Chapter 7
... Newton later demonstrated that these laws were consequences of the gravitational force between any two objects together with Newton’s laws of motion ...
... Newton later demonstrated that these laws were consequences of the gravitational force between any two objects together with Newton’s laws of motion ...
Physics 220 – Exam #1
... 11. In class we did a demonstration involving two people on flat carts. One exerted a force on one end of a rope while the other would just hang on. Which of the following principles or ideas was this demonstration designed to illustrate? (a) Newton’s second law: F = ma. (b) Some motion can be frict ...
... 11. In class we did a demonstration involving two people on flat carts. One exerted a force on one end of a rope while the other would just hang on. Which of the following principles or ideas was this demonstration designed to illustrate? (a) Newton’s second law: F = ma. (b) Some motion can be frict ...
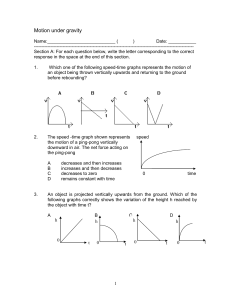
Quiz on Motion under gravity
... the downward motion; At maximum height, the velocity of the object is zero; If air resistance is negligible, the time for the upward motion is equal to the time for the downward motion ...
... the downward motion; At maximum height, the velocity of the object is zero; If air resistance is negligible, the time for the upward motion is equal to the time for the downward motion ...
NEWTONS LAW`S OF MOTION
... velocity (acceleration )of an object is proportional to the force and in the direction of force. • Similarly it takes less stopping force to stop an object moving with less velocity (acceleration) ...
... velocity (acceleration )of an object is proportional to the force and in the direction of force. • Similarly it takes less stopping force to stop an object moving with less velocity (acceleration) ...
“I Can” Statement Template
... +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++---------------------------------------------Force and Motion 7th Grade ...
... +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++---------------------------------------------Force and Motion 7th Grade ...
Impulse and Momentum - Mrs. Haug`s Website
... average force (F) and the time interval (∆t) during which the force acts: Impulse is a vector quantity Direction is the same as average force direction SI Unit: Newton •second (N•s) ...
... average force (F) and the time interval (∆t) during which the force acts: Impulse is a vector quantity Direction is the same as average force direction SI Unit: Newton •second (N•s) ...
Physics First Semester Exam Review Contrast constant speed
... 33. At the instant a ball is thrown horizontally with a large force, an identical ball is dropped from the same height. Which ball hits the ground first? ___________________________________________________________ 34. Describe the resultant of a pair of 6-unit vectors at right angles to each other. ...
... 33. At the instant a ball is thrown horizontally with a large force, an identical ball is dropped from the same height. Which ball hits the ground first? ___________________________________________________________ 34. Describe the resultant of a pair of 6-unit vectors at right angles to each other. ...
File - Mrs. Haug`s Website
... average force (F) and the time interval (∆t) during which the force acts: Impulse is a vector quantity Direction is the same as average force direction SI Unit: Newton •second (N•s) ...
... average force (F) and the time interval (∆t) during which the force acts: Impulse is a vector quantity Direction is the same as average force direction SI Unit: Newton •second (N•s) ...
Lecture 10 (Feb 15) - West Virginia University
... The driver of a car (m = 1000 kg) traveling on the interstate at 35 m/s slams on his brakes to avoid hitting a second vehicle in front of him, which had come to rest because of congestion ahead. After the brakes are applied, a constant friction force of 8000 N acts on the car. A. At what minimum dis ...
... The driver of a car (m = 1000 kg) traveling on the interstate at 35 m/s slams on his brakes to avoid hitting a second vehicle in front of him, which had come to rest because of congestion ahead. After the brakes are applied, a constant friction force of 8000 N acts on the car. A. At what minimum dis ...
Chapter 4
... 15. Another name for starting friction is static friction, it is the frictional force that is needed to budge a static or stationary object. If a power supply weighing 22Lb is to be slid across a table where the coefficient of starting friction is 0.5, how much force is needed to budge the supply? 1 ...
... 15. Another name for starting friction is static friction, it is the frictional force that is needed to budge a static or stationary object. If a power supply weighing 22Lb is to be slid across a table where the coefficient of starting friction is 0.5, how much force is needed to budge the supply? 1 ...
Conservative and Non-conservative Forces F
... With each conservative force, we can associate a stored energy. The energy stored depends on the relative position(s) of the object(s). This stored energy is also called potential energy, because there is the potential to do work. The difference in stored (potential) energies between two object p ...
... With each conservative force, we can associate a stored energy. The energy stored depends on the relative position(s) of the object(s). This stored energy is also called potential energy, because there is the potential to do work. The difference in stored (potential) energies between two object p ...
Mechanical Equilibrium(star wars)
... Q: Is there motion in this situation? Is there a net force? normal force ...
... Q: Is there motion in this situation? Is there a net force? normal force ...
Do now
... A force is a push or pull upon an object resulting from the object's interaction with another object. ...
... A force is a push or pull upon an object resulting from the object's interaction with another object. ...
6.67 x 10 -11 m 3 /(kg s 2 )
... • Why aren’t the tides due mainly to the Sun than the Moon? • A) they are mainly due to the Sun • B) the difference in the Sun’s pull on the different sides of the Earth is smaller than the Moon’s • C) the forces due to the Moon and Sun contribute equally to the tides • D) the tides are not due to f ...
... • Why aren’t the tides due mainly to the Sun than the Moon? • A) they are mainly due to the Sun • B) the difference in the Sun’s pull on the different sides of the Earth is smaller than the Moon’s • C) the forces due to the Moon and Sun contribute equally to the tides • D) the tides are not due to f ...