N and there is a 12 N frictional force? ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... Bat hitting a baseball Newton’s 3rd law: Whatever magnitude of force the bat applies to the ball, the ball applies the same magnitude of force back (opposite direction) onto the bat. The bat is slowed by the force of the ball on the bat, and the ball is accelerated by the force of the bat A gun fir ...
... Bat hitting a baseball Newton’s 3rd law: Whatever magnitude of force the bat applies to the ball, the ball applies the same magnitude of force back (opposite direction) onto the bat. The bat is slowed by the force of the ball on the bat, and the ball is accelerated by the force of the bat A gun fir ...
Chapter 7
... explain the principles of how a telescope works discover and describe total internal reflection. explain that tides are caused by the Moon. He tried to use stellar parallax caused by the Earth's orbit to measure the distance to the stars; the same principle as depth perception. Today this branch of ...
... explain the principles of how a telescope works discover and describe total internal reflection. explain that tides are caused by the Moon. He tried to use stellar parallax caused by the Earth's orbit to measure the distance to the stars; the same principle as depth perception. Today this branch of ...