Circular motion: Extra problems
... centripetal force is 88.0 N, what is the girls mass? 19. A bicyclist is riding at a linear speed of 13.2 m/s around a circular track. The magnitude of the centripetal force is 377 N, and the combined mass of the bike and the rider is 86.5 kg. What is the track’s radius? 20. A 905 kg car travels arou ...
... centripetal force is 88.0 N, what is the girls mass? 19. A bicyclist is riding at a linear speed of 13.2 m/s around a circular track. The magnitude of the centripetal force is 377 N, and the combined mass of the bike and the rider is 86.5 kg. What is the track’s radius? 20. A 905 kg car travels arou ...
Chapter 3: Newton*s Second Law of motion
... • Suppose you are offered either ¼ of an apple pie or 1/8 of the pie. Which piece is larger? • Suppose you apply the same amount of force to two carts, one cart with a mass of 4 kg and the other with a mass a 8 kg. • Which cart will accelerate more? • How much greater will the acceleration be? ...
... • Suppose you are offered either ¼ of an apple pie or 1/8 of the pie. Which piece is larger? • Suppose you apply the same amount of force to two carts, one cart with a mass of 4 kg and the other with a mass a 8 kg. • Which cart will accelerate more? • How much greater will the acceleration be? ...
Force due to gravity: A field force (a vector quantity) that always is
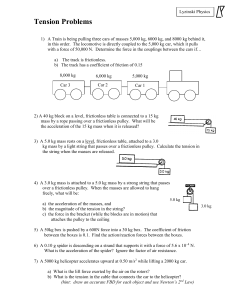
... What is the acceleration of the spider? Ignore the factor of air resistance. 7) A 5000 kg helicopter accelerates upward at 0.50 m/s2 while lifting a 2000 kg car. a) What is the lift force exerted by the air on the rotors? b) What is the tension in the cable that connects the car to the helicopter? ( ...
... What is the acceleration of the spider? Ignore the factor of air resistance. 7) A 5000 kg helicopter accelerates upward at 0.50 m/s2 while lifting a 2000 kg car. a) What is the lift force exerted by the air on the rotors? b) What is the tension in the cable that connects the car to the helicopter? ( ...
Chapter 10: Energy, Work and Simple Machines
... opposing force equals the change in kinetic energy. 4.state and apply the relationship that work done against gravity equals the change in gravitational potential energy. 5.Define and calculate power from calculating the amount of work done by an object. ...
... opposing force equals the change in kinetic energy. 4.state and apply the relationship that work done against gravity equals the change in gravitational potential energy. 5.Define and calculate power from calculating the amount of work done by an object. ...
Equilibrium is not just translational, is is also rotational. While a set
... 580 N. An obstruction in the floor keeps it from sliding when pushed, but a great enough force could cause it to tip over. What minimum horizontal force is needed to tip it over and where should that force be applied? ...
... 580 N. An obstruction in the floor keeps it from sliding when pushed, but a great enough force could cause it to tip over. What minimum horizontal force is needed to tip it over and where should that force be applied? ...
acceleration
... Finally, take your result from 1 and divide it by your result from 2. That’s the force of gravity between the two objects. ...
... Finally, take your result from 1 and divide it by your result from 2. That’s the force of gravity between the two objects. ...
Unit C2: Scheme of Work
... origin), displacement (vector: measured from any position) and distance (scalar: total movement). Then move onto speed (the rate at which an object covers distance) and velocity (the rate of change of displacement). In one direction, this is a speed with a direction attached. Mention the units: metr ...
... origin), displacement (vector: measured from any position) and distance (scalar: total movement). Then move onto speed (the rate at which an object covers distance) and velocity (the rate of change of displacement). In one direction, this is a speed with a direction attached. Mention the units: metr ...
What you need to be able to do
... (b) No force is needed; moving objects tend to slow down. (c) The puck is moving one direction and friction is pushing in the opposite direction. 9) Ingrid drops the 3-kg steel puck and the 1-kg aluminum puck at the same time from the same height. Ingrid observes that the pucks land at the same time ...
... (b) No force is needed; moving objects tend to slow down. (c) The puck is moving one direction and friction is pushing in the opposite direction. 9) Ingrid drops the 3-kg steel puck and the 1-kg aluminum puck at the same time from the same height. Ingrid observes that the pucks land at the same time ...
APB jeopardy
... An electron e and a proton p are simultaneously released from rest in a uniform electric field E, as shown. Assume that the particles are sufficiently far apart so that the only force acting on each particle after it is released is that due to the electric field. At a later time when the particles ...
... An electron e and a proton p are simultaneously released from rest in a uniform electric field E, as shown. Assume that the particles are sufficiently far apart so that the only force acting on each particle after it is released is that due to the electric field. At a later time when the particles ...
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... the time derivative of the vectors AB , AA' and DC ' , which are attached to the cube (you can think of them as being painted on the cube). You should do this problem in two ways: • Calculate the positions of the points A, A’, B, C’ and D as a function time. Obtain an expression for the vectors AB , ...
... the time derivative of the vectors AB , AA' and DC ' , which are attached to the cube (you can think of them as being painted on the cube). You should do this problem in two ways: • Calculate the positions of the points A, A’, B, C’ and D as a function time. Obtain an expression for the vectors AB , ...
AP Quiz #z22 Centripital Motion AP FR Quiz #22 Centripital Force_3
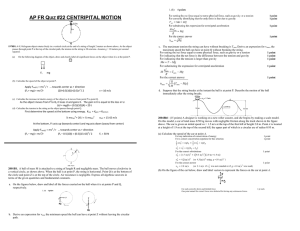
... above. The car is given an initial speed vo = 1.5 m/s at the top of the first hill of height 2.0 m. Point A is located at a height of 1.9 m at the top of the second hill, the upper part of which is a circular arc of radius 0.95 m. (a) Calculate the speed of the car at point A. ...
... above. The car is given an initial speed vo = 1.5 m/s at the top of the first hill of height 2.0 m. Point A is located at a height of 1.9 m at the top of the second hill, the upper part of which is a circular arc of radius 0.95 m. (a) Calculate the speed of the car at point A. ...