Problem 1 - University of Rochester
... Problem 3 (20 pts, no need to show work): Put “T” next to statements you believe to be true, “F” next to statements you believe to be false, and “N” next to statements that are sometimes true and sometimes false. ____ Sir Issac Newton formulated a useful theory of gravitation. ____ Charles Coulomb d ...
... Problem 3 (20 pts, no need to show work): Put “T” next to statements you believe to be true, “F” next to statements you believe to be false, and “N” next to statements that are sometimes true and sometimes false. ____ Sir Issac Newton formulated a useful theory of gravitation. ____ Charles Coulomb d ...
Dynamics
... III. When traveling in a car around a curve on the highway (at a constant speed), people inside the vehicle feel as though they are being forced towards the outside of the curve. The person continues to move at the speed that the car was moving at, and in a straight line. When the car is forced in o ...
... III. When traveling in a car around a curve on the highway (at a constant speed), people inside the vehicle feel as though they are being forced towards the outside of the curve. The person continues to move at the speed that the car was moving at, and in a straight line. When the car is forced in o ...
Solution to PHY 152 Practice Problem Set 2
... 4 The net electric force on the central charge is then F = 2qE = 2.9 × 10−5 N x̂ − 1.6 × 10−5 N ŷ 2.a. First, it is obvious that −q experiences no net electric force. By symmetry, the electric force on one of the two +Q’s is zero if and only if the other is zero. Therefore, we can just focus on one ...
... 4 The net electric force on the central charge is then F = 2qE = 2.9 × 10−5 N x̂ − 1.6 × 10−5 N ŷ 2.a. First, it is obvious that −q experiences no net electric force. By symmetry, the electric force on one of the two +Q’s is zero if and only if the other is zero. Therefore, we can just focus on one ...
Test 1 - Practice
... m/s. Find the position and time of collision if object B is moving to the left and the position and time of collision if object B is moving to the right. d. use calculus to derive motion equations, derivatives and integrals ...
... m/s. Find the position and time of collision if object B is moving to the left and the position and time of collision if object B is moving to the right. d. use calculus to derive motion equations, derivatives and integrals ...
Newtons 2nd Law - VCC Library
... explicitly say we’re in space, there’s gravity!) The force of gravity is equal to the object’s weight: W or Fg = mg, where g = 9.81 m⁄s² is the acceleration due to gravity. You might be told to round to 10 m⁄s². Gravity always points straight down, never to the side. Normal force. An object experien ...
... explicitly say we’re in space, there’s gravity!) The force of gravity is equal to the object’s weight: W or Fg = mg, where g = 9.81 m⁄s² is the acceleration due to gravity. You might be told to round to 10 m⁄s². Gravity always points straight down, never to the side. Normal force. An object experien ...
Day 3
... As you hurry to catch your flight at the local airport, you encounter a moving walkway that is 85 m long and has a speed of 2.2 m/s relative to the ground. If it takes you 68 s to cover 85 m when walking on the ground, how long will it take you to cover the same distance on the walkway? Assume that ...
... As you hurry to catch your flight at the local airport, you encounter a moving walkway that is 85 m long and has a speed of 2.2 m/s relative to the ground. If it takes you 68 s to cover 85 m when walking on the ground, how long will it take you to cover the same distance on the walkway? Assume that ...
Physics 102 Introduction to Physics
... Units of mass = kg English Units of weight = pounds (lb) A brick with a mass of 1kg weighs 2.2 lb In metric units, weight is expressed in Newtons (N) The acceleration of gravity is g = 9.8 m/s2 (or about 10 m/s2) A brick with a mass of 1kg weighs 9.8 N (or about 10 N) Problem: What is the weight of ...
... Units of mass = kg English Units of weight = pounds (lb) A brick with a mass of 1kg weighs 2.2 lb In metric units, weight is expressed in Newtons (N) The acceleration of gravity is g = 9.8 m/s2 (or about 10 m/s2) A brick with a mass of 1kg weighs 9.8 N (or about 10 N) Problem: What is the weight of ...
Monday, Sept. 22, 2008
... Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained as long as the external causes of retardation are removed!! Galileo’s statement is formulated by Newton into the 1st law of motion (Law of Inertia): In the absence of external forc ...
... Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained as long as the external causes of retardation are removed!! Galileo’s statement is formulated by Newton into the 1st law of motion (Law of Inertia): In the absence of external forc ...
South Pasadena · AP Chemistry
... state the two situations where acceleration is zero (standing still & moving at a constant speed in a straight line) and relate these situations to net force (zero net force). 4-Newton’s First Law ...
... state the two situations where acceleration is zero (standing still & moving at a constant speed in a straight line) and relate these situations to net force (zero net force). 4-Newton’s First Law ...
force
... stay the same? • What will have to happen to the amount of force needed if the mass of an object increases? – It would have to INCREASE ...
... stay the same? • What will have to happen to the amount of force needed if the mass of an object increases? – It would have to INCREASE ...
Forces-part2 [Compatibility Mode]
... Inertial reference frame • An inertial reference frame is one in which an observer: Sees no change in the velocity if the sum of all forces exerted on the system object is zero The force diagram and the motion diagram match. ...
... Inertial reference frame • An inertial reference frame is one in which an observer: Sees no change in the velocity if the sum of all forces exerted on the system object is zero The force diagram and the motion diagram match. ...
Definitions
... reference system for measuring position and time that is not accelerating. If we wish to use Newton’s Second Law in an accelerating reference frame, we need to add extra terms to the equation that can be considered as forces operating on every object that we track using the accelerating reference fr ...
... reference system for measuring position and time that is not accelerating. If we wish to use Newton’s Second Law in an accelerating reference frame, we need to add extra terms to the equation that can be considered as forces operating on every object that we track using the accelerating reference fr ...
GSCI 101A - Section 006
... b) The force due to air resistance can increase until it reaches a value of 350 N. c) The force due to air resistance can increase until it reaches 350·g. d) None of the above. b) the total air resistance will never be greater than mg =350 N for the object. **** We didn’t cover the material for this ...
... b) The force due to air resistance can increase until it reaches a value of 350 N. c) The force due to air resistance can increase until it reaches 350·g. d) None of the above. b) the total air resistance will never be greater than mg =350 N for the object. **** We didn’t cover the material for this ...
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER 2015 – I, 2015 SCIENCE Class – IX
... (ii) mass of one object is increased four times (iii) distance is reduced to one fourth. 23. State Newton’s first law of motion. Show that Newton’s first law of motion is a special case of Newton’s second law. Determine the acceleration of a car of mass 800 kg, on application of a force of 200 N on ...
... (ii) mass of one object is increased four times (iii) distance is reduced to one fourth. 23. State Newton’s first law of motion. Show that Newton’s first law of motion is a special case of Newton’s second law. Determine the acceleration of a car of mass 800 kg, on application of a force of 200 N on ...
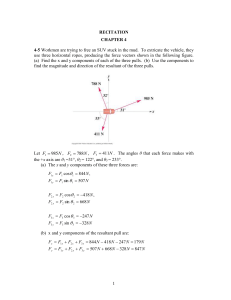
Recitation Ch 4-1
... The stopping distance is proportional to the square of the initial speed. 4-34 A factory worker pushes horizontally on a 250 N crate with a force of 75 N on a horizontal rough floor. A 135 N crate rests on top of the one being pushed and moves along with it. Make a free-body diagram of each crate if ...
... The stopping distance is proportional to the square of the initial speed. 4-34 A factory worker pushes horizontally on a 250 N crate with a force of 75 N on a horizontal rough floor. A 135 N crate rests on top of the one being pushed and moves along with it. Make a free-body diagram of each crate if ...


















![Forces-part2 [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008777900_1-5d589672d0a73f66816cf69cd76bbed3-300x300.png)