Chapter 5, Part IV
... • 2) If a (point) particle is inside a thin spherical shell, the gravitational force on the particle is zero. So, we can model a sphere as a series of thin shells. For a mass outside any large spherically symmetric mass, the gravitational force acts as though all the mass of the sphere is at the sph ...
... • 2) If a (point) particle is inside a thin spherical shell, the gravitational force on the particle is zero. So, we can model a sphere as a series of thin shells. For a mass outside any large spherically symmetric mass, the gravitational force acts as though all the mass of the sphere is at the sph ...
Hooke`s Law and Simple Harmonic Motion Name:
... 8. Repeat 1-7 for the other two springs. 9. Enter the above data in Excel and for each spring; create two more columns for Stretch (m) and Stretching force (N). Calculate these values and make a single XY scatter Plot Stretching force VS. Stretch for all three springs, and find the spring constant f ...
... 8. Repeat 1-7 for the other two springs. 9. Enter the above data in Excel and for each spring; create two more columns for Stretch (m) and Stretching force (N). Calculate these values and make a single XY scatter Plot Stretching force VS. Stretch for all three springs, and find the spring constant f ...
Ch 2.1 and 2.2 PPT Chap 2.1 and 2.2
... 2. 3.A.1.3: To analyze experimental data describing the motion of an object and to express the result using above representation. ...
... 2. 3.A.1.3: To analyze experimental data describing the motion of an object and to express the result using above representation. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Equilibrium and Torque
... Imagine a bicycle wheel that can only spin about its axle. What affects the torque? 1. The distance from the axis rotation “r” that the force is applied 2. The component of force perpendicular to the r-vector ...
... Imagine a bicycle wheel that can only spin about its axle. What affects the torque? 1. The distance from the axis rotation “r” that the force is applied 2. The component of force perpendicular to the r-vector ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Equilibrium and Torque
... Imagine a bicycle wheel that can only spin about its axle. What affects the torque? 1. The distance from the axis rotation “r” that the force is applied 2. The component of force perpendicular to the r-vector ...
... Imagine a bicycle wheel that can only spin about its axle. What affects the torque? 1. The distance from the axis rotation “r” that the force is applied 2. The component of force perpendicular to the r-vector ...
Chapter 18 Standardized Test Preparation
... 8. The gravitational force between 1 kg of lead and Earth is the gravitational force between 1 kg of marshmallows and Earth. c. equal to Chapter menu ...
... 8. The gravitational force between 1 kg of lead and Earth is the gravitational force between 1 kg of marshmallows and Earth. c. equal to Chapter menu ...
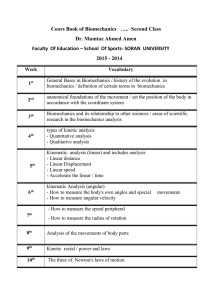
18 th - Soran University
... That which differentiates angular momentum of linear motion is the existence of the axis of rotation moves the entire body or a part of it's parts. This significantly alter the mechanical values. We find that the speed parts of the body vary depending on the distance from the axis of rotation (ie, t ...
... That which differentiates angular momentum of linear motion is the existence of the axis of rotation moves the entire body or a part of it's parts. This significantly alter the mechanical values. We find that the speed parts of the body vary depending on the distance from the axis of rotation (ie, t ...
Ch 14 - Vibrations and Waves
... A: The restoring force depends on mg, and therefore, because anet = Fnet/m, anet is independent of m. Because motion depends on anet and the initial conditions, the motion is independent of the mass. Also, anet is a ratio of F due to gravity and mass. As mass increases, so does Fg in direct proporti ...
... A: The restoring force depends on mg, and therefore, because anet = Fnet/m, anet is independent of m. Because motion depends on anet and the initial conditions, the motion is independent of the mass. Also, anet is a ratio of F due to gravity and mass. As mass increases, so does Fg in direct proporti ...
physics 8866/02 - A Level Tuition
... The system is modified to have a longer wrench so that the applied force required to move the boxes at the same speed as in (i) may be reduced. Deduce with explanation how this modification affects, if at all, the energy required to move the boxes by the same distance. ...
... The system is modified to have a longer wrench so that the applied force required to move the boxes at the same speed as in (i) may be reduced. Deduce with explanation how this modification affects, if at all, the energy required to move the boxes by the same distance. ...
Equality of Column Vectors
... A scalar quantity has a magnitude but no direction. For example, a pen may have length "10 cm". The length 10 cm is a scalar quantity - it has magnitude, but no direction is involved. In vectors, a fixed numeric value is called a scalar. We can increase or decrease the magnitude of a vector by multi ...
... A scalar quantity has a magnitude but no direction. For example, a pen may have length "10 cm". The length 10 cm is a scalar quantity - it has magnitude, but no direction is involved. In vectors, a fixed numeric value is called a scalar. We can increase or decrease the magnitude of a vector by multi ...
Force motion and machines powerpoint
... can be summarized by the equation F=ma. • More mass takes more force to move. (Kick a wall or a ball?) • Newtons second law of motion explains why an unbalanced forces cause an object to accelerate in the direction of the greatest force. • Balanced forced lead to NO acceleration – or constant speed ...
... can be summarized by the equation F=ma. • More mass takes more force to move. (Kick a wall or a ball?) • Newtons second law of motion explains why an unbalanced forces cause an object to accelerate in the direction of the greatest force. • Balanced forced lead to NO acceleration – or constant speed ...
Tuesday, June 3, 2008
... Weight of an object is the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted on the object. Not an inherent property of an object!!! Weight will change if you measure on the Earth or on the moon but the mass won’t!! kg 21 Unit of mass? Tuesday, June 3, 2008 PHYS 1441-001, Summer 2008 Dr. Jaehoon Yu ...
... Weight of an object is the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted on the object. Not an inherent property of an object!!! Weight will change if you measure on the Earth or on the moon but the mass won’t!! kg 21 Unit of mass? Tuesday, June 3, 2008 PHYS 1441-001, Summer 2008 Dr. Jaehoon Yu ...
During a relay race, runner A runs a certain distance due north and
... 14. Two forces act on a moving object that has a mass of 5 kg. One has a magnitude of 12 N and points due south, while the other has a magnitude of 37 N and points due north. What is the acceleration of the object? A 5 m/s2 directed south B 10 m/s2 directed south C 5 m/s2 directed north D 10 m/s2 di ...
... 14. Two forces act on a moving object that has a mass of 5 kg. One has a magnitude of 12 N and points due south, while the other has a magnitude of 37 N and points due north. What is the acceleration of the object? A 5 m/s2 directed south B 10 m/s2 directed south C 5 m/s2 directed north D 10 m/s2 di ...
Newton
... (either magnitude, or direction or both) • If an object is accelerating, it is being acted upon by a force, and F = ma. No exceptions. ...
... (either magnitude, or direction or both) • If an object is accelerating, it is being acted upon by a force, and F = ma. No exceptions. ...