
Force and Motion
... Gravity The attractive force of two masses like the earth and an object on its surface. Gravity makes a falling object accelerate at 9.8m s2 ...
... Gravity The attractive force of two masses like the earth and an object on its surface. Gravity makes a falling object accelerate at 9.8m s2 ...
Chapter 3 Golden Ticket
... 3. The quantity of matter in an object. More specifically, it is the measure of the inertia or sluggishness that an object exhibits in response to any effort made to start it, stop it, deflect it, or change in any way its state of motion. 4. When two values change in opposite directions, so that if ...
... 3. The quantity of matter in an object. More specifically, it is the measure of the inertia or sluggishness that an object exhibits in response to any effort made to start it, stop it, deflect it, or change in any way its state of motion. 4. When two values change in opposite directions, so that if ...
f (x) - mrdsample
... equilibrium: Points of equilibrium are where the force is zero (slope = zero). x3 and x5 are points of stable equilibrium or energy wells. If the system is slightly displaced to either side the forces on either side will return the object back to these positions. x6 is a position of neutral equilibr ...
... equilibrium: Points of equilibrium are where the force is zero (slope = zero). x3 and x5 are points of stable equilibrium or energy wells. If the system is slightly displaced to either side the forces on either side will return the object back to these positions. x6 is a position of neutral equilibr ...
Monday, Oct. 6, 2008
... People have been very curious about the stars in the sky, making observations for a long time. The data people collected, however, have not been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly pr ...
... People have been very curious about the stars in the sky, making observations for a long time. The data people collected, however, have not been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly pr ...
Statics Lecture
... Dynamics is the branch of Mechanics that deals with objects/materials that are accelerating due to an imbalance of forces. Examples: 1. A rollercoaster executing a loop (dynamics) 2. Flow of water from a hose (hydrodynamics) ...
... Dynamics is the branch of Mechanics that deals with objects/materials that are accelerating due to an imbalance of forces. Examples: 1. A rollercoaster executing a loop (dynamics) 2. Flow of water from a hose (hydrodynamics) ...
Conceptual Physics Review # 3
... else does it change? A. the mass of the ball B. the weight of the ball C. impossible to determine ...
... else does it change? A. the mass of the ball B. the weight of the ball C. impossible to determine ...
Course CE 25000 – Statics Cross-listed Course ME 25000 – Statics
... R. C. Hibbeler, Engineering Mechanics: Statics, Pearson Prentice Hall, current edition. ...
... R. C. Hibbeler, Engineering Mechanics: Statics, Pearson Prentice Hall, current edition. ...
Motion
... • Universal Law of Gravitation – Every object in the universe is attracted to every other object in the universe by a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distances between them. • F = G(m1m2)/d2 • G is a proportionality ...
... • Universal Law of Gravitation – Every object in the universe is attracted to every other object in the universe by a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distances between them. • F = G(m1m2)/d2 • G is a proportionality ...
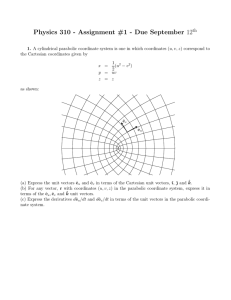
Physics 310 - Assignment #1 - Due September 12
... 2. Find a solution for the motion of an object of mass m with initial velocity v0 , moving through a fluid that produces both linear and quadratic fiscous drag, that is, find x(t) when the only forces acting on the object are Fdrag = −c1 v − c2 v|v|. Consider separately the two cases when the initi ...
... 2. Find a solution for the motion of an object of mass m with initial velocity v0 , moving through a fluid that produces both linear and quadratic fiscous drag, that is, find x(t) when the only forces acting on the object are Fdrag = −c1 v − c2 v|v|. Consider separately the two cases when the initi ...
2. Newton`s Second Law of Motion [ F=ma]
... From the units of mass and acceleration you can see that the units for force are kg m/s2 = N (Newton). 1 Newton is a little less than ¼ lb. Newton’s Third Law—action-reaction [F12=-F21] Newton’s 3rd law states that whenever an object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an e ...
... From the units of mass and acceleration you can see that the units for force are kg m/s2 = N (Newton). 1 Newton is a little less than ¼ lb. Newton’s Third Law—action-reaction [F12=-F21] Newton’s 3rd law states that whenever an object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an e ...
Acceleration Characteristics for Circular Motion
... same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. In what path do objects naturally travel? Straight lines. What is required for objects to move in circles? An unbalanced force. Newton's second law of motion says that… if acceleration is present then net force is present ...
... same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. In what path do objects naturally travel? Straight lines. What is required for objects to move in circles? An unbalanced force. Newton's second law of motion says that… if acceleration is present then net force is present ...
Lecture #4, June12
... car it is either the force of the belt or the force of friction between the passenger and the seat. As you can see, it is not some special centripetal force, but just one of the regular forces acting on this person. Another good example would be motion of the Moon around the Earth. Considering Moon' ...
... car it is either the force of the belt or the force of friction between the passenger and the seat. As you can see, it is not some special centripetal force, but just one of the regular forces acting on this person. Another good example would be motion of the Moon around the Earth. Considering Moon' ...
Newton`s Laws and Force Review
... 18. According to Newton’s second law, the acceleration of an object ______ its mass. a. is directly proportional to b. is inversely proportional to c. doesn’t depend on 19. The acceleration produced by a net force on an object is _____. a. directly proportional the magnitude of the net force. b. in ...
... 18. According to Newton’s second law, the acceleration of an object ______ its mass. a. is directly proportional to b. is inversely proportional to c. doesn’t depend on 19. The acceleration produced by a net force on an object is _____. a. directly proportional the magnitude of the net force. b. in ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Newton`s Laws of
... Newton’s First Law: Objects in motion tend to stay in motion and objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s Second Law: Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma). Newton’s Third Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...
... Newton’s First Law: Objects in motion tend to stay in motion and objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s Second Law: Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma). Newton’s Third Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...
Forces and Motion Quiz 1
... A) The initial force that started the ball ran out. B) The opposing force of friction stopped the ball. C) The natural state of the ball is not to be in motion. D) The force of gravity slowed the ball until it stopped. 12) Which of these is a good example of Newton's First Law of inertia A) a ball s ...
... A) The initial force that started the ball ran out. B) The opposing force of friction stopped the ball. C) The natural state of the ball is not to be in motion. D) The force of gravity slowed the ball until it stopped. 12) Which of these is a good example of Newton's First Law of inertia A) a ball s ...











![2. Newton`s Second Law of Motion [ F=ma]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010436228_1-b6fe4738d0a51f6e98031f7b8ffab8ff-300x300.png)










