Ph211_CH6_worksheet
... b. If the road design is banked, what is the minimum steepness (angle of incline for the bank) required to keep cars safely on the road at 15.6 m/s? For simplicity, neglect any friction between tire and road. ...
... b. If the road design is banked, what is the minimum steepness (angle of incline for the bank) required to keep cars safely on the road at 15.6 m/s? For simplicity, neglect any friction between tire and road. ...
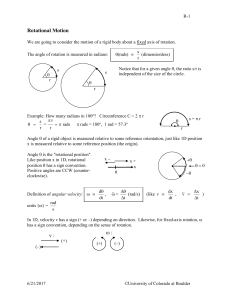
RotationalMotion - University of Colorado Boulder
... perpendicular to the plane defined by the vectors A and B plus right-hand-rule. (Curl fingers from first vector A to second vector B, thumb points in direction of A B ...
... perpendicular to the plane defined by the vectors A and B plus right-hand-rule. (Curl fingers from first vector A to second vector B, thumb points in direction of A B ...
1a - cloudfront.net
... 4. The distance vs. time graph for an object moving in a straight line is drawn to the right. What is the acceleration of the object? 5a. If an object has only 1 force acting on it, can its acceleration be 0m/s 2? b. An object starts at rest and is pulled by a constant force. Draw a sketch of the ve ...
... 4. The distance vs. time graph for an object moving in a straight line is drawn to the right. What is the acceleration of the object? 5a. If an object has only 1 force acting on it, can its acceleration be 0m/s 2? b. An object starts at rest and is pulled by a constant force. Draw a sketch of the ve ...
chapter 2 - UniMAP Portal
... 2.3 Equation of Motion for a System of Particles The equation of motion can be extended to include systems of particles. This includes the motion of solids, liquids, or gas systems. As in statics, there are internal forces and external forces acting on the system. What is the difference between the ...
... 2.3 Equation of Motion for a System of Particles The equation of motion can be extended to include systems of particles. This includes the motion of solids, liquids, or gas systems. As in statics, there are internal forces and external forces acting on the system. What is the difference between the ...
True or False - Hauserphysics
... 1. An object can have a constant speed and a changing velocity. 2. An object can have a constant velocity and a changing speed. 3. An object can have a constant speed and be accelerating. 4. As a ball falls freely the distance it falls each second is the same. 5. If an object slows down in the posit ...
... 1. An object can have a constant speed and a changing velocity. 2. An object can have a constant velocity and a changing speed. 3. An object can have a constant speed and be accelerating. 4. As a ball falls freely the distance it falls each second is the same. 5. If an object slows down in the posit ...
Conceptual Physics Review # 3
... else does it change? A. the mass of the ball B. the weight of the ball C. impossible to determine ...
... else does it change? A. the mass of the ball B. the weight of the ball C. impossible to determine ...
Chapter 8, Part V
... Section 8-7: Rotational Kinetic Energy • Translational motion (Ch. 6): (KE)trans = (½)mv2 • Rigid body rotation, angular velocity ω. Rigid ...
... Section 8-7: Rotational Kinetic Energy • Translational motion (Ch. 6): (KE)trans = (½)mv2 • Rigid body rotation, angular velocity ω. Rigid ...
Impulse Momentum (Problem and Solutions) 1. An object travels
... ΔP=40kg.m/s Impulse=change in momentum I=ΔP=40kg.m/s 3. Find the impulse and force which make 12m/s change in the velocity of object having 16kg mass in 4 s. F.Δt=ΔP=m.ΔV F.4s=16kg.12m/s F=48N F.Δt=Impulse=192kg.m/s 4. Applied force vs. time graph of object is given below. Find the impulse of the ob ...
... ΔP=40kg.m/s Impulse=change in momentum I=ΔP=40kg.m/s 3. Find the impulse and force which make 12m/s change in the velocity of object having 16kg mass in 4 s. F.Δt=ΔP=m.ΔV F.4s=16kg.12m/s F=48N F.Δt=Impulse=192kg.m/s 4. Applied force vs. time graph of object is given below. Find the impulse of the ob ...
Simple Harmonic Motion and Elastic Energy
... In mechanical systems, energy can be stored in springs. For example a compressed spring on a popgun can provide energy to a pellet and shoot it from the gun. Even a simple slingshot uses the elastic energy stored in a rubber band to shoot it projectile. When two balls collide it is as if a spring is ...
... In mechanical systems, energy can be stored in springs. For example a compressed spring on a popgun can provide energy to a pellet and shoot it from the gun. Even a simple slingshot uses the elastic energy stored in a rubber band to shoot it projectile. When two balls collide it is as if a spring is ...