11-2 Vector Cross Product
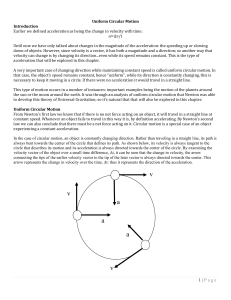
... 11-1 Angular Momentum—Objects Rotating About a Fixed Axis The rotational analog of linear momentum is angular momentum, L: Then the rotational analog of Newton’s second law is: This form of Newton’s second law is valid even if I is not constant. ...
... 11-1 Angular Momentum—Objects Rotating About a Fixed Axis The rotational analog of linear momentum is angular momentum, L: Then the rotational analog of Newton’s second law is: This form of Newton’s second law is valid even if I is not constant. ...
Alignment to Michigan Educational Standards- Physical Science Safety
... Identify the force(s) acting on objects moving with uniform circular motion (e.g., a car on a circular track, satellites in orbit). Solve problems involving force, mass, and acceleration in two-dimensional projectile motion restricted to an initial horizontal velocity with no initial vertical veloc ...
... Identify the force(s) acting on objects moving with uniform circular motion (e.g., a car on a circular track, satellites in orbit). Solve problems involving force, mass, and acceleration in two-dimensional projectile motion restricted to an initial horizontal velocity with no initial vertical veloc ...
彈簧水平振和垂直振,週期會不會一樣?
... Even large-scale structures, such as towers, bridges, and airplanes, can oscillate. If the frequency of the driving mechanism is close to the natural frequency, the object can literally be shaken to pieces. A dramatic example of resonance is the collapse of the Tacoma Narrows Bridge in Washington. T ...
... Even large-scale structures, such as towers, bridges, and airplanes, can oscillate. If the frequency of the driving mechanism is close to the natural frequency, the object can literally be shaken to pieces. A dramatic example of resonance is the collapse of the Tacoma Narrows Bridge in Washington. T ...
實驗3:轉動-剛體的轉動運動Lab. 3 : Rotation
... a rotating object is analogous to KELinear and can be expressed in terms of the moment of inertia and angular velocity. The total kinetic energy of an extended object can be expressed as the sum PhysicsNTHU of the translational kinetic energy of the center of mass and the rotational MFTai-戴明鳳 kine ...
... a rotating object is analogous to KELinear and can be expressed in terms of the moment of inertia and angular velocity. The total kinetic energy of an extended object can be expressed as the sum PhysicsNTHU of the translational kinetic energy of the center of mass and the rotational MFTai-戴明鳳 kine ...
Document
... Step 2: The balls are in equilibrium positions. That means the sum of all forces acting on the ball is zero! ...
... Step 2: The balls are in equilibrium positions. That means the sum of all forces acting on the ball is zero! ...
Chapter 1 Falling Chapter Check In You have two balls of the same
... That’s it! You can see the product of the masses in the numerator and the square of the distance between them in the denominator. What about this big G? That’s Newton’s gravitational constant, a number whose value is assumed not to vary with time or location in the universe. The value for G relates ...
... That’s it! You can see the product of the masses in the numerator and the square of the distance between them in the denominator. What about this big G? That’s Newton’s gravitational constant, a number whose value is assumed not to vary with time or location in the universe. The value for G relates ...
Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line
... situations (in each equation, x is in meters, t is in seconds, and t > 0): (1) x = (3 m/s)t – (2 m); (2) x = (–4 m/s2)t2 – (2 m); (3) x = (–4 m/s2)t2; (4) x = –2 m. • (a) In which situations is the velocity of the particle constant? • (b) In which is the vector pointing in the negative x direction? ...
... situations (in each equation, x is in meters, t is in seconds, and t > 0): (1) x = (3 m/s)t – (2 m); (2) x = (–4 m/s2)t2 – (2 m); (3) x = (–4 m/s2)t2; (4) x = –2 m. • (a) In which situations is the velocity of the particle constant? • (b) In which is the vector pointing in the negative x direction? ...