5.6. Visualize: Please refer to Figure Ex5.6. Solve: For the diagram
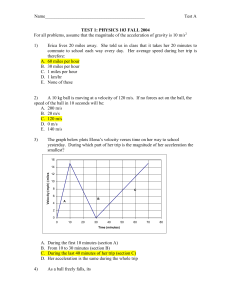
... Visualize: Please refer to Figure Ex5.14. The graph has three segments corresponding to different conditions: (1) increasing velocity, meaning an upward acceleration, (2) a period of constant upward velocity, and (3) decreasing velocity, indicating a period of deceleration (negative acceleration). S ...
... Visualize: Please refer to Figure Ex5.14. The graph has three segments corresponding to different conditions: (1) increasing velocity, meaning an upward acceleration, (2) a period of constant upward velocity, and (3) decreasing velocity, indicating a period of deceleration (negative acceleration). S ...
Rotational Motion
... Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the ...
... Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the ...
SAMPLE TEST 1: PHYSICS 103
... positioned at an angle of 45 degrees above the ground and the initial velocity of the cannonball is 125 m/s, how far from the base of the cliff will the cannonball land? A. 80 m B. 120 m C. 483 m D. 354 m E. Cannot be determined ...
... positioned at an angle of 45 degrees above the ground and the initial velocity of the cannonball is 125 m/s, how far from the base of the cliff will the cannonball land? A. 80 m B. 120 m C. 483 m D. 354 m E. Cannot be determined ...
No Slide Title
... forces provide the driving forces necessary for objects that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. ...
... forces provide the driving forces necessary for objects that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. ...
Chapter 14 - Simple Harmonic Motion
... forces provide the driving forces necessary for objects that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. ...
... forces provide the driving forces necessary for objects that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. ...
FORCE and NEWTON`S LAWS of MOTION
... 7. The SI ( metric) unit of velocity is___. 8. The SI (metric) unit of mass is ____. 9. The SI ( metric) unit of distance or displacement is ____. 10. The SI ( metric) unit of acceleration is ____. 11. The SI ( metric) unit of force is ____. ...
... 7. The SI ( metric) unit of velocity is___. 8. The SI (metric) unit of mass is ____. 9. The SI ( metric) unit of distance or displacement is ____. 10. The SI ( metric) unit of acceleration is ____. 11. The SI ( metric) unit of force is ____. ...
Monday, Sept. 16, 2002 - UTA HEP WWW Home Page
... not move while to the person outside the car they are moving in the same speed and direction as your car is. Frame S v0 ...
... not move while to the person outside the car they are moving in the same speed and direction as your car is. Frame S v0 ...
Physics 11 Assignment #2
... 8. An Atwood machine consists of two masses (m1=3.8 kg) and (m2=4.2 kg). What is the acceleration of the masses? What is the tension in the rope? Note: you must derive the equation for tension using a free-body diagram to receive full credit. (2) ...
... 8. An Atwood machine consists of two masses (m1=3.8 kg) and (m2=4.2 kg). What is the acceleration of the masses? What is the tension in the rope? Note: you must derive the equation for tension using a free-body diagram to receive full credit. (2) ...
Example 2.1. on pg 30
... 1. you are expected to know how to work with powers and run your calculator 2. simplifying equations and substituting one equation into another is a common practice in AP physics 3. all students are expected to have a working knowledge of advanced algebra and trigonometry 4. all tests will consist o ...
... 1. you are expected to know how to work with powers and run your calculator 2. simplifying equations and substituting one equation into another is a common practice in AP physics 3. all students are expected to have a working knowledge of advanced algebra and trigonometry 4. all tests will consist o ...
True or False
... 1. An object can have a constant speed and a changing velocity. 2. An object can have a constant velocity and a changing speed. 3. An object can have a constant speed and be accelerating. 4. As a ball falls freely the distance it falls each second is the same. 5. If an object slows down in the posit ...
... 1. An object can have a constant speed and a changing velocity. 2. An object can have a constant velocity and a changing speed. 3. An object can have a constant speed and be accelerating. 4. As a ball falls freely the distance it falls each second is the same. 5. If an object slows down in the posit ...
Liang`s first semester Physics final practice
... d. tangent to the tire and in a forward direction. e. tangent to the tire and in a direction opposite to the motion. A spacecraft traveling around the Sun along the Earth's orbit but FASTER than Earth: a. would have a greater acceleration than the Earth. b. would have a smaller acceleration than the ...
... d. tangent to the tire and in a forward direction. e. tangent to the tire and in a direction opposite to the motion. A spacecraft traveling around the Sun along the Earth's orbit but FASTER than Earth: a. would have a greater acceleration than the Earth. b. would have a smaller acceleration than the ...
Chapter 8 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative
... 15) If a constant net torque is applied to an object, that object will A) having an increasing moment of inertia. B) having a decreasing moment of inertia. C) rotate with constant angular velocity. D) rotate with constant angular acceleration. ...
... 15) If a constant net torque is applied to an object, that object will A) having an increasing moment of inertia. B) having a decreasing moment of inertia. C) rotate with constant angular velocity. D) rotate with constant angular acceleration. ...
lecture ch7-8-Circles
... than “with his knees” can be injured by large forces exerted on the muscles and vertebrae. The spine pivots mainly at the fifth lumbar vertebra, with the principal supporting force provided by the erector spinalis muscle in the back. Consider the model of a person bending forward to lift a 200-N obj ...
... than “with his knees” can be injured by large forces exerted on the muscles and vertebrae. The spine pivots mainly at the fifth lumbar vertebra, with the principal supporting force provided by the erector spinalis muscle in the back. Consider the model of a person bending forward to lift a 200-N obj ...
Newton`s Second Law
... 1. Inertia is the tendency of an object to continue moving at a constant ________. 2. Things with more ________ have more inertia and are more difficult to __________. 3. The rate _____ changes is directly proportional to the net force, and inversely proportional to the _______. 4. An unbalanced for ...
... 1. Inertia is the tendency of an object to continue moving at a constant ________. 2. Things with more ________ have more inertia and are more difficult to __________. 3. The rate _____ changes is directly proportional to the net force, and inversely proportional to the _______. 4. An unbalanced for ...