Energy, Work and Simple Machines
... • Resistance force • Mechanical advantage • Ideal mechanical advantage • Efficiency • Compound machine ...
... • Resistance force • Mechanical advantage • Ideal mechanical advantage • Efficiency • Compound machine ...
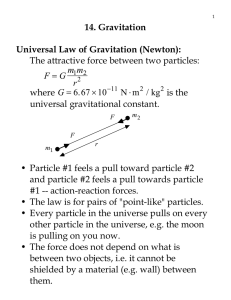
14. Gravitation Universal Law of Gravitation (Newton): G
... Calculate the gravitational force due to a hollowed sphere, assuming that the mass of the ...
... Calculate the gravitational force due to a hollowed sphere, assuming that the mass of the ...
speed momentum acceleration
... Formula: Acc= Final speed- Initial speed/time 10m/s – 30 m/s Acc = 10 sec = -2.0 m/s2 Newton’s Second Law Force = Mass X Acceleration for example: 1 Newton = 1Kg X 1 m/s2 ...
... Formula: Acc= Final speed- Initial speed/time 10m/s – 30 m/s Acc = 10 sec = -2.0 m/s2 Newton’s Second Law Force = Mass X Acceleration for example: 1 Newton = 1Kg X 1 m/s2 ...
Document
... 6. Starting at time t = 0, and object moves along a straight line with velocity in m/s given by v(t) = 98 - 2t2 , where t is in seconds. When it momentarily stops its acceleration is: 7. A car, initially at rest , travels 20 m in 4 s along a straight line with constant acceleration. The acceleration ...
... 6. Starting at time t = 0, and object moves along a straight line with velocity in m/s given by v(t) = 98 - 2t2 , where t is in seconds. When it momentarily stops its acceleration is: 7. A car, initially at rest , travels 20 m in 4 s along a straight line with constant acceleration. The acceleration ...
File jeopardy_review_ch_4
... Choose a category. You will be given the answer. You must give the correct question. Click to begin. ...
... Choose a category. You will be given the answer. You must give the correct question. Click to begin. ...
Instructions - People Server at UNCW
... direction of wave motion b) the vibrating particles move in circles c) the energy carried by each particle is not transmitted to adjacent particles d) the direction of particle displacement is perpendicular to the direction of wave motion _____ l) In the absence of a net force, an object will always ...
... direction of wave motion b) the vibrating particles move in circles c) the energy carried by each particle is not transmitted to adjacent particles d) the direction of particle displacement is perpendicular to the direction of wave motion _____ l) In the absence of a net force, an object will always ...
1 In free fall, when two objects (one twice as massive as the other
... When objects are in free fall, the air resistance (__________ _________) is negligible and the only force on the falling object is the force of _____________________ which is _______________. ...
... When objects are in free fall, the air resistance (__________ _________) is negligible and the only force on the falling object is the force of _____________________ which is _______________. ...
PHYSICS 151 – Notes for Online Lecture 2.2
... Part of the applied force acts to the right and part acts downward. The cabinet is accelerating to the right – not up and down, so the net force on the cabinet must be zero. That means that part of the applied force adds with the weight. The normal force has to support both the weight of the box and ...
... Part of the applied force acts to the right and part acts downward. The cabinet is accelerating to the right – not up and down, so the net force on the cabinet must be zero. That means that part of the applied force adds with the weight. The normal force has to support both the weight of the box and ...