to the whole? - Vasil Penchev
... Cause causes effect with some probability ‘p’: AB If cause is available, then effect is available with probability p. If p = 1: classical causality; if p=0:A, B are absolutely independent ...
... Cause causes effect with some probability ‘p’: AB If cause is available, then effect is available with probability p. If p = 1: classical causality; if p=0:A, B are absolutely independent ...
sample lab report
... the pulley, keeps moving along the track at a constant speed. (This balances out the friction force.) Then hook the string to the cart. 3. Activate the “smart pulley” program in Logger Pro. Adjust the photogate so the spokes in the pulley cut through the photogate beam. Part 1: Varying total mass wi ...
... the pulley, keeps moving along the track at a constant speed. (This balances out the friction force.) Then hook the string to the cart. 3. Activate the “smart pulley” program in Logger Pro. Adjust the photogate so the spokes in the pulley cut through the photogate beam. Part 1: Varying total mass wi ...
SPRING 2016 PHYS 1211 (as of Jan. 11/2016)
... everything falls into place and it all makes sense. But until the “click,” you can’t be sure how much time you need to “get it” and it’s difficult to plan… As you solve a physics problem, stop and ask yourself: What (exactly) are you doing? Why are you doing it? How does it help you? ...
... everything falls into place and it all makes sense. But until the “click,” you can’t be sure how much time you need to “get it” and it’s difficult to plan… As you solve a physics problem, stop and ask yourself: What (exactly) are you doing? Why are you doing it? How does it help you? ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... Force of friction acts to oppose motion: Parallel to a surface Perpendicular to a Normal force. ...
... Force of friction acts to oppose motion: Parallel to a surface Perpendicular to a Normal force. ...
Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem for Rotational Motion
... curve. Now, imagine trying to apply the linear motion analysis to a spinning object. All of the parts of the spinning object are moving in different directions, but the object itself may be stationary. We need a new analysis system to cover items that are spinning about an axis. Rotation is the moti ...
... curve. Now, imagine trying to apply the linear motion analysis to a spinning object. All of the parts of the spinning object are moving in different directions, but the object itself may be stationary. We need a new analysis system to cover items that are spinning about an axis. Rotation is the moti ...
Kinematics Multiples
... This one is tricky. Because the spring is nonlinear, the solution to the differential equation is not a sine function and the period does depend on the amplitude. If you look at the graph closely, you will see that the FORCE of spring 2 increases with displacement faster than the force for spring 1. ...
... This one is tricky. Because the spring is nonlinear, the solution to the differential equation is not a sine function and the period does depend on the amplitude. If you look at the graph closely, you will see that the FORCE of spring 2 increases with displacement faster than the force for spring 1. ...
Simple Harmonic Motion
... F is the restoring force x represents the displacement from the equilibrium k is a positive constant If F is the only force acting on a system, the system is called a simple harmonic oscillator and it is said to undergo simple harmonic motion (SHM). SHM is a motion that is neither driven nor damped ...
... F is the restoring force x represents the displacement from the equilibrium k is a positive constant If F is the only force acting on a system, the system is called a simple harmonic oscillator and it is said to undergo simple harmonic motion (SHM). SHM is a motion that is neither driven nor damped ...
Problem I
... equation when the flow is turbulent, u U y . a) Using the Blasius equation when appropriate, determine the limit layer thickness on sections S1 and S2, each at distances x1=0,75 m and x2=1,5 m. Verify this is a slim limit layer. (Answer: 0,0119 m e 0,0168 m) b) Calculate the mass flow and mo ...
... equation when the flow is turbulent, u U y . a) Using the Blasius equation when appropriate, determine the limit layer thickness on sections S1 and S2, each at distances x1=0,75 m and x2=1,5 m. Verify this is a slim limit layer. (Answer: 0,0119 m e 0,0168 m) b) Calculate the mass flow and mo ...
A. Momentum Conservation in Collisions
... 1. Decide which objects are included in the system. 2. Verify that the system is isolated ( Fexternal = 0); if it is not, you will have to include the other objects causing the forces 3. Set the total final momentum equal to the total initial momentum; remember that momentum is a vector quantity, t ...
... 1. Decide which objects are included in the system. 2. Verify that the system is isolated ( Fexternal = 0); if it is not, you will have to include the other objects causing the forces 3. Set the total final momentum equal to the total initial momentum; remember that momentum is a vector quantity, t ...
Dynamics Multiple Choice Problems
... 24. Earth pulls downward on a pen, of mass m, which is sitting on a table; the magnitude of the force is mg. If that is called the action force, what is the reaction force? A. The table pushing up on the pen with a force equal to mg B. The pen pushing down on the table with a force equal to mg C. T ...
... 24. Earth pulls downward on a pen, of mass m, which is sitting on a table; the magnitude of the force is mg. If that is called the action force, what is the reaction force? A. The table pushing up on the pen with a force equal to mg B. The pen pushing down on the table with a force equal to mg C. T ...
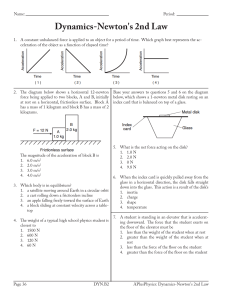
Newton`s 2nd Law, friction
... Mechanics is the branch of physics that deals with the analysis of motion and its causes. Specifically, kinematics is the descriptive branch of mechanics, and dynamics is the causal. Newton's second law relates the net sum of vector forces that are dynamical to the acceleration of an object. In this ...
... Mechanics is the branch of physics that deals with the analysis of motion and its causes. Specifically, kinematics is the descriptive branch of mechanics, and dynamics is the causal. Newton's second law relates the net sum of vector forces that are dynamical to the acceleration of an object. In this ...
Answers to Coursebook questions – Chapter 2.6
... s to get to the front, where v is the speed with respect to the v boat. Let u be the speed with which the boat moves backwards. Then from the point of view of an observer at rest in the water the person moves with speed v u . The initial 70v momentum is zero, and so 70.0 (v u) 200 u 0 ...
... s to get to the front, where v is the speed with respect to the v boat. Let u be the speed with which the boat moves backwards. Then from the point of view of an observer at rest in the water the person moves with speed v u . The initial 70v momentum is zero, and so 70.0 (v u) 200 u 0 ...
Experiment P09: Acceleration of a Dynamics Cart I (Smart Pulley)
... For this activity, a Smart Pulley will measure the motion of a cart as it is pulled by a string that is attached to an object suspended over the pulley. The Science Workshop program calculates the changing speed of the cart as it moves. A graph of speed and time can give the acceleration of the ...
... For this activity, a Smart Pulley will measure the motion of a cart as it is pulled by a string that is attached to an object suspended over the pulley. The Science Workshop program calculates the changing speed of the cart as it moves. A graph of speed and time can give the acceleration of the ...
F - learnphysics
... of motion e.g. during a game of badminton, a player intercepts and hits the shuttlecock to change its direction and motion. 22 May 2017 ...
... of motion e.g. during a game of badminton, a player intercepts and hits the shuttlecock to change its direction and motion. 22 May 2017 ...
Phys101 Final Code: 20 Term: 123 Monday, July 29, 2013 Page: 1
... A projectile is fired with initial velocity vo and angle θo = 60o from the top of a building (Figure 1) and is observed to reach a maximum height of 19.6 m. It later hits the ground at a horizontal distance of 50.0 m from the base of the building. Find the time of flight of the projectile. (Neglect ...
... A projectile is fired with initial velocity vo and angle θo = 60o from the top of a building (Figure 1) and is observed to reach a maximum height of 19.6 m. It later hits the ground at a horizontal distance of 50.0 m from the base of the building. Find the time of flight of the projectile. (Neglect ...