7.5 Test Review- Circular Motion and Gravitation
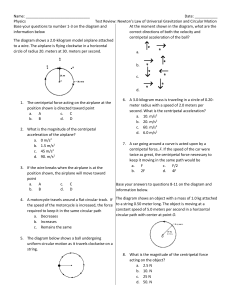
... 6. A 3.0-kilogram mass is traveling in a circle of 0.20meter radius with a speed of 2.0 meters per second. What is the centripetal acceleration? a. 10. m/s2 b. 20. m/s2 c. 60. m/s2 d. 6.0 m/s2 7. A car going around a curve is acted upon by a centripetal force, F. If the speed of the car were twice a ...
... 6. A 3.0-kilogram mass is traveling in a circle of 0.20meter radius with a speed of 2.0 meters per second. What is the centripetal acceleration? a. 10. m/s2 b. 20. m/s2 c. 60. m/s2 d. 6.0 m/s2 7. A car going around a curve is acted upon by a centripetal force, F. If the speed of the car were twice a ...
integrated-science-5th-edition-tillery-solution
... straight line retains its straight-line motion in the absence of an unbalanced force. The analysis of why a ball moving across a smooth floor comes to a stop, as presented in the previous chapter, is an important part of the development of this concept. Newton's first law of motion is also known as ...
... straight line retains its straight-line motion in the absence of an unbalanced force. The analysis of why a ball moving across a smooth floor comes to a stop, as presented in the previous chapter, is an important part of the development of this concept. Newton's first law of motion is also known as ...
DV_Matter-Teacher
... • Why does gravity exert a force on you? • If an object is not moving does that mean that there are no forces on it? ...
... • Why does gravity exert a force on you? • If an object is not moving does that mean that there are no forces on it? ...
Chapter 9
... Find the center of mass of the uniform, solid cone of height h, base radius R, and constant density shown in the figure. (Hint: Integrate over disk-shaped mass elements of thickness dy, as shown in the figure.) ...
... Find the center of mass of the uniform, solid cone of height h, base radius R, and constant density shown in the figure. (Hint: Integrate over disk-shaped mass elements of thickness dy, as shown in the figure.) ...
Document
... • According to Newton’s 2nd law, when the same force is applied to two objects of different masses, A. the object with greater mass will experience a great acceleration and the object with less mass will experience an even greater acceleration. B. the object with greater mass will experience a small ...
... • According to Newton’s 2nd law, when the same force is applied to two objects of different masses, A. the object with greater mass will experience a great acceleration and the object with less mass will experience an even greater acceleration. B. the object with greater mass will experience a small ...
Ch 5 Newton`s 2nd Law
... Suppose you are standing on the ground. Do you exert more pressure when you stand on both feet or stand on one foot? • The force, your weight, is the same in both cases. Two feet have more area than one foot, therefore, there will be more pressure exerted if you are standing on one foot. ...
... Suppose you are standing on the ground. Do you exert more pressure when you stand on both feet or stand on one foot? • The force, your weight, is the same in both cases. Two feet have more area than one foot, therefore, there will be more pressure exerted if you are standing on one foot. ...
Phy 201: General Physics I
... • When there is no net torque acting on an object (or no net torque acts on a system) its angular momentum (L) will remain constant or L1 = L2 = … = a constant value ...
... • When there is no net torque acting on an object (or no net torque acts on a system) its angular momentum (L) will remain constant or L1 = L2 = … = a constant value ...
Unit Two Chapter 3, Part 2 Projectile Motion
... 1. Projectiles always maintain a constant horizontal velocity (neglecting air resistance) ...
... 1. Projectiles always maintain a constant horizontal velocity (neglecting air resistance) ...
Comprehensive Final Exam Review 2014
... the displacement during this acceleration? 16. A pilot stops a plane of mass 45000 kg in a distance of 555 m. If the plane had a uniform acceleration of -6.00 m/s2, how fast was the plane moving before the braking began? What is the average force exerted on the plane through friction? 17. A ball is ...
... the displacement during this acceleration? 16. A pilot stops a plane of mass 45000 kg in a distance of 555 m. If the plane had a uniform acceleration of -6.00 m/s2, how fast was the plane moving before the braking began? What is the average force exerted on the plane through friction? 17. A ball is ...
Also covers: 7.1.5 (Detailed standards begin on page IN8
... What is gravity? The force of gravity exists between any two objects that have mass. Gravity always is attractive and pulls objects toward each other. A gravitational attraction exists between you and every object in the universe that has mass. However, the force of gravity depends on the mass of th ...
... What is gravity? The force of gravity exists between any two objects that have mass. Gravity always is attractive and pulls objects toward each other. A gravitational attraction exists between you and every object in the universe that has mass. However, the force of gravity depends on the mass of th ...























