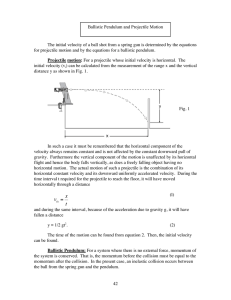
Review the study notes and homework for the hour tests and
... Know how to find the proper banking angle for banked curves (Equation 5.4). Be able to recognize Equations (5.5) and (5.6) as formulas for the speed and period, respectively of an object in a circular orbit. Chapter 6 Work and Energy Summary is on p.186. Know how to find the work done by a constant ...
... Know how to find the proper banking angle for banked curves (Equation 5.4). Be able to recognize Equations (5.5) and (5.6) as formulas for the speed and period, respectively of an object in a circular orbit. Chapter 6 Work and Energy Summary is on p.186. Know how to find the work done by a constant ...
Chapter 5 Lecture
... When an object is in motion on a surface or through a viscous medium, there will be a resistance to the motion. This is due to the interactions between the object and its environment. This resistance is called the force of friction. ...
... When an object is in motion on a surface or through a viscous medium, there will be a resistance to the motion. This is due to the interactions between the object and its environment. This resistance is called the force of friction. ...
Review the study notes and homework for the hour tests and
... Know how to find the proper banking angle for banked curves (Equation 5.4). Be able to recognize Equations (5.5) and (5.6) as formulas for the speed and period, respectively of an object in a circular orbit. Chapter 6 Work and Energy Summary is on p.186. Know how to find the work done by a constant ...
... Know how to find the proper banking angle for banked curves (Equation 5.4). Be able to recognize Equations (5.5) and (5.6) as formulas for the speed and period, respectively of an object in a circular orbit. Chapter 6 Work and Energy Summary is on p.186. Know how to find the work done by a constant ...
Gravitation Introduction we are going to identify one of the forces
... Question (12): State Newton's law of gravitation and using this law, show that if the earth exerts equal force on the two bodies on its surface, then their masses are equal. Answer: Newton's law of gravitation states that every particle in this universe attracts every other particle with a force whi ...
... Question (12): State Newton's law of gravitation and using this law, show that if the earth exerts equal force on the two bodies on its surface, then their masses are equal. Answer: Newton's law of gravitation states that every particle in this universe attracts every other particle with a force whi ...
Momentum - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... force acts on an object, its velocity is constant. Its mass will not change. Therefore, if no force acts on an object, momentum is constant. Momentum is ...
... force acts on an object, its velocity is constant. Its mass will not change. Therefore, if no force acts on an object, momentum is constant. Momentum is ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... 7. You are now ready to collect force and acceleration data. Grasp the Force Sensor hook. Click and take several seconds to move the cart back and forth on the table. Vary the motion so that both small and large forces are applied. Make sure that your hand is only touching the hook on the Force Sens ...
... 7. You are now ready to collect force and acceleration data. Grasp the Force Sensor hook. Click and take several seconds to move the cart back and forth on the table. Vary the motion so that both small and large forces are applied. Make sure that your hand is only touching the hook on the Force Sens ...
Physics 201
... distance the meter stick falls before the other person catches it. 7. Use this distance along with the accepted value for gravitational acceleration (g) to calculate the reaction time. 8. Repeat the process so that everyone in your group gets to measure their reaction time. If you want to, write you ...
... distance the meter stick falls before the other person catches it. 7. Use this distance along with the accepted value for gravitational acceleration (g) to calculate the reaction time. 8. Repeat the process so that everyone in your group gets to measure their reaction time. If you want to, write you ...
Quiz3 Solutions
... = R F sin , where R is the distance from the part's center of gravity to the pivot point (here, the streetlight base) and F is the gravity force on that part, and θ is the angle between the two. For the vertical rod, θ is 180°, because the vector from the lamp base to the center of gravity of th ...
... = R F sin , where R is the distance from the part's center of gravity to the pivot point (here, the streetlight base) and F is the gravity force on that part, and θ is the angle between the two. For the vertical rod, θ is 180°, because the vector from the lamp base to the center of gravity of th ...
Tuesday, June 27, 2006
... What do you think the term “An object is at its equilibrium” means? The object is either at rest (Static Equilibrium) or its center of mass is moving with a constant velocity (Dynamic Equilibrium). When do you think an object is at its equilibrium? Translational Equilibrium: Equilibrium in linear mo ...
... What do you think the term “An object is at its equilibrium” means? The object is either at rest (Static Equilibrium) or its center of mass is moving with a constant velocity (Dynamic Equilibrium). When do you think an object is at its equilibrium? Translational Equilibrium: Equilibrium in linear mo ...



![Physics for SciEngrs [3rd]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015834502_1-903d7f9c800dd53147166e2caa63cce8-300x300.png)