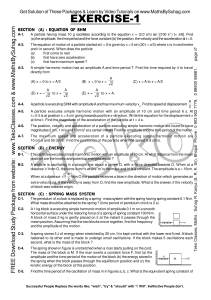
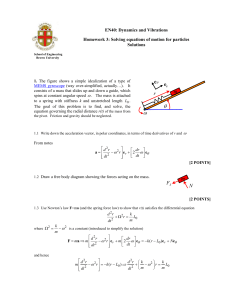
Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Dynamics
... Of all possible paths along which a dynamical system may move from one point to another within a specified time interval (consistent with any constraints), the actual path followed is that which minimizes the time integral of the difference between the kinetic and potential energy. ...
... Of all possible paths along which a dynamical system may move from one point to another within a specified time interval (consistent with any constraints), the actual path followed is that which minimizes the time integral of the difference between the kinetic and potential energy. ...
Chapter 6
... • To examine the idea of weight and relate it to mass and Newton's law of gravitation. • To study the motion of objects in orbit as a special application of Newton's law of gravitation. ...
... • To examine the idea of weight and relate it to mass and Newton's law of gravitation. • To study the motion of objects in orbit as a special application of Newton's law of gravitation. ...
shm-intro - Mrs Physics
... metres (how far it stretched from the equilibrium position). The relationship F = -kx, can also be used where, F represents the restoring force of the spring and the negative sign indicates that this force is in the opposite direction of the displacement x. This relationship is known as Hooke's Law. ...
... metres (how far it stretched from the equilibrium position). The relationship F = -kx, can also be used where, F represents the restoring force of the spring and the negative sign indicates that this force is in the opposite direction of the displacement x. This relationship is known as Hooke's Law. ...
TEKS 5 - Pearson School
... other car exerts on your car is the reaction force. These two forces are equal in size and opposite in direction. Pressing your hand against a wall also produces a pair of forces. As you press against the wall, your hand exerts a force on the wall. This is the action force. The wall exerts an equal ...
... other car exerts on your car is the reaction force. These two forces are equal in size and opposite in direction. Pressing your hand against a wall also produces a pair of forces. As you press against the wall, your hand exerts a force on the wall. This is the action force. The wall exerts an equal ...
Time (s)
... 2. A sprinter crosses the finishing line at a speed of 8m/s and comes to rest 10s later. Calculate the deceleration of the sprinter. acceleration = change in velocity time ...
... 2. A sprinter crosses the finishing line at a speed of 8m/s and comes to rest 10s later. Calculate the deceleration of the sprinter. acceleration = change in velocity time ...
Jeopardy
... $400 -- Gravity If the mass of the earth is 5.9742 × 1024 kg and the mass of the moon is 7.36 × 1022 kg and they are separated by a center-to-center distance of 384,403,000 m, this is the force of gravity of the earth on the moon. Where there is gravity. ...
... $400 -- Gravity If the mass of the earth is 5.9742 × 1024 kg and the mass of the moon is 7.36 × 1022 kg and they are separated by a center-to-center distance of 384,403,000 m, this is the force of gravity of the earth on the moon. Where there is gravity. ...
Dt © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
... Principle of Work and Energy for a Rigid Body • Work and kinetic energy are scalar quantities. • Assume that the rigid body is made of a large number of particles. T1 U12 T2 T1 , T2 initial and final total kinetic energy of particles forming body U12 total work of internal and external for ...
... Principle of Work and Energy for a Rigid Body • Work and kinetic energy are scalar quantities. • Assume that the rigid body is made of a large number of particles. T1 U12 T2 T1 , T2 initial and final total kinetic energy of particles forming body U12 total work of internal and external for ...
File
... Distance – a measure of the p…………….. a body takes in moving from one position to another. Displacement – the sh…………………possible route between the starting and finishing point of a body that has mo………………... This will normally be in a straight line For example, consider a 400m runner who has just compl ...
... Distance – a measure of the p…………….. a body takes in moving from one position to another. Displacement – the sh…………………possible route between the starting and finishing point of a body that has mo………………... This will normally be in a straight line For example, consider a 400m runner who has just compl ...
Test 2 Review
... Center of Mass. Objects don’t have their mass distributed evenly. Archimedes, an ancient Greek mathematician, showed that the effect on rigid bar by weights resting at various points along it is the same as it would be if all the weights were moved to a single point. This point is called the center ...
... Center of Mass. Objects don’t have their mass distributed evenly. Archimedes, an ancient Greek mathematician, showed that the effect on rigid bar by weights resting at various points along it is the same as it would be if all the weights were moved to a single point. This point is called the center ...
lcp 14: the physics of star trek
... would naturally occur to Captain Kirk and Mr. Spock in travelling on their journeys or planning them. Since this is an advanced assignment it will not be specifically spelled out what you must know before attempting to solve the problems. The physics required beyond elementary relativity theory, how ...
... would naturally occur to Captain Kirk and Mr. Spock in travelling on their journeys or planning them. Since this is an advanced assignment it will not be specifically spelled out what you must know before attempting to solve the problems. The physics required beyond elementary relativity theory, how ...
f - Edublogs
... If you push hard enough to just get the box moving, the acceleration is zero in that Weight = mg case also, but the friction is static, not kinetic. ...
... If you push hard enough to just get the box moving, the acceleration is zero in that Weight = mg case also, but the friction is static, not kinetic. ...
Chapter 6 - SFA Physics
... Internal forces cannot cause a change in momentum of the system. For conservation of momentum, the external forces must be zero. ...
... Internal forces cannot cause a change in momentum of the system. For conservation of momentum, the external forces must be zero. ...
PHY 101 Lecture Notes
... – First you try practice page 10 – Then we’ll look at a demo to see the jump and ...
... – First you try practice page 10 – Then we’ll look at a demo to see the jump and ...