AP C UNIT 4 - student handout
... Total acceleration, Direction for ω and α RHR: direction is along axis of rotation - curl fingers along direction of spin and direction of thumb is direction of ω and α. Explanation is in your book as to why…it stems from mathematical definition of vector in rotation. If object is speeding up, α is ...
... Total acceleration, Direction for ω and α RHR: direction is along axis of rotation - curl fingers along direction of spin and direction of thumb is direction of ω and α. Explanation is in your book as to why…it stems from mathematical definition of vector in rotation. If object is speeding up, α is ...
topic 2
... 2.3 Equation of Motion for a System of Particles The equation of motion can be extended to include systems of particles. This includes the motion of solids, liquids, or gas systems. As in statics, there are internal forces and external forces acting on the system. What is the difference between the ...
... 2.3 Equation of Motion for a System of Particles The equation of motion can be extended to include systems of particles. This includes the motion of solids, liquids, or gas systems. As in statics, there are internal forces and external forces acting on the system. What is the difference between the ...
Chapter 5
... momentum and energy may flow into and out of the system. The absolute stream velocity in the x direction Vx is related to the system velocity Vsx and the stream velocity relative to the system Vrx by the relation Vx = Vsx + Vrx The analysis for a system moving with a constant velocity will be simpli ...
... momentum and energy may flow into and out of the system. The absolute stream velocity in the x direction Vx is related to the system velocity Vsx and the stream velocity relative to the system Vrx by the relation Vx = Vsx + Vrx The analysis for a system moving with a constant velocity will be simpli ...
“Who Wants To Be A Millionaire?” Inertia Style Created by Claire
... B)Speed and direction C)A force that happens when things rub against each other D)Change in position The answer is C. ...
... B)Speed and direction C)A force that happens when things rub against each other D)Change in position The answer is C. ...
Circular Motion - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... r is not a radius, it is the distance between the objects measured from center to center. Is the problem asking for the height of a satellite above earth’s surface? After you get r from the equation subtract earth’s radius. Are you given height above the surface? Add the earth’s radius to get r and ...
... r is not a radius, it is the distance between the objects measured from center to center. Is the problem asking for the height of a satellite above earth’s surface? After you get r from the equation subtract earth’s radius. Are you given height above the surface? Add the earth’s radius to get r and ...
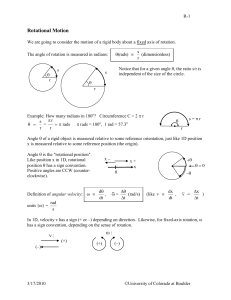
Rotational Motion - University of Colorado Boulder
... perpendicular to the plane defined by the vectors A and B plus right-hand-rule. (Curl fingers from first vector A to second vector B, thumb points in direction of A B ...
... perpendicular to the plane defined by the vectors A and B plus right-hand-rule. (Curl fingers from first vector A to second vector B, thumb points in direction of A B ...
Vectors
... • To add 2 vectors geometrically simply place the tail of one vector to the head of the other. The solution, or Resultant vector, is the vector from the point of origin of the 1st vector to the end point of the 2nd. • When adding vectors geometrically, one often places the first vector at the origin ...
... • To add 2 vectors geometrically simply place the tail of one vector to the head of the other. The solution, or Resultant vector, is the vector from the point of origin of the 1st vector to the end point of the 2nd. • When adding vectors geometrically, one often places the first vector at the origin ...
Circular Motion
... probably because it could be divided up so many different ways, i.e. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 12, 24 and 30. This got picked up by the Babylonians and passed on to the Egyptians. And from there to us. The circle has 6 × 60, or 360 parts. It’s popularity may also be related to fact that it is close to th ...
... probably because it could be divided up so many different ways, i.e. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 12, 24 and 30. This got picked up by the Babylonians and passed on to the Egyptians. And from there to us. The circle has 6 × 60, or 360 parts. It’s popularity may also be related to fact that it is close to th ...
ECE 3300 Portfolio 1..
... we have an equation for E , it will be a vector that acts a s a function of x, y and z or whatever coordinate system applies. As we “plug-in” different values of x, y, and z, a vector with a specific angle and magnitude will result. Multiple points will form a “sketch” of fields comprised of vector ...
... we have an equation for E , it will be a vector that acts a s a function of x, y and z or whatever coordinate system applies. As we “plug-in” different values of x, y, and z, a vector with a specific angle and magnitude will result. Multiple points will form a “sketch” of fields comprised of vector ...
Components of Vectors
... Components of Vectors Vectors that are perpendicular to each other are independent of each other, and their effects can be considered separately. If a vector can be taken apart so that we have only its effects on the X and Y axes, then one-dimensional equations can be used on each axis. Taking apart ...
... Components of Vectors Vectors that are perpendicular to each other are independent of each other, and their effects can be considered separately. If a vector can be taken apart so that we have only its effects on the X and Y axes, then one-dimensional equations can be used on each axis. Taking apart ...
Circular Motion
... greater distance in one rotation than a point closer to the center of the object. ...
... greater distance in one rotation than a point closer to the center of the object. ...
Unit Review
... 18.) Object A has a mass of 5 kg, and is moving at a velocity of 3 m/s at 30o to the horizontal. Object B has a mass of 3 kg, and is moving at a velocity of 5 m/s at 200o to the horizontal. The two objects collide. Object B bounces at a velocity of 2 m/s at 70o to the horizontal. Determine the veloc ...
... 18.) Object A has a mass of 5 kg, and is moving at a velocity of 3 m/s at 30o to the horizontal. Object B has a mass of 3 kg, and is moving at a velocity of 5 m/s at 200o to the horizontal. The two objects collide. Object B bounces at a velocity of 2 m/s at 70o to the horizontal. Determine the veloc ...