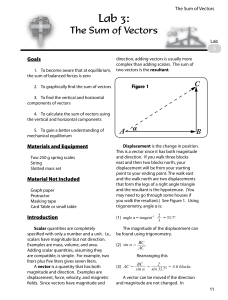
Ch26 Electric Charges and Forces
... t=t’ Situations: 1. If both source and test charges are at rest, the force pairs no doubt obey Coulomb’s Law. 2. If the source charge suddenly starts moving, as shown by arrow. In response, the force vector on the test charge must pivot to follow the source charge. Does this happen ? Or is t ...
... t=t’ Situations: 1. If both source and test charges are at rest, the force pairs no doubt obey Coulomb’s Law. 2. If the source charge suddenly starts moving, as shown by arrow. In response, the force vector on the test charge must pivot to follow the source charge. Does this happen ? Or is t ...
act04
... the string, and friction of the cart on the track. Check to see if any of these forces are related by Newton’s Third Law (Third Law pairs). Newton’s Third Law pairs are forces between the same two objects, but which object is exerting the force and which is being acted on are exchanged. (For the pur ...
... the string, and friction of the cart on the track. Check to see if any of these forces are related by Newton’s Third Law (Third Law pairs). Newton’s Third Law pairs are forces between the same two objects, but which object is exerting the force and which is being acted on are exchanged. (For the pur ...
1 - CSUN.edu
... 7. Calculate the percent error in table C. 8. Repeat the steps above for table D,E,F. Be sure to keep NET FORCE CONSTANT and increase mass while experimenting to find the answer for question b. You will need to recalculate the kinetic friction every time you add more mass. ...
... 7. Calculate the percent error in table C. 8. Repeat the steps above for table D,E,F. Be sure to keep NET FORCE CONSTANT and increase mass while experimenting to find the answer for question b. You will need to recalculate the kinetic friction every time you add more mass. ...
Linear Motion
... speed. Consider a point on flywheel rim, at distance R from the axis of rotation. If the flywheel speeds up from initial angular speed ω1 to angular speed ω2 in time t, then the speed of the point increases from speed u = ω1 R to speed v = ω2 R in time t. By using acceleration, a = (v-u)/t, the line ...
... speed. Consider a point on flywheel rim, at distance R from the axis of rotation. If the flywheel speeds up from initial angular speed ω1 to angular speed ω2 in time t, then the speed of the point increases from speed u = ω1 R to speed v = ω2 R in time t. By using acceleration, a = (v-u)/t, the line ...
Chapter 5 Rotational Motion File
... straight line tangent to the circle of motion • Centripetal force is a classification that includes forces acting toward a central point – It is not a force in itself – A centripetal force must be supplied by some actual, physical force Section 7.4 ...
... straight line tangent to the circle of motion • Centripetal force is a classification that includes forces acting toward a central point – It is not a force in itself – A centripetal force must be supplied by some actual, physical force Section 7.4 ...
uniform circular motion
... Velocity can be constant in magnitude, and we still have acceleration because the direction changes. • Direction: towards the center of the circle ...
... Velocity can be constant in magnitude, and we still have acceleration because the direction changes. • Direction: towards the center of the circle ...
Principles and Problems Chapter 9 Linear
... momentum is conserved. Momentum is conserved during a collision. Kinetic energy is also conserved in an ...
... momentum is conserved. Momentum is conserved during a collision. Kinetic energy is also conserved in an ...
FE ANS
... The diagram above applies to a four-wheel drive car. When the car accelerates forward or cruises at constant velocity, the force exerted by the road on the driving wheels points forward. . The contact force exerted by the road on the car (located at the car's wheels) can be described as a normal (ve ...
... The diagram above applies to a four-wheel drive car. When the car accelerates forward or cruises at constant velocity, the force exerted by the road on the driving wheels points forward. . The contact force exerted by the road on the car (located at the car's wheels) can be described as a normal (ve ...
Work and Simple Machines Info
... reduce the amount of force needed by increasing the distance over which that force is applied. This means that it requires less force to twist a screw in than it would to push it in directly. Second, screws also change the direction of the applied force. A twisting, or rotational force is applied to ...
... reduce the amount of force needed by increasing the distance over which that force is applied. This means that it requires less force to twist a screw in than it would to push it in directly. Second, screws also change the direction of the applied force. A twisting, or rotational force is applied to ...
Ch 6 - Momentum
... A 1400kg car moving westward with a velocity of 15 m/s collides with a utility pole and is brought to rest in 0.30s. Find the magnitude of the force exerted on the car during the collision. ...
... A 1400kg car moving westward with a velocity of 15 m/s collides with a utility pole and is brought to rest in 0.30s. Find the magnitude of the force exerted on the car during the collision. ...