constant velocity
... Position is the location of some object relative to a fixed point. Velocity is the slope of position vs. time. It tells you how position is changing. Acceleration is the slope of velocity vs. time. It tells you how velocity is ...
... Position is the location of some object relative to a fixed point. Velocity is the slope of position vs. time. It tells you how position is changing. Acceleration is the slope of velocity vs. time. It tells you how velocity is ...
Chapter 6 Forces and Motion
... Terminal Velocity- The constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of gravity. Free fall - the motion of a body when only the force of gravity is acting on the body. Projectile motion- the curved path that an obj ...
... Terminal Velocity- The constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of gravity. Free fall - the motion of a body when only the force of gravity is acting on the body. Projectile motion- the curved path that an obj ...
Rotational Motion - Damien Honors Physics
... • A bolt on a car engine needs to be tightened with a torque of 35 mN. You use a 25cm long wrench and pull on the end of the wrench at an angle of 60.0 from perpendicular. How long is the lever arm and how much force do you have to exert? • Sketch the problem before solving ...
... • A bolt on a car engine needs to be tightened with a torque of 35 mN. You use a 25cm long wrench and pull on the end of the wrench at an angle of 60.0 from perpendicular. How long is the lever arm and how much force do you have to exert? • Sketch the problem before solving ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... move while to the person outside the car they are moving in the same speed and direction as your car is. Frame S v0 ...
... move while to the person outside the car they are moving in the same speed and direction as your car is. Frame S v0 ...
A constant net force is applied to a person on
... 1.Move at a constant velocity 2.Continually change velocity 3.Move for a while at a constant velocity and then change velocity 4.It depends on how big the frictional forces are ...
... 1.Move at a constant velocity 2.Continually change velocity 3.Move for a while at a constant velocity and then change velocity 4.It depends on how big the frictional forces are ...
Circular Motion
... Units of angular acceleration are rad/s² Positive angular accelerations are in the counterclockwise direction and negative accelerations are in the clockwise direction When a rigid object rotates about a fixed axis, every portion of the object has the same angular speed and the same angular accelera ...
... Units of angular acceleration are rad/s² Positive angular accelerations are in the counterclockwise direction and negative accelerations are in the clockwise direction When a rigid object rotates about a fixed axis, every portion of the object has the same angular speed and the same angular accelera ...
Vector Practice
... Dot product of two vectors is the product of a vector to the projection of the other vector on the vector. a. b is called the dot product of the two vectors. a. b = a b cos . If the two vectors are parallel, then a. b = a b And if the two vectors are perpendicular to each other, then a. b = 0 Cross ...
... Dot product of two vectors is the product of a vector to the projection of the other vector on the vector. a. b is called the dot product of the two vectors. a. b = a b cos . If the two vectors are parallel, then a. b = a b And if the two vectors are perpendicular to each other, then a. b = 0 Cross ...
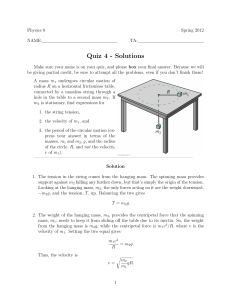
ysics P2 Graded Task Bungee Jumping with equations
... velocity he could reach as he falls to the ground. Explain why this is not reached by the jumper. ...
... velocity he could reach as he falls to the ground. Explain why this is not reached by the jumper. ...
FE_Review_Dynamics - Department of Mechanical Engineering
... Potential Energy Potential energy is energy which results from position or configuration. An object may have the capacity for doing work as a result of its position in a gravitational field. It may have elastic potential energy as a result of a stretched spring or other elastic ...
... Potential Energy Potential energy is energy which results from position or configuration. An object may have the capacity for doing work as a result of its position in a gravitational field. It may have elastic potential energy as a result of a stretched spring or other elastic ...