hp1f2013_class15_rolling_motion_and_accelerating_frames
... Galilean transformations Consider measurements of the motion of a mass m made from each of two coordinate systems. For simplicity let’s assume that corresponding axes are parallel and the scale units (time and distance) are the same. The origins of the two systems are displaced by S so ...
... Galilean transformations Consider measurements of the motion of a mass m made from each of two coordinate systems. For simplicity let’s assume that corresponding axes are parallel and the scale units (time and distance) are the same. The origins of the two systems are displaced by S so ...
Dipole Force
... Write reusable functions to calculate the potential, V, and the electric fields, Ex, and Ey for the conductors. The new functions may use the dipolePotential.m and dipoleField.m functions and then set the potential to a constant inside the conductor, and the electric field to NaN inside the conducto ...
... Write reusable functions to calculate the potential, V, and the electric fields, Ex, and Ey for the conductors. The new functions may use the dipolePotential.m and dipoleField.m functions and then set the potential to a constant inside the conductor, and the electric field to NaN inside the conducto ...
Unit 1 – Linear Motion
... Scientific notation is a way of writing very large or small numbers to shorten their appearance and make them easier to compare with other numbers by utilizing a decimal rounded to no more than 2 decimal places multiplied by a ten with an exponent that represents the number of places the decimal wou ...
... Scientific notation is a way of writing very large or small numbers to shorten their appearance and make them easier to compare with other numbers by utilizing a decimal rounded to no more than 2 decimal places multiplied by a ten with an exponent that represents the number of places the decimal wou ...
Question Bank 07
... 54. A baseball thrown from the outfield is thrown from shoulder height. The initial velocity is 29.4 m/s at an initial angle of 30.0° above the horizon. It is in flight for a total of 3.00 seconds before it is caught by the third baseman at shoulder height. (Assume air resistance is negligible.) Wha ...
... 54. A baseball thrown from the outfield is thrown from shoulder height. The initial velocity is 29.4 m/s at an initial angle of 30.0° above the horizon. It is in flight for a total of 3.00 seconds before it is caught by the third baseman at shoulder height. (Assume air resistance is negligible.) Wha ...
Class #13 - Department of Physics | Oregon State University
... With his Third Law of motion, Isaac Newton observed the “double-ended” nature of any force. But he had also begun to examine how a force—or, more generally, a vector combination of forces, Fnet—affects the motion of any mass. He first described that in terms of its impulse—its effect upon momentum ...
... With his Third Law of motion, Isaac Newton observed the “double-ended” nature of any force. But he had also begun to examine how a force—or, more generally, a vector combination of forces, Fnet—affects the motion of any mass. He first described that in terms of its impulse—its effect upon momentum ...
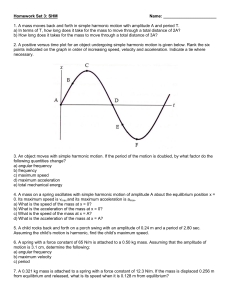
SHM Dynamics WS (honors)
... The speed starts at zero, increases continuously until bob reaches the equilibrium point. It then begins to decrease continuously, becoming zero at the opposite endpoint. ...
... The speed starts at zero, increases continuously until bob reaches the equilibrium point. It then begins to decrease continuously, becoming zero at the opposite endpoint. ...
ExamView - Newton`s Laws Review.tst
... d. all of the above ____ 19. Which of the following statements is true? a. An object that is accelerating is always changing direction. b. An object has an instantaneous acceleration, even if the acceleration vector is zero. c. An object at rest has an instantaneous acceleration of zero. d. Instanta ...
... d. all of the above ____ 19. Which of the following statements is true? a. An object that is accelerating is always changing direction. b. An object has an instantaneous acceleration, even if the acceleration vector is zero. c. An object at rest has an instantaneous acceleration of zero. d. Instanta ...
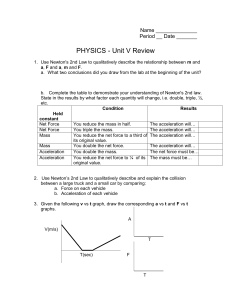
Unit V review
... 3. Determine the net force acting on an object by: a. drawing a force diagram for an object given a written description of the forces acting on it. b. resolving forces into x and y components, then finding the vector sum of the forces. c. analysis of the kinematic behavior of the object. 4. Solve qu ...
... 3. Determine the net force acting on an object by: a. drawing a force diagram for an object given a written description of the forces acting on it. b. resolving forces into x and y components, then finding the vector sum of the forces. c. analysis of the kinematic behavior of the object. 4. Solve qu ...