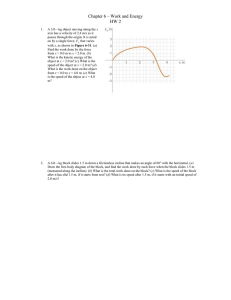
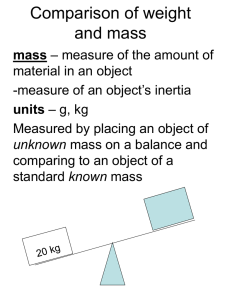
Newton`s 2nd Law Note
... motion can be described (words, graphs, diagrams, numbers, etc.) were discussed. In this unit (Newton's Laws of Motion), the ways in which motion can be explained will be discussed. Isaac Newton (a 17th century scientist) put forth a variety of laws which explain why objects move (or don't move) as ...
... motion can be described (words, graphs, diagrams, numbers, etc.) were discussed. In this unit (Newton's Laws of Motion), the ways in which motion can be explained will be discussed. Isaac Newton (a 17th century scientist) put forth a variety of laws which explain why objects move (or don't move) as ...
L 6
... • Objects have a property called inertia which causes them to resist changes in their motion (Newton’s1st Law or Galileo’s law of inertia) if it is at rest, it stays at rest if it is moving, it keeps moving • forces overcome inertia to produce acceleration (2nd Law) change in velocity ...
... • Objects have a property called inertia which causes them to resist changes in their motion (Newton’s1st Law or Galileo’s law of inertia) if it is at rest, it stays at rest if it is moving, it keeps moving • forces overcome inertia to produce acceleration (2nd Law) change in velocity ...
Motion and Forces ppt.
... according to the inverse-square law. The force of gravity weakens as the distance squared. Ex: If you were three times farther from the center of the Earth as you are now, your weight would be 1/9 of what it is now. ...
... according to the inverse-square law. The force of gravity weakens as the distance squared. Ex: If you were three times farther from the center of the Earth as you are now, your weight would be 1/9 of what it is now. ...
2 - ScienceScene
... III. Unit Objectives for Motion 1. Given the following list of terms, identify each term's correct definition. Conversely, given the definition, identify the correct term. acceleration, constant acceleration, force, inertia, kinetic energy, linear motion, mass, momentum, speed, time, velocity, weig ...
... III. Unit Objectives for Motion 1. Given the following list of terms, identify each term's correct definition. Conversely, given the definition, identify the correct term. acceleration, constant acceleration, force, inertia, kinetic energy, linear motion, mass, momentum, speed, time, velocity, weig ...
Force
... magnitude of a push or pull in Newtons. • Forces exist as contact or long range. • Use free body diagrams to represent forces when problem solving. • Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion states that the rate of acceleration of an object is proportion to the force applied and inversely proportional to its mass ...
... magnitude of a push or pull in Newtons. • Forces exist as contact or long range. • Use free body diagrams to represent forces when problem solving. • Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion states that the rate of acceleration of an object is proportion to the force applied and inversely proportional to its mass ...
Newtons 2nd law
... is a force, and is measured in Newtons. • The force of gravity causes all objects near Earth’s surface to fall with an acceleration of 9.8 m/s². • Your weight on Earth is the gravitational force between you and Earth. ...
... is a force, and is measured in Newtons. • The force of gravity causes all objects near Earth’s surface to fall with an acceleration of 9.8 m/s². • Your weight on Earth is the gravitational force between you and Earth. ...
Phys Sci Chapter 3 notes
... When you jump on a trampoline, you exert a force downward; the trampoline exerts an equal force upward—sending you back in the air. If forces are equal, how does anything ever happen? Action-reaction forces are acting on different objects! ...
... When you jump on a trampoline, you exert a force downward; the trampoline exerts an equal force upward—sending you back in the air. If forces are equal, how does anything ever happen? Action-reaction forces are acting on different objects! ...
Force and Motion
... • The symbol F is a vector and represents the size and direction of a force, while F represents only the magnitude. ...
... • The symbol F is a vector and represents the size and direction of a force, while F represents only the magnitude. ...
What is a Force? (PowerPoint)
... Before we go any further we need to talk about types of forces. There are many types of forces but we will only touch on seven in detail. There are two others I’d like to mention: Nuclear force: The strong nuclear force is the force that holds the protons and neutrons together in the nucleus of a ...
... Before we go any further we need to talk about types of forces. There are many types of forces but we will only touch on seven in detail. There are two others I’d like to mention: Nuclear force: The strong nuclear force is the force that holds the protons and neutrons together in the nucleus of a ...